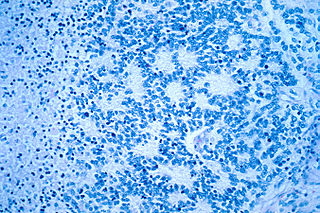
Neuroblastoma (NB) is a type of cancer that forms in certain types of nerve tissue. It most frequently starts from one of the adrenal glands but can also develop in the neck, chest, abdomen, or spine. Symptoms may include bone pain, a lump in the abdomen, neck, or chest, or a painless bluish lump under the skin.
Zbtb7, originally named Pokemon, is a gene that may act as a master switch for cancer, and is responsible for the proliferation of cancer throughout surrounding cells. The leader of the research team which discovered this, geneticist Pier Paolo Pandolfi from the Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center (MSKCC) in New York City, said the gene is unique in that it is needed for other oncogenes to cause cancer. Discovery of the gene was first published in the January 2005 issue of Nature.

N-myc proto-oncogene protein also known as N-Myc or basic helix-loop-helix protein 37 (bHLHe37), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MYCN gene.

GLUT5 is a fructose transporter expressed on the apical border of enterocytes in the small intestine. GLUT5 allows for fructose to be transported from the intestinal lumen into the enterocyte by facilitated diffusion due to fructose's high concentration in the intestinal lumen. GLUT5 is also expressed in skeletal muscle, testis, kidney, fat tissue (adipocytes), and brain.

Zinc finger and BTB domain-containing protein 16 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ZBTB16 gene.

Krueppel-like factor 6 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KLF6 gene.

Kruppel-like factor 4 is a member of the KLF family of zinc finger transcription factors, which belongs to the relatively large family of SP1-like transcription factors. KLF4 is involved in the regulation of proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis and somatic cell reprogramming. Evidence also suggests that KLF4 is a tumor suppressor in certain cancers, including colorectal cancer. It has three C2H2-zinc fingers at its carboxyl terminus that are closely related to another KLF, KLF2. It has two nuclear localization sequences that signals it to localize to the nucleus. In embryonic stem cells (ESCs), KLF4 has been demonstrated to be a good indicator of stem-like capacity. It is suggested that the same is true in mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs).
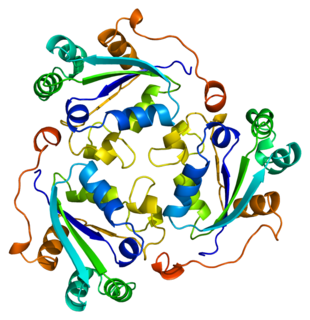
Nucleoside diphosphate kinase A is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the NME1 gene. It is thought to be a metastasis suppressor.

RE1-Silencing Transcription factor (REST), also known as Neuron-Restrictive Silencer Factor (NRSF), is a protein which in humans is encoded by the REST gene, and acts as a transcriptional repressor. REST is expressly involved in the repression of neural genes in non-neuronal cells. Many genetic disorders have been tied to alterations in the REST expression pattern, including colon and small-cell lung carcinomas found with truncated versions of REST. In addition to these cancers, defects in REST have also been attributed a role in Huntington Disease, neuroblastomas, and the effects of epileptic seizures and ischemia.

DNA-binding protein inhibitor ID-3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ID3 gene.

PITSLRE serine/threonine-protein kinase CDC2L2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CDC2L2 gene.

Krüppel-like Factor 2 (KLF2), also known as lung Krüppel-like Factor (LKLF), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KLF2 gene on chromosome 19. It is in the Krüppel-like factor family of zinc finger transcription factors, and it has been implicated in a variety of biochemical processes in the human body, including lung development, embryonic erythropoiesis, epithelial integrity, T-cell viability, and adipogenesis.

Transcriptional regulator Kaiso is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ZBTB33 gene. This gene encodes a transcriptional regulator with bimodal DNA-binding specificity, which binds to methylated CGCG and also to the non-methylated consensus KAISO-binding site TCCTGCNA. The protein contains an N-terminal POZ/BTB domain and 3 C-terminal zinc finger motifs. It recruits the N-CoR repressor complex to promote histone deacetylation and the formation of repressive chromatin structures in target gene promoters. It may contribute to the repression of target genes of the Wnt signaling pathway, and may also activate transcription of a subset of target genes by the recruitment of catenin delta-2 (CTNND2). Its interaction with catenin delta-1 (CTNND1) inhibits binding to both methylated and non-methylated DNA. It also interacts directly with the nuclear import receptor Importin-α2, which may mediate nuclear import of this protein. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding the same protein have been identified.

Carbonic anhydrase 6 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CA6 gene. It is also called 'gustin' because of its presence in saliva, and lower-than-normal levels of salivary zinc in individuals with hypogeusia.

Zinc finger and BTB domain-containing protein 7A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ZBTB7A gene.

Krueppel-like factor 12 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KLF12 gene.

Zinc finger and BTB domain-containing protein 32 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the 1960 bp ZBTB32 gene. The 52 kDa protein is a transcriptional repressor and the gene is expressed in T and B cells upon activation, but also significantly in testis cells. It is a member of the Poxviruses and Zinc-finger (POZ) and Krüppel (POK) family of proteins, and was identified in multiple screens involving either immune cell tumorigenesis or immune cell development.

Krueppel-related zinc finger protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HKR1 gene.

Zinc finger protein 160 is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the ZNF160 gene.

Homeobox containing 1, also known as homeobox telomere-binding protein 1 (HOT1), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HMBOX1 gene. HMBOX1 directly binds to the double-stranded repeat sequence of telomeres.
















