The desert iguana is an iguana species found in the Sonoran and Mojave Deserts of the Southwestern United States and northwestern Mexico, as well as on several Gulf of California islands.

The bay duiker, also known as the black-striped duiker and the black-backed duiker, is a forest-dwelling duiker native to western and southern Africa. It was first described by British zoologist John Edward Gray in 1846. Two subspecies are identified. The bay duiker is reddish-brown and has a moderate size. Both sexes reach 44–49 cm (17–19 in) at the shoulder. The sexes do not vary considerably in their weights, either; the typical weight range for this duiker is 18–23 kg (40–51 lb). Both sexes have a pair of spiky horns, measuring 5–8 cm (2.0–3.1 in). A notable feature of this duiker is the well-pronounced solid stripe of black extending from the back of the head to the tail.

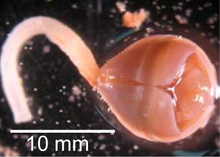
The Mexican burrowing toad is the only species in the genus Rhinophrynus and the family Rhinophrynidae of order Anura. Their distribution stretches from south Texas through Mexico, Belize, Guatemala, Honduras, and El Salvador to Nicaragua and Costa Rica. R. dorsalis mostly commonly inhabits the subtropical and tropical dry forests within its range characterized by wet and dry seasons, but may also be found during periods of heavy rain in pastures, cultivated field, roadside ditches or other open areas. The family was once more widespread, including species ranging as far north as Canada, but these died out in the Oligocene.

Pholadidae, known as piddocks or angelwings, are a family of bivalve molluscs similar to a clam.

The American three-toed woodpecker is a medium-sized woodpecker, which is native to North America.

The sharptooth smooth-hound is a houndshark of the family Triakidae. It is found on the continental shelves of the tropical eastern Pacific from southern Mexico to Peru between latitudes 20°N and 5°S. Its length is up to 64 cm.

Bactrocera dorsalis, previously known as Dacus dorsalis and commonly referred to as the oriental fruit fly, is a species of tephritid fruit fly that is endemic to Southeast Asia. It is one of the major pest species in the genus Bactrocera with a broad host range of cultivated and wild fruits. Male B. dorsalis respond strongly to methyl eugenol, which is used to monitor and estimate populations, as well as to annihilate males as a form of pest control. They are also important pollinators and visitors of wild orchids, Bulbophyllum cheiri and Bulbophyllum vinaceum in Southeast Asia, which lure the flies using methyl eugenol.
The northern zigzag salamander is a species of salamander in the family Plethodontidae. It is endemic to the eastern United States. It has been found in Illinois, Kentucky, Tennessee, Alabama, and Mississippi. The northern zigzag salamander's natural habitat includes temperate forests, rocky areas, and caves. It is threatened by habitat loss.

Thomas's broad-nosed bat is a species of bat in the family Phyllostomidae. It is found in Bolivia, Colombia, Ecuador, Panama, and Peru.

The western tree hyrax, also called the western tree dassie or Beecroft's tree hyrax, is a species of tree hyrax within the family Procaviidae. It can be distinguished from other hyraxes by short coarse fur, presence of white patch of fur beneath the chin, lack of hair on the rostrum, and lower crowns of the cheek teeth compared to other members of the same genus.

The chilli thrips or yellow tea thrips, Scirtothrips dorsalis Hood, is an extremely successful invasive species of pest-thrips which has expanded rapidly from Asia over the last twenty years, and is gradually achieving a global distribution. It has most recently been reported in St. Vincent (2004) Florida (2005), Texas (2006), and Puerto Rico (2007). It is a pest of economic significance with a broad host range, with prominent pest reports on crops including pepper, mango, citrus, strawberry, grapes, cotton, tea, peanuts, blueberry, and roses. Chilli thrips appear to feed preferentially on new growth, and infested plants usually develop characteristic wrinkled leaves, with distinctive brown scarring along the veins of leaves, the buds of flowers, and the calyx of fruit. Feeding damage can reduce the sale value of crops produced, and in sufficient numbers, kill plants already aggravated by environmental stress. This thrips has also been implicated in the transmission of three tospoviruses, but there is some controversy over its efficiency as a vector.

The threadfin jack or thread pompano is a species of coastal marine fish in the jack family Carangidae. The species inhabits the tropical waters of the eastern Pacific Ocean from Baja California in the north to Ecuador and the Galapagos Islands in the south. It is a moderately large fish, growing to 60 cm (24 in) and may be recognized by its filamentous dorsal and anal fin lobes. The threadfin jack inhabits both deeper coastal waters and inshore environments, including reefs and estuaries, where it preys on minute benthic and pelagic organisms, including small fishes and crustaceans. Very little is known about the ecology and reproductive cycle in the species. The threadfin jack is of importance to fisheries throughout its distribution, caught by hook-and-line and net methods and marketed fresh and salted, and is considered a very good table fish. The species was named Carangoides dorsalis by Theodore Gill 20 years before the name Caranx otrynter was introduced, but confusion with Vomer dorsalis led to the proposal of the new name to separate the two species.

The western banjo frog is a species of frog from the family Limnodynastidae. The informal names for this species are pobblebonk, sand frog and bullfrog. It is one of the endemic amphibians of Western Australia.

The southern painted turtle is a species of turtle in the family Emydidae. It is endemic to the south-central United States.

The bigmouth shiner, is one of the 324 fish species found in Tennessee. It is a common minnow species found in the midwest region, but found as far as the east coast. There has been little information researched about this minnow outside of the general body plan and habitat. They are often found along with common shiner in streams.

Xylophaga dorsalis is a species of bivalves in the family Xylophagaidae.

Platyrrhinus ismaeli is a species of bat found in South America.

Habroscelimorpha dorsalis, commonly known as the eastern beach tiger beetle, is a species of flashy tiger beetle in the family Carabidae. It is found in Central America and North America.

Psiloteredo megotara is a species of saltwater clam, a marine bivalve mollusc in the family Teredinidae, the shipworms.

Xylophagaidae is a family of deep-sea woodboring bivalve molluscs, similar to shipworms.