Albanites is a genus of extinct cephalopods belonging to the ammonoid order Ceratitida that lived during the Early Triassic epoch.

Asklepioceras is a genus in the Ceratitid family Arpaditidae from the Middle and Upper Triassic of Italy, Romania, Turkey, and British Columbia (Canada).
Anderssonoceras is a genus of small, smooth ammonites with a flared umbilical shoulder, like Prototoceras, assigned to the ceratitid family Anderssonoceratidae as the type, but once included in the Otoceratidae.
Arctohungarites is a genus of Triassic ammonoids now placed in the ceratitid family Danubitidae, but previously included in the Hungeritidae.
Badiotites is a genus of extinct ammonoid cephalopods belonging to the ceratitid family Badiotitidae. It was previously included with Lecanites in the Lecanitidae, a family formerly of the Clydonitaceae but reassigned by Tozer (1981) to the Danubitaceae. The Badiotitidae is included in the Ceratitaceae.
Griesbachites is a genus of Late Triassic ceratitids included in the Haloritidae, with widespread distribution from the Alps through the Himalaya and Timur to British Columbia.
Biltnerites is a genus of ammonites (s.l.) from the lower Triassic included in the ceratitacean family Tirolitidae of the order Ceratitida, characterized by a flat, evolute shell with moderately compressed, rounded whorls. The spinose stage characteristic of the Tirolitidae is absent, but the outer whorl does have indistinct ribs that cross the venter.
Ussuria is a genus of Lower Triassic ammonites with a smooth, involute discoidal shell with submonophyllic sutures, belonging to the ceratitid family Ussuriidae.
The Ophiceratidae is a family in the ammonoid order Ceratitida from the Lower Triassic, previously included in the Otocerataceae but now placed in the Noritiaceae as revised.
Clydonitoidea, formerly Clydonitaceae, is a superfamily in the ammonoid cephalopod order Ceratitida characterized by generally costate and tuberculate shells with smooth, grooved, or keeled venters and sutures that are commonly ceratitic or ammonitic but goniatitic in a few offshoots.
Lecanites is a ceratitid genus assigned to the Danubitaceae, with an essentially smooth, evolute, discoidal shell and a goniatitic suture with many elements. It is the type and now only genus of the Lecanitidae.
The Danubitoidea is a large and diverse superfamily in the order Ceratitida of the Ammonoidea that combines five families removed from the Ceratitaceae, Clydonitaceae, and Ptychitaceae.
Longobarditidae is a family of ceratitd ammonoids known from the early Triassic, included in the Danubitaceae. Longobarditidae includes genera formerly placed in Hungaritidae by the American Treatise on Invertebrate Paleontology, Part L, 1957 as well as genera that have been described since.
The Haloritidae is a family of subglobular, involute, Triassic ammonoids belonging to the ceratitid superfamily Tropitoidea. Their shells may be smooth or may have ribs that cross or are interrupted on the venter, and may have nodes. Keels and ventral furrows are not typical. The last volution is commonly eccentric. The Suture may be ammonitic, ceratitic, or goniatitic.
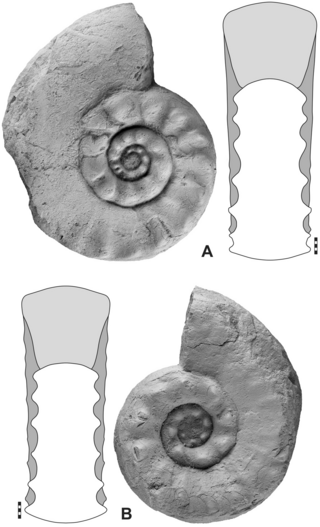
Paratirolites is a genus of latest Permian and earliest Triassic ceratites from Armenia, Azerbaijan, Afghanistan, China and Iran with distinct ribs, prominent ventro-lateral tubercles, and a broadly arched venter. The suture is ceratitic with a large ventral saddle. Ceratites are ammonoid cephalopods that lived during the Late Permian and Triassic.

Gymnitidae is a family of Lower to Middle Triassic ammonite cephalopods with evolute, discoidal shells.
Aplococeratidae is a family of ceratitids from the Middle Triassic with very simplified sutures and a tendency to lose their ornamentation. Shells are generally evolute, more or less compressed, with rounded venters. Ornamentation if present consists of umbilical ribs that disappear outwardly, toward the venter. The suture is ceratitic or goniatitic.
Inyoites is an ammonoid genus from the Lower Triassic, included in the ceratitid family Inyoitidae.
Stenopopanoceras is a genus of involute, discoidal ceratitid ammonites from the Middle Triassic that has been found on Spitsbergen and in arctic Russia and British Columbia.

Meekoceras is an extinct genus of ceratitid ammonites with a discoidal shell that lived during the Early Triassic Epoch.



