
A grape is a fruit, botanically a berry, of the deciduous woody vines of the flowering plant genus Vitis. Grapes are a non-climacteric type of fruit, generally occurring in clusters.

The Vitaceae are a family of flowering plants, with 14 genera and around 910 known species, including common plants such as grapevines and Virginia creeper. The family name is derived from the genus Vitis.

Resveratrol (3,5,4′-trihydroxy-trans-stilbene) is a stilbenoid, a type of natural phenol, and a phytoalexin produced by several plants in response to injury or when the plant is under attack by pathogens, such as bacteria or fungi. Sources of resveratrol in food include the skin of grapes, blueberries, raspberries, mulberries, and peanuts.

The health effects of wine are mainly determined by its active ingredient – alcohol. Preliminary studies found that drinking small quantities of wine, particularly of red wine, may be associated with a decreased risk of cardiovascular diseases, cognitive decline, stroke, diabetes mellitus, metabolic syndrome, and early death. Other studies found no such effects.

The phenolic content in wine refers to the phenolic compounds—natural phenol and polyphenols—in wine, which include a large group of several hundred chemical compounds that affect the taste, color and mouthfeel of wine. These compounds include phenolic acids, stilbenoids, flavonols, dihydroflavonols, anthocyanins, flavanol monomers (catechins) and flavanol polymers (proanthocyanidins). This large group of natural phenols can be broadly separated into two categories, flavonoids and non-flavonoids. Flavonoids include the anthocyanins and tannins which contribute to the color and mouthfeel of the wine. The non-flavonoids include the stilbenoids such as resveratrol and phenolic acids such as benzoic, caffeic and cinnamic acids.

ε-Viniferin is a naturally occurring phenol, belonging to the stilbenoids family. It is a resveratrol dimer.
Vitis chunganensis is a species of climbing vine in the grape family native to China. In Chinese it is called dong nan pu tao, or Southeast grape.
Cissus adnata is a woody vine species in the genus Cissus found in Asia and Australia.

Astringin is a stilbenoid, the 3-β-D-glucoside of piceatannol. It can be found in the bark of Picea sitchensis or Picea abies.

Parthenocissus laetevirens is a climbing plant species in the genus Parthenocissus found in China.

Hopeaphenol is a stilbenoid. It is a resveratrol tetramer. It has been first isolated from Dipterocarpaceae like Shorea ovalis. It has also been isolated from wines from North Africa.

Wine is a complex mixture of chemical compounds in a hydro-alcoholic solution with a pH around 4. The chemistry of wine and its resultant quality depend on achieving a balance between three aspects of the berries used to make the wine: their sugar content, acidity and the presence of secondary compounds. Vines store sugar in grapes through photosynthesis, and acids break down as grapes ripen. Secondary compounds are also stored in the course of the season. Anthocyanins give grapes a red color and protection against ultraviolet light. Tannins add bitterness and astringency which acts to defend vines against pests and grazing animals.

trans-Resveratrol-3-O-glucuronide is a metabolite of resveratrol and trans-resveratrol-3-O-glucoside (piceid).

δ-Viniferin is a resveratrol dehydrodimer. It is an isomer of epsilon-viniferin. It can be isolated from stressed grapevine leaves. It is also found in plant cell cultures and wine. It can also be found in Rheum maximowiczii.
Propelargonidins are a type of condensed tannins formed from epiafzelechin. They yield pelargonidin when depolymerized under oxidative conditions.

Quadrangularin A is an oligostilbene found in Cissus quadrangularis and in Parthenocissus laetevirens. It is a resveratrol dimer.
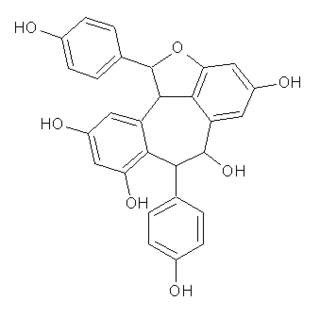
Ampelopsin A is a resveratrol dimer found in Ampelopsis glandulosa var. hancei.

Cyphostemmin B is an oligostilbene found in Cyphostemma crotalarioides (Vitaceae). It is a resveratrol dimer.
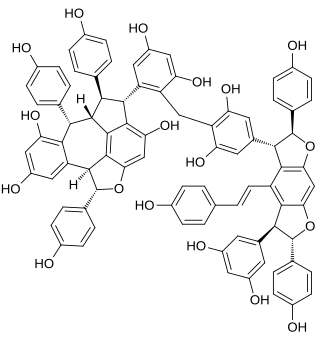
Chunganenol is a resveratrol hexamer found in Vitis chunganensis.
















