
A grape is a fruit, botanically a berry, of the deciduous woody vines of the flowering plant genus Vitis.

Resveratrol (3,5,4′-trihydroxy-trans-stilbene) is a stilbenoid, a type of natural phenol, and a phytoalexin produced by several plants in response to injury or when the plant is under attack by pathogens, such as bacteria or fungi. Sources of resveratrol in food include the skin of grapes, blueberries, raspberries, mulberries, and peanuts.

Vitis vinifera, the common grape vine, is a species of flowering plant, native to the Mediterranean region, Central Europe, and southwestern Asia, from Morocco and Portugal north to southern Germany and east to northern Iran. There are currently between 5,000 and 10,000 varieties of Vitis vinifera grapes though only a few are of commercial significance for wine and table grape production.

Vitis rotundifolia, or muscadine, is a grapevine species native to the southeastern and south-central United States. The growth range extends from Florida to New Jersey coast, and west to eastern Texas and Oklahoma. It has been extensively cultivated since the 16th century. The plants are well-adapted to their native warm and humid climate; they need fewer chilling hours than better known varieties, and thrive in summer heat.

The phenolic content in wine refers to the phenolic compounds—natural phenol and polyphenols—in wine, which include a large group of several hundred chemical compounds that affect the taste, color and mouthfeel of wine. These compounds include phenolic acids, stilbenoids, flavonols, dihydroflavonols, anthocyanins, flavanol monomers (catechins) and flavanol polymers (proanthocyanidins). This large group of natural phenols can be broadly separated into two categories, flavonoids and non-flavonoids. Flavonoids include the anthocyanins and tannins which contribute to the color and mouthfeel of the wine. The non-flavonoids include the stilbenoids such as resveratrol and phenolic acids such as benzoic, caffeic and cinnamic acids.

ε-Viniferin is a naturally occurring phenol, belonging to the stilbenoids family. It is a resveratrol dimer.

α-Viniferin is a stilbene trimer. It can be isolated from Caragana chamlagu and from Caragana sinica and from the stem bark of Dryobalanops aromatica. It is also present in relation to resistance to Botrytis cinerea and Plasmopara viticola in Vitis vinifera and Vitis riparia.
Vitis chunganensis is a species of climbing vine in the grape family native to China. In Chinese it is called dong nan pu tao, or Southeast grape.

Astringin is a stilbenoid, the 3-β-D-glucoside of piceatannol. It can be found in the bark of Picea sitchensis or Picea abies.
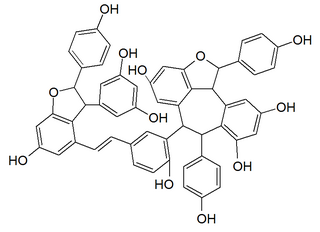
Vitisin A is a resveratrol tetramer found in plants of the genus Vitis. It is a complex of two resveratrol dimers, (+)-epsilon-viniferin and ampelopsin B.
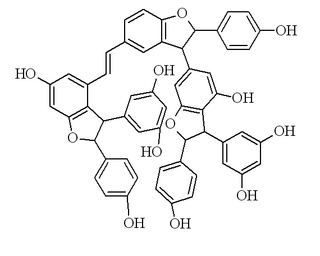
Vitisin B is a resveratrol tetramer found in plants of the genus Vitis.

Vitisin C is a hydroxystilbenoid. It is a resveratrol tetramer found in plants of the genus Vitis (grapevines).

δ-Viniferin is a resveratrol dehydrodimer. It is an isomer of epsilon-viniferin. It can be isolated from stressed grapevine leaves. It is also found in plant cell cultures and wine. It can also be found in Rheum maximowiczii.

Miyabenol C is a stilbenoid. It is a resveratrol trimer. It is found in Vitis vinifera (grape), in Foeniculi fructus, in Caragana sinica.

Flexuosol A is a resveratrol tetramer found in Vitis flexuosa.

Amurensin K is an oligostilbene. It is a resveratrol tetramer found in Vitis amurensis. Preliminary tests have shown it to be an effective neuraminidase inhibitor against the influenza A virus subtype H1N1.

Amurensin E is an oligostilbene found in Vitis amurensis. It is a pentamer of resveratrol.

Amurensin A is an oligostilbene isolated from the roots of Vitis amurensis. It is a partially oxidized resveratrol dimer with a C8-C8' connection.
Grape therapy, also known as ampelotherapy, is a form of naturopathic alternative medicine that involves heavy consumption of grapes, including seeds, and parts of the vine, including leaves. The concept has no scientific basis and is widely regarded as quackery.

















