 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
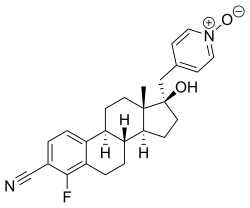
| Other names | 4-Fluoro-17β-hydroxy-17α-[(1-oxidopyridin-1-ium-4-yl)methyl]estra-1,3,5(10)-triene-3-carbonitrile |
| Drug class | Steroidal antiandrogen |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C25H27FN2O2 |
| Molar mass | 406.501 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
EM-5854 is a steroidal antiandrogen which was under development by Endoceutics, Inc. (formerly Endorecherche, Inc.) for the treatment of prostate cancer. [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] It was first described in a patent in 2008, and was further characterized in 2012. [2] [4] EM-5854 reached phase I/II clinical trials for the treatment of prostate cancer but development was discontinued in March 2019. [1]
The drug acts as a potent and selective competitive antagonist of the androgen receptor (AR). [4] [5] Unlike other steroidal antiandrogens like cyproterone acetate, but similarly to nonsteroidal antiandrogens like bicalutamide and enzalutamide, EM-5854 is a pure or silent antagonist of the AR and shows no intrinsic partial androgenic activity. [4] EM-5854 and its metabolite EM-5855 show 3.7-fold and 94-fold higher affinity for the human AR than bicalutamide (0.66% and 17% of the RBA of metribolone, respectively, compared to 0.18% for bicalutamide). [4] [5] They also show dramatically increased antiandrogenic potency relative to bicalutamide in in vivo assays. [4] [5] [6] On the basis of the available research, it has been said that EM-5854 may possibly have 70- to 140-fold the antiandrogenic potency of bicalutamide in humans. [4] EM-5854 and EM-5855 show little to no affinity for other steroid hormone receptors including the estrogen, progesterone, and glucocorticoid receptors. [4] EM-5854 bears a cyano phenyl group, the structural motif of the nonsteroidal antiandrogens. [7]
| Activity | Specifics | Bica | Flu | OH‑Flu | Enza | EM‑5854 | EM‑5855 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AR RBA (%) | Human | 0.18 | NA | 0.17 | 0.07 | 0.66 | 17 |
| Metri = 100% | Rat | 0.13 | NA | 0.07 | 0.02 | 0.35 | 2.6 |
| Shionogi cells AA activity | Ki (nM) | 81 | NA | NA | 170 | 2.0 | 0.77 |
| LNCaP cells (PSA ) AA activity and stim of basal prolif | De50 (nM) (Inhib at 10−7 M (%)) | 1750 (6 ± 10) | NA | NA | 1380 (−20 ± 3) | 127 (36 ± 7) | 66 (66 ± 1) |
| Stim at 10−7 M (%) | 0 ± 1 | NA | NA | 1 ± 1 | 19 ± 1 | 29 ± 2 | |
| ER RBA (%) | Rat (E2 = 100%) | 0 | NA | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| PR RBA (%) | Rat (Prom = 100%) | ND | NA | 0 | ND | 0.2 | ND |
| GR RBA (%) | Rat (Dexa = 100%) | 0 | NA | 0 | <0.1 | 0 | 0 |