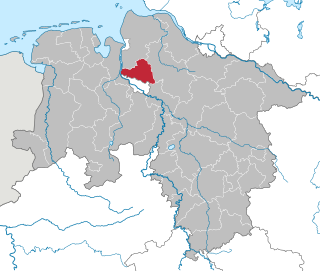
Osterholz is a district (Landkreis) in Lower Saxony, Germany. It is bounded by the districts of Wesermarsch, Cuxhaven, Rotenburg and Verden, and by the city of Bremen.

Rotenburg is a district (Landkreis) in Lower Saxony, Germany. It is landlocked by the districts of Stade, Harburg, Heidekreis, Verden, Osterholz and Cuxhaven.

Rotenburg an der Wümme is a town in Lower Saxony, Germany. It is the capital of the district of Rotenburg.

Bouches-de-l'Elbe was a department of the First French Empire in present-day Germany that survived for three years. It was named after the mouth of the river Elbe. It was formed in 1811, when the region, originally belonging partially to Bremen-Verden, to Hamburg, Lübeck and Saxe-Lauenburg, was annexed by France. Its territory is part of the present-day German states of Lower Saxony, Schleswig-Holstein and Hamburg. Its capital was Hamburg.

The Oste is a river in northern Lower Saxony, Germany with a length of 149 km, left tributary of the Elbe. It flows through the districts of Harburg, Rotenburg, Stade and Cuxhaven and empties into the Elbe river near Otterndorf. Its drainage area is 1.715 km² and the decline between the source and the estuary is 31 m. Tributaries are Ramme, Aue, Twiste, Bade, Bever and Mehe.

Sottrum is a municipality in the district of Rotenburg, in Lower Saxony, Germany. It is situated approximately 11 km west of Rotenburg, and 30 km east of Bremen.

Metronom Eisenbahngesellschaft mbH is a German non-entirely-state-owned railway company based in Uelzen, Lower Saxony since December 2005. The company's activities focus exclusively on passenger transport, operating services from Hamburg to Bremen, Uelzen, Wolfsburg and Lüneburg. Services listed on the timetables are abbreviated ME.

Ahausen is a village in the district of Rotenburg, in Lower Saxony, Germany. Ahausen is administratively part of the collective community of Sottrum.

Brobergen is a village in the German municipality of Kranenburg in the district of Stade, Lower Saxony. The village of 6.06 km² has 220 inhabitants.

The Bundesstraße 71 is one of the longer German federal roads numbered in the 60s and 70s series. It begins at the B 6 in Bremerhaven by the Unterweser and ends in Könnern near Halle (Saale) in Saxony-Anhalt. To begin with it is one of the east-west links across the Elbe-Weser Triangle and runs in a gentle curve via Bremervörde and Zeven (71 km) over the Hansa Line A 1 (83 km) to the district town of Rotenburg (Wümme) (97 km). Here it crosses the B 75 and continues past the Lüneburg Heath to Soltau (133 km), where it crosses the B 3. Carrying on towards the east it runs through heathland to Uelzen (190 km), where the road again crosses another major federal route, the B 4. Next it runs through the Elbufer-Drawehn Nature Park and crosses the old Inner German Border and present-day state border between Lower Saxony and Saxony-Anhalt at kilometre marker 222.
The Bremervörde–Walsrode railway was a railway route of regional importance in the German state of Lower Saxony. It linked Bremervörde via Zeven, Rotenburg (Wümme) and Visselhövede to Walsrode. Passenger trains were divided in Rotenburg. Originally the link was conceived as part of a long-distance through route from Hanover to Geestemünde, but long-distance trains never worked the line.

The region between the Elbe and Weser rivers forms the Elbe–Weser triangle, also rendered Elbe-Weser Triangle, in northern Germany. It is also colloquially referred to as the Nasses Dreieck or "wet triangle".

The Geeste is a river in northwestern Germany, running through Lower Saxony and Bremen. It is the most downstream tributary of the River Weser and joins it near Bremerhaven. The Geeste rises in Hipstedt in the district of Rotenburg (Wümme) ten kilometres west of Bremervörde and drains a large part of the old district of Wesermünde.

The Wümme Depression is a bog, geest and forest landscape within the Elbe-Weser Triangle in the German state of Lower Saxony. It belongs mainly to the district of Rotenburg and is part of the Stade Geest. To the south it borders on the Achim-Verden Geest. It has no sharply defined boundary with the Lüneburg Heath; as a result many places are seen as belonging to both regions. Typical of the gently undulating terrain are the many small rivers, streams and lakes. These include the rivers Wümme, Wieste, Fintau, Rodau, Wiedau and Vissel, as well as the twin lakes known in German as the Bullenseen. In this ancient landscape Low German is commonly spoken.
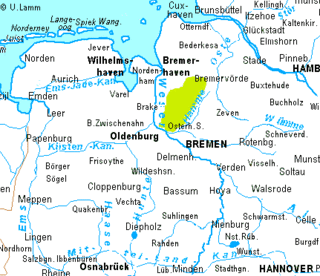
The Osterholz Geest is an undulating, sandy area of ground moraine between the city of Bremen and the towns of Bremerhaven and Bremervörde.

The 3rd Armoured Division was formed on 2 July 1956 in Hamburg and was one of the first major formations of the new German Army or Bundeswehr after the Second World War. The 3rd Armoured Division was stationed on the North German Plain between the rivers Elbe and Weser. Its last headquarters location was Buxtehude. It was part of the I Corps alongside the 1st Panzer, 7th Panzer, and 11th Panzergrenadier Divisions.
The Wesermünde Geest is the collective name for several geest ridges in the west of Cuxhaven district and Bremen's North Borough in northern Germany. The ridges are separated from one another by wetlands. These terminal moraines were formed during the Saale glaciation, are up to between 10 to 70 m above sea level (NN), and are covered by scattered woods and farmland. The wetland areas, between 0 to 5 m above sea level, are predominantly used for grazing.
The Achim-Verden Geest is part of the Stade Geest. Its main part is in the northeast of the German state of Lower Saxony, a smaller part in the state of Bremen.
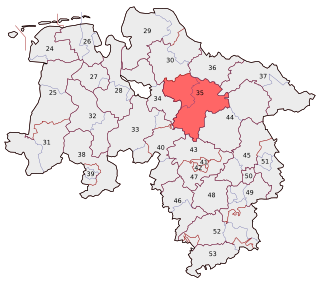
Rotenburg I - Heidekreis is one of the 299 single member constituencies used for the German parliament, the Bundestag. The constituency elects one representative under the mixed member proportional representation (MMP) system. Under the current constituency numbering system, it is designated as constituency 35.
























