Calcineurin (CaN) is a calcium and calmodulin dependent serine/threonine protein phosphatase. It activates the T cells of the immune system and can be blocked by drugs. Calcineurin activates nuclear factor of activated T cell cytoplasmic (NFATc), a transcription factor, by dephosphorylating it. The activated NFATc is then translocated into the nucleus, where it upregulates the expression of interleukin 2 (IL-2), which, in turn, stimulates the growth and differentiation of the T cell response. Calcineurin is the target of a class of drugs called calcineurin inhibitors, which include ciclosporin, voclosporin, pimecrolimus and tacrolimus.

The p53 upregulated modulator of apoptosis (PUMA) also known as Bcl-2-binding component 3 (BBC3), is a pro-apoptotic protein, member of the Bcl-2 protein family. In humans, the Bcl-2-binding component 3 protein is encoded by the BBC3 gene. The expression of PUMA is regulated by the tumor suppressor p53. PUMA is involved in p53-dependent and -independent apoptosis induced by a variety of signals, and is regulated by transcription factors, not by post-translational modifications. After activation, PUMA interacts with antiapoptotic Bcl-2 family members, thus freeing Bax and/or Bak which are then able to signal apoptosis to the mitochondria. Following mitochondrial dysfunction, the caspase cascade is activated ultimately leading to cell death.

Survivin, also called baculoviral inhibitor of apoptosis repeat-containing 5 or BIRC5, is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the BIRC5 gene.

Ursolic acid, is a pentacyclic triterpenoid identified in the epicuticular waxes of apples as early as 1920 and widely found in the peels of fruits, as well as in herbs and spices like rosemary and thyme.
Limonin is a limonoid, and a bitter, white, crystalline substance found in citrus and other plants. It is also known as limonoate D-ring-lactone and limonoic acid di-delta-lactone. Chemically, it is a member of the class of compounds known as furanolactones.

Neuregulin 1, or NRG1, is a gene of the epidermal growth factor family that in humans is encoded by the NRG1 gene. NRG1 is one of four proteins in the neuregulin family that act on the EGFR family of receptors. Neuregulin 1 is produced in numerous isoforms by alternative splicing, which allows it to perform a wide variety of functions. It is essential for the normal development of the nervous system and the heart.

Caspase-3 is a caspase protein that interacts with caspase-8 and caspase-9. It is encoded by the CASP3 gene. CASP3 orthologs have been identified in numerous mammals for which complete genome data are available. Unique orthologs are also present in birds, lizards, lissamphibians, and teleosts.

Apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 (ASK1) also known as mitogen-activated protein kinase 5 (MAP3K5) is a member of MAP kinase family and as such a part of mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. It activates c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinases in a Raf-independent fashion in response to an array of stresses such as oxidative stress, endoplasmic reticulum stress and calcium influx. ASK1 has been found to be involved in cancer, diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, cardiovascular and neurodegenerative diseases.
Mitogen-activated protein kinase 14, also called p38-α, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MAPK14 gene.

Protein kinase C epsilon type (PKCε) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PRKCE gene. PKCε is an isoform of the large PKC family of protein kinases that play many roles in different tissues. In cardiac muscle cells, PKCε regulates muscle contraction through its actions at sarcomeric proteins, and PKCε modulates cardiac cell metabolism through its actions at mitochondria. PKCε is clinically significant in that it is a central player in cardioprotection against ischemic injury and in the development of cardiac hypertrophy.

Protocatechuic acid (PCA) is a dihydroxybenzoic acid, a type of phenolic acid. It is a major metabolite of antioxidant polyphenols found in green tea. It has mixed effects on normal and cancer cells in in vitro and in vivo studies.

Voltage-dependent anion-selective channel protein 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the VDAC2 gene on chromosome 10. This protein is a voltage-dependent anion channel and shares high structural homology with the other VDAC isoforms. VDACs are generally involved in the regulation of cell metabolism, mitochondrial apoptosis, and spermatogenesis. Additionally, VDAC2 participates in cardiac contractions and pulmonary circulation, which implicate it in cardiopulmonary diseases. VDAC2 also mediates immune response to infectious bursal disease (IBD).

H-89 is a protein kinase inhibitor with greatest effect on protein kinase A (PKA). H-89, derived from H-8, was initially believed to act specifically as an inhibitor of PKA, being 30 times more potent than H-8 at inhibiting PKA and 10 times less potent at inhibiting protein kinase G. It achieves this through competitive inhibition of the adenosine triphosphate (ATP) site on the PKA catalytic subunit. However, subsequent work has suggested a variety of additional effects such as inhibition of other protein kinases, and direct inhibition of various potassium currents.
12-Hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid (12-HETE) is a derivative of the 20 carbon polyunsaturated fatty acid, arachidonic acid, containing a hydroxyl residue at carbon 12 and a 5Z,8Z,10E,14Z Cis–trans isomerism configuration in its four double bonds. It was first found as a product of arachidonic acid metabolism made by human and bovine platelets through their 12S-lipoxygenase enzyme(s). However, the term 12-HETE is ambiguous in that it has been used to indicate not only the initially detected "S" stereoisomer, 12S-hydroxy-5Z,8Z,10E,14Z-eicosatetraenoic acid, made by platelets, but also the later detected "R" stereoisomer, 12(R)-hydroxy-5Z,8Z,10E,14Z-eicosatetraenoic acid made by other tissues through their 12R-lipoxygenase enzyme, ALOX12B. The two isomers, either directly or after being further metabolized, have been suggested to be involved in a variety of human physiological and pathological reactions. Unlike hormones which are secreted by cells, travel in the circulation to alter the behavior of distant cells, and thereby act as Endocrine signalling agents, these arachidonic acid metabolites act locally as Autocrine signalling and/or Paracrine signaling agents to regulate the behavior of their cells of origin or of nearby cells, respectively. In these roles, they may amplify or dampen, expand or contract cellular and tissue responses to disturbances.
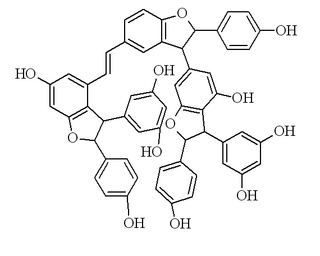
Vitisin B is a resveratrol tetramer found in plants of the genus Vitis.

Vitisin C is a hydroxystilbenoid. It is a resveratrol tetramer found in plants of the genus Vitis (grapevines).
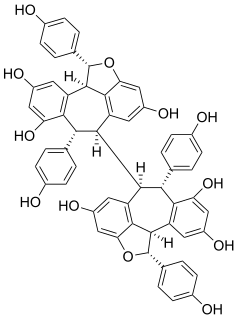
Hopeaphenol is a stilbenoid. It is a resveratrol tetramer. It has been first isolated from Dipterocarpaceae like Shorea ovalis. It has also been isolated from wines from North Africa.

Rottlerin (mallotoxin) is a polyphenol natural product isolated from the Asian tree Mallotus philippensis. Rottlerin displays a complex spectrum of pharmacology.

Isorhapontigenin is a tetrahydroxylated stilbenoid with a methoxy group. It is an isomer of rhapontigenin and an analog of resveratrol. It is found in the Chinese herb Gnetum cleistostachyum, in Gnetum parvifolium and in the seeds of the palm Aiphanes aculeata.