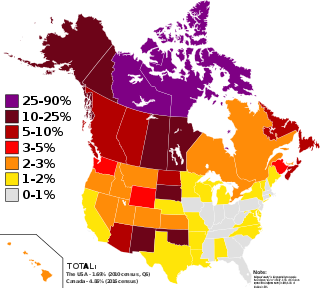
Native Americans, also known as American Indians, First Americans, Indigenous Americans, Native Americans of the United States, Native Americans in the United States, and other terms, are the Indigenous peoples of the United States; sometimes including Hawaii and territories of the United States, and other times limited to the mainland. There are 574 federally recognized tribes living within the US, about half of which are associated with Indian reservations. "Native Americans" are Indigenous tribes that are originally from the contiguous United States, along with Alaska Natives.

The term tribe is used in many different contexts to refer to a category of human social group. The predominant usage of the term is in the discipline of anthropology. The definition is contested, in part due to conflicting theoretical understandings of social and kinship structures, and also reflecting the problematic application of this concept to extremely diverse human societies. The concept is often contrasted by anthropologists with other social and kinship groups, being hierarchically larger than a lineage or clan, but smaller than a chiefdom, nation or state. These terms are equally disputed. In some cases tribes have legal recognition and some degree of political autonomy from national or federal government, but this legalistic usage of the term may conflict with anthropological definitions.
The Sioux or Oceti Sakowin are groups of Native American tribes and First Nations peoples in North America. The modern Sioux consist of two major divisions based on language divisions: the Dakota and Lakota; collectively they are known as the Očhéthi Šakówiŋ. The term "Sioux" is an exonym created from a French transcription of the Ojibwe term "Nadouessioux", and can refer to any ethnic group within the Great Sioux Nation or to any of the nation's many language dialects.
The Indian Territory and the Indian Territories are terms that generally described an evolving land area set aside by the United States Government for the relocation of Native Americans who held aboriginal title to their land as a sovereign independent state. In general, the tribes ceded land they occupied in exchange for land grants in 1803. The concept of an Indian Territory was an outcome of the US federal government's 18th- and 19th-century policy of Indian removal. After the American Civil War (1861–1865), the policy of the US government was one of assimilation.

The Bedouin, Beduin or Bedu are nomadic Arab tribes who have historically inhabited the desert regions in the Levant, the Arabian Peninsula, Iraq, and North Africa. However, the Arabian Peninsula is the historic and original homeland of the Bedouin Arabs. The English word bedouin comes from the Arabic badawī, which means "desert dweller", and is traditionally contrasted with ḥāḍir, the term for sedentary people. Bedouin territory stretches from the vast deserts of North Africa to the rocky sands of the Middle East. They are traditionally divided into tribes, or clans, and historically share a common culture of herding camels and goats. The vast majority of Bedouins adhere to Sunni Islam, although there are some fewer numbers of Christian Bedouins present in the Fertile Crescent.

Survivor is a reality-competition television franchise produced in many countries around the world. The show features a group of contestants deliberately marooned in an isolated location, where they must provide food, water, fire, and shelter for themselves. The contestants compete in challenges for rewards and immunity from elimination. The contestants are progressively eliminated from the game as they are voted out by their fellow-contestants until only one remains to be awarded the grand prize and named the "Sole Survivor".

A Tribe Called Quest was an American hip hop group formed in St. Albans, Queens, New York in 1985, originally composed of rapper and main producer Q-Tip, rapper Phife Dawg, DJ and co-producer Ali Shaheed Muhammad, and rapper Jarobi White. The group is regarded as a pioneer of alternative hip hop music.
The Seminole are a Native American people originally from Florida. Today, they live in Oklahoma and Florida, and comprise three federally recognized tribes: the Seminole Nation of Oklahoma, the Seminole Tribe of Florida, and Miccosukee Tribe of Indians of Florida, as well as independent groups. The Seminole people emerged in a process of ethnogenesis from various Native American groups who settled in Spanish Florida beginning in the early 1700s, most significantly northern Muscogee Creeks from what is now Georgia and Alabama. The word "Seminole" is derived from the Muscogee word simanó-li, which may itself be derived from the Spanish word cimarrón, meaning "runaway" or "wild one". Seminole culture is largely derived from that of the Creek; the most important ceremony is the Green Corn Dance; other notable traditions include use of the black drink and ritual tobacco. As the Seminole adapted to Florida environs, they developed local traditions, such as the construction of open-air, thatched-roof houses known as chickees. Historically the Seminole spoke Mikasuki and Creek, both Muskogean languages.
In biology, a tribe is a taxonomic rank above genus, but below family and subfamily. It is sometimes subdivided into subtribes. By convention, all taxonomic ranks from genus upwards are capitalized, including both tribe and subtribe.

