This article concerns the period 119 BC – 110 BC.
Year 111 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Serapio and Bestia and the Sixth Year of Yuanding. The denomination 111 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Year 112 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Drusus and Caesoninus and the Fifth Year of Yuanding. The denomination 112 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

The Baiyue, Hundred Yue, or simply Yue, were various ethnic groups who inhabited the regions of Southern China and Northern Vietnam during the 1st millennium BC and 1st millennium AD. They were known for their short hair, body tattoos, fine swords, and naval prowess.

Zhao Tuo, rendered as Triệu Đà in Vietnamese, was a Qin dynasty Chinese general and first emperor of Nanyue. He participated in the conquest of the Baiyue peoples of Guangdong, Guangxi and Northern Vietnam. After the fall of the Qin, he established the independent kingdom of Nanyue with its capital in Panyu in 204 BCE. Some traditional Vietnamese history scholars considered him the founder of the Triệu dynasty while some contemporary historians contest that he was a foreign invader.

Nanyue, was an ancient kingdom founded in 204 BC by the Chinese general Zhao Tuo, whose family continued to rule until 111 BC. Nanyue's geographical expanse covered the modern Chinese subdivisions of Guangdong, Guangxi, Hainan, Hong Kong, Macau, southern Fujian and central to northern Vietnam. Zhao Tuo, then Commander of Nanhai Commandery of the Qin dynasty, established Nanyue in 204 BC after the collapse of the Qin dynasty. At first, it consisted of the commanderies of Nanhai, Guilin, and Xiang.

Zhao Mo was the second ruler of Nanyue. He succeeded his grandfather Zhao Tuo in 137 BC and reigned until his death in 124 BC.

The Triệu dynasty or Zhao dynasty ruled the kingdom of Nanyue, which consisted of parts of southern China as well as northern Vietnam. Its capital was Panyu, in modern Guangzhou. The founder of the dynasty, Zhao Tuo, was a Chinese general from Hebei and originally served as a military governor under the Qin dynasty. He asserted the state's independence in 207 BC as the Qin dynasty was collapsing. The ruling elite included both native Yue and immigrant Han peoples. Zhao Tuo conquered the Vietnamese state of Âu Lạc and led a coalition of Yuè states in a war against the Han dynasty, which had been expanding southward. Subsequent rulers were less successful in asserting their independence and the Han dynasty finally conquered the kingdom in 111 BC.

An Dương Vương, personal name Thục Phán, was the founding king and the only ruler of the kingdom of Âu Lạc, an ancient state centered in the Red River Delta. As the leader of the Âu Việt tribes, he defeated the last Hùng king of the state of Văn Lang and united its people – known as the Lạc Việt – with his people, the Âu Việt. An Dương Vương fled and committed suicide after the war with Nanyue forces in 179 BCE.
The First Era of Northern Domination refers to the period of Vietnamese history during which present-day northern Vietnam was under the rule of the Han dynasty and the Xin dynasty as Jiaozhi province and Jiaozhou province. It is considered the first of four periods of Chinese rule over Vietnam, and the first of the three in which were almost continuous and was referred to as Bắc thuộc.

The Đại Việt sử ký toàn thư is the official national chronicle of the Đại Việt, that was originally compiled by the royal historian Ngô Sĩ Liên under the order of the Emperor Lê Thánh Tông and was finished in 1479 during the Lê period. The 15-volume book covered the period from Hồng Bàng dynasty to the coronation of Lê Thái Tổ, the first emperor of the Lê dynasty in 1428. In compiling his work, Ngô Sĩ Liên based on two principal historical sources which were Đại Việt sử ký by Lê Văn Hưu and Đại Việt sử ký tục biên by Phan Phu Tiên. After its publication, Đại Việt sử ký toàn thư was continually supplemented by other historians of the royal court such as Vũ Quỳnh and Phạm Công Trứ. Today the most popular version of Đại Việt sử ký toàn thư is the Nội các quan bản edition which was completed in 1697 with the additional information up to 1656 during the reign of the Emperor Lê Thần Tông and the Lord Trịnh Tráng. Đại Việt sử ký toàn thư is considered the most important and comprehensive historical book. The chronicle, which was modeled after Sima Qian’s Records of the Grand Historian, provides a chronological history beginning with the legendary Hồng Bàng dynasty and continuing to the founding of the house of Lê in 1428.

