History
Precolonial contact
The island of Timor is thought to have been settled in three waves. The first wave to arrive on the island were the Vedo-Australoide roughly 40,000-20,000 BCE, near the end of the fourth and final global glacier period, when much of Indonesia was a continuous body of land, and Timor was much closer to other islands in the archipelago. The second wave is thought to have come from Melanesia, specifically from Papua New-Guinea, Vanuatu, and the Salomon Islands, around 3,000 BCE. The Melanesian people had well-developed agriculture, so they could explore the surrounding ocean better than other oceanic people's at the time. The Melanesian languages Fataluco, Macaçai, and Búnac are still spoken in some parts of East and West Timor to this day. The third and final pre-colonial wave, known as the Proto-Malay, came to Timor from Southern China and Northern Indochina around 2,500 BCE. The Proto-Malay populated most of modern-day Indonesia. [4]
Postcolonial contact
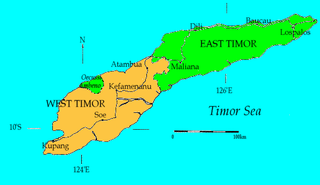
Timor was contacted by the Portuguese in 1515, and claimed as a territory of Portugal in 1520. The Dutch East India Company settled the west end of the island in 1640, pushing the Portuguese out and to the east side of the island. The Dutch government officially acknowledged their occupation in 1799, and an unsteady border was formed, separating the two sides. A treaty between the Portuguese and the Dutch was signed in 1859, and reformed in 1893, but it was not until as late as 1914 when the treaty was finalized and border disputes were finally laid to rest. Shortly after, in 1942, both sides of Timor were conquered by Empire of Japan during its invasion of the pacific. Timor participated in the Indonesian Interdependence cause, and joined the Republic of Indonesia in 1949. East Timor voted to leave the republic in 1999, becoming the first new sovereign nation of the 21st century. [4]
Amarasi in Timor

The Amarasi were a powerful princedom in the west section of Timor during the initial occupation of the Portuguese beginning in the 16th century. According to legend, a young man named Nafi Rasi, accidentally broke a family heirloom and left his home in East Timor to the west, out of fear of retaliation. He acquired guns from the Portuguese-Timoric Topasses, and used them to gain power and prestige, collecting a following from his home province of Belu, and forming a lasting dynasty. [6] By the mid 17th century, the Amarasi had been mostly converted to Catholicism by Dominican missionaries, an influence that has lasted to present day. A 2010 census found that 96.9% of the population in Timor is Catholic, and that 2.2% are Protestant. [7] Because of their debt to the Portuguese for helping found their dynasty, Amarasi sided with them to help resist the Dutch East India Company's settlement in 1640. For over a hundred years the Amarasi fought against the Dutch in the Kupang area along the west coast of Timor, engaging in "low-scale warfare" and headhunting. [8]
The Amarasi suffered a severe loss at the hands of the Dutch in 1752, after attempting a large-scale resistance with the Topasses against the Dutch occupying the west coast in 1749. The Topasses were completely defeated, and the Amarasi attempted to retreat to their Portuguese allies, but were cut off by the Dutch East India Company's forces. Facing defeat, the Amarasi King killed himself rather than be taken prisoner, and a majority of his people were killed or taken as slaves. After several years, the Amarasi were released from their bondage and allowed to return to their native homes, with the condition that they relinquish any affiliation with the Portuguese, and remain loyal to Dutch interests, which they did until West Timor joined the Republic of Indonesia in the 1940s. [9] During this time, the Amarasi dynasty split into three parts, Buwarein, who remained loyal to the bloodline of Nafi Rasi, andTaiba and Houmen, who believed that the bloodline was what had led them to their defeat at the hands of the Dutch. In the early part of the 20th century infighting let to further subdividing of the Amarasi, resulting in a total of five much smaller factions. [10]
These factions were lost during the Japanese occupation of Indonesia between 1942 and 1945, when the Amarasi were united once again. The princedom returned to power for the first few years of the Republic on Indonesia, until in 1962, when "traditional forms of government" were abolished in their region. [4]
Because of its complex occupational history, Amarasi and other Timoric languages use many loan words from Dutch, Portuguese, Japanese, and various other Oceanic languages. Their long alliance with the Portuguese also accounts for why they seem to have had the largest influence on the Amarasi language. For example, the Amarasi for 'thank you' is obrigadu, derived from the Portuguese obrigado.