Nagaland is a state in northeastern India. It is bordered by the state of Arunachal Pradesh to the north, Assam to the west, Manipur to the south and the Sagaing Region of Myanmar to the east. Nagaland's capital city is Kohima and its largest city is Dimapur. It has an area of 16,579 square kilometres (6,401 sq mi) with a population of 1,980,602 per the 2011 Census of India, making it one of the smallest states of India.

Swallowtail butterflies are large, colorful butterflies in the family Papilionidae, and include over 550 species. Though the majority are tropical, members of the family inhabit every continent except Antarctica. The family includes the largest butterflies in the world, the birdwing butterflies of the genus Ornithoptera.

Indian reservation is a legal designation for an area of land managed by a federally recognized Native American tribe under the U.S. Bureau of Indian Affairs rather than the state governments of the United States in which they are physically located. Each of the 326 Indian reservations in the United States is associated with a particular Native American nation. Some of the country's 574 federally recognized tribes have more than one reservation, while some share reservations, and others have no reservations at all. In addition, because of past land allotments, leading to some sales to non–Native Americans, some reservations are severely fragmented, with each piece of tribal, individual, and privately held land being a separate enclave. This jumble of private and public real estate creates significant administrative, political, and legal difficulties.

Adivasi is the collective term for tribes of the Indian subcontinent, who are considered indigenous to places within India wherein they live, either as foragers or as tribalistic sedentary communities. The term is also used for ethnic minorities, such as Chakmas of Bangladesh, Khas of Nepal, and Vedda of Sri Lanka. However India doesn't recognise tribes as indigenous people. India ratified the International Labour Organization (ILO) Convention 107 on Indigenous and Tribal Peoples of the United Nations (1957). In 1989, India refused to sign the ILO Convention 169.
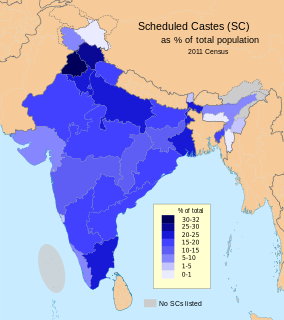
The Scheduled Caste (SCs) and Scheduled Tribes (STs) are officially designated groups of people in India. The terms are recognised in the Constitution of India and the groups are designated in one or other of the categories. For much of the period of British rule in the Indian subcontinent, they were known as the Depressed Classes.

Noctuoidea is the superfamily of noctuid or "owlet" moths, and has more than 70,000 described species, the largest number of for any Lepidopteran superfamily. Its classification has not yet reached a satisfactory or stable state. Since the end of the 20th century, increasing availability of molecular phylogenetic data for this hugely successful radiation has led to several competing proposals for a taxonomic arrangement that correctly represents the relationships between the major lineages.
The Twelve Tribes of Israel are, according to Judeo-Christian texts, the descendants of the Biblical patriarch Jacob, also known as Israel, through his twelve sons by various women, who collectively form the Israelite nation. Within ancient Judaism, one's tribal affiliation had a great impact on his or her practices and opportunities, as some tribes enjoyed privileges others did not and some tribes received more blessings than others. Modern scholars dispute whether there ever were (exactly) twelve Israelite tribes, and think that the number 12 more likely signifies a symbolic invented tradition as part of a national founding myth.

The ten lost tribes were the ten of the Twelve Tribes of Israel that were said to have been exiled from the Kingdom of Israel after its conquest by the Neo-Assyrian Empire circa 722 BCE. These are the tribes of Reuben, Simeon, Dan, Naphtali, Gad, Asher, Issachar, Zebulun, Manasseh, and Ephraim; all but Judah and Benjamin. The Jewish historian Josephus wrote that "there are but two tribes in Asia and Europe subject to the Romans, while the ten tribes are beyond Euphrates till now, and are an immense multitude, and not to be estimated by numbers".

Allancastria deyrollei is a butterfly belonging to the family Papilionidae. It was described by Oberthür in 1869. It is found only in western Iran, Turkey, Syria, northwestern Iraq, Lebanon, Jordan, and Israel.

Slavery among Native Americans in the United States includes slavery by and slavery of Native Americans roughly within what is currently the United States of America.