The Museum of the Western Han Dynasty Mausoleum of the Nanyue King houses the 2,000-year-old tomb of the Nanyue King Zhao Mo in Guangzhou. Zhao Mo ruled from 137 BC to 122 BC, and his tomb was discovered in downtown Guangzhou in 1983. The museum, which opened in 1988, showcases the tomb and its complete trove of artifacts. It was named a Major National Historical Site in 1996 and is renowned for its rare assemblage of funerary artifacts representing the diffusion of cultures throughout the Lingnan region during the Han dynasty.

Zhao Xing, was the second son of Zhao Yingqi and the fourth ruler of Nanyue. His rule began in 115 BC and ended with his death in 112 BC, when he was overthrown and killed by Lü Jia.
Zhao Jiande was the last king of Nanyue. His rule began in 112 BC and ended in the next year. He was executed by Western Han forces during the reign of Emperor Wu of Han.

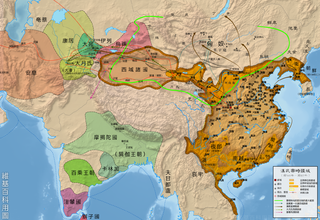
The Han conquest of Nanyue was a military conflict between the Han Empire and the Nanyue kingdom in modern Guangdong, Guangxi, and Northern Vietnam. During the reign of Emperor Wu, Imperial Han military forces formally launched a punitive campaign against Nanyue and successfully conquered it in 111 BC.

The southward expansion of the Han dynasty was a series of Chinese military campaigns and expeditions in what is now modern Southern China and Northern Vietnam. Military expansion to the south began under the previous Qin dynasty and continued during the Han era. Campaigns were dispatched to conquer the Yue tribes, leading to the annexation of Minyue by the Han in 135 BC and 111 BC, Nanyue in 111 BC, and Dian in 109 BC.

The Han campaigns against Minyue were a series of three Han military campaigns dispatched against the Minyue state. The first campaign was in response to Minyue's invasion of Eastern Ou in 138 BC. In 135 BC, a second campaign was sent to intervene in a war between Minyue and Nanyue. After the campaign, Minyue was partitioned into Minyue, ruled by a Han proxy king named Zou Yushan, and Dongyue. During the concluding months of 111 BC, after the unsuccessful uprising led by Zou Yushan in thwarting General Yang Pu's conspiratorial intentions to undermine him, the aspiration for autonomous rule in Dongyue gradually waned. The rebellion instigated by Zou was suppressed, prompting the Han dynasty's complete annexation of Dongyue into its dominion and the conquest of the residual territories that constituted the former Minyue, effectively consolidating the permanent integration of both domains into the Han empire indefinitely.

Lü Jia, or Lữ Gia in Vietnamese, also called Bảo Công (保公), was the prime minister of Nanyue during the reigns of its three last kings. Lü overthrew and killed Zhao Xing and Queen Jiu of Nanyue. Eventually Lü was killed and defeated by Han forces.
Emperor at home, king abroad was a system of conducting relations between states within the Chinese cultural sphere. Rulers of lesser regimes would adopt the title of emperor and/or other imperial titles domestically, and adopt the title of king when dealing with the dominant Chinese regime. Instead of using the styles Imperial Majesty and Majesty (陛下), rulers of lesser realms were styled as Highness (殿下). This system was applicable to Japan, Korea and Vietnam, as well as less powerful Chinese states, among others.
Queen Jiu or Cù Hậu, was a queen consort and regent of Nanyue. She was originally from Handan. She was married to King Zhao Yingqi and was the mother of king Zhao Xing. She served as regent of Nanyue during the minority of her son between 113 and 112 BC. She and her son were deposed and murdered by prime minister Lü Jia for having submitted to the Han dynasty as vassals.