An androgen prohormone, or proandrogen, is a prohormone of an anabolic-androgenic steroid (AAS). They can be prohormones of testosterone or of synthetic AAS, for example, nandrolone (19-nortestosterone). Dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA), DHEA sulfate (DHEA-S), and androstenedione may all be considered proandrogens of testosterone.
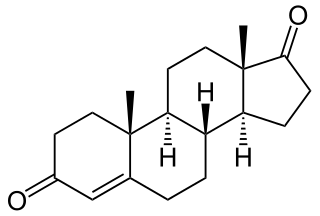
Androstenedione, or 4-androstenedione, also known as androst-4-ene-3,17-dione, is an endogenous weak androgen steroid hormone and intermediate in the biosynthesis of estrone and of testosterone from dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA). It is closely related to androstenediol (androst-5-ene-3β,17β-diol).
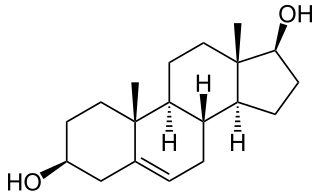
Androstenediol, or 5-androstenediol, also known as androst-5-ene-3β,17β-diol, is an endogenous weak androgen and estrogen steroid hormone and intermediate in the biosynthesis of testosterone from dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA). It is closely related to androstenedione (androst-4-ene-3,17-dione).

1-Testosterone, also known as δ1-dihydrotestosterone (δ1-DHT), as well as dihydroboldenone, is a synthetic anabolic–androgenic steroid (AAS) and a 5α-reduced derivative of boldenone (Δ1-testosterone). It differs from testosterone by having a 1(2)-double bond instead of a 4(5)-double bond in its A ring. It was legally sold online in the United States until 2005, when it was reclassified as a Schedule III drug.

Bolandione, also known as 19-norandrostenedione, as well as 19-norandrost-4-en-3,17-dione or estr-4-ene-3,17-dione, is a precursor of the anabolic-androgenic steroid (AAS) nandrolone (19-nortestosterone). Until 2005, bolandione was available without prescription in United States, where it was marketed as a prohormone, but it is now classified as a Schedule III drug. It is also banned from use in many sports, including the Olympic Games, under the World Anti-Doping Code. Bolandione is readily metabolized to nandrolone after oral administration, but its potency to transactivate the androgen receptor dependent reporter gene expression is 10 times lower as compared to dihydrotestosterone (DHT).

Epiandrosterone, or isoandrosterone, also known as 3β-androsterone, 3β-hydroxy-5α-androstan-17-one, or 5α-androstan-3β-ol-17-one, is a steroid hormone with weak androgenic activity. It is a metabolite of testosterone and dihydrotestosterone (DHT). It was first isolated in 1931, by Adolf Friedrich Johann Butenandt and Kurt Tscherning. They distilled over 17,000 litres of male urine, from which they got 50 milligrams of crystalline androsterone, which was sufficient to find that the chemical formula was very similar to estrone.

7-Ketodehydroepiandrosterone (7-keto-DHEA,7-oxo-DHEA), also known as 7-oxoprasterone, is a prohormone produced by metabolism of the prohormone dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA).
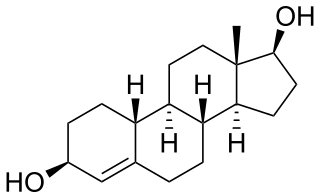
Bolandiol is an anabolic-androgenic steroid (AAS) that was never marketed. However, a dipropionate ester derivative, bolandiol dipropionate, has been marketed. Bolandiol and its dipropionate ester are unique among AASs in that they reportedly also possesses estrogenic and progestogenic activity.
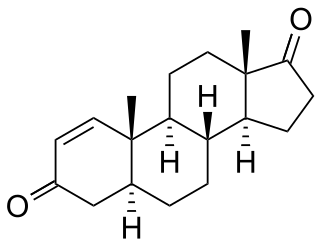
1-Androstenedione, or 5α-androst-1-ene-3,17-dione, also known as 4,5α-dihydro-δ1-4-androstenedione, is a synthetic androgen and anabolic steroid. It is a 5α-reduced isomer of the endogenous steroid 4-androstenedione and acts as an androgen prohormone of 1-testosterone (4,5α-dihydro-δ1-testosterone), a derivative of dihydrotestosterone (DHT).

Androstanedione, also known as 5α-androstanedione or as 5α-androstane-3,17-dione, is a naturally occurring androstane (5α-androstane) steroid and an endogenous metabolite of androgens like testosterone, dihydrotestosterone (DHT), dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA), and androstenedione. It is the C5 epimer of etiocholanedione (5β-androstanedione). Androstanedione is formed from androstenedione by 5α-reductase and from DHT by 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase. It has some androgenic activity.
Androstenedione may refer to:
Androstenolone may refer to:

7α-Methyl-19-norandrostenedione, or 7α-methyl-19-norandrost-4-ene-3,17-dione, also known as trestione, as well as 7α-methylestr-4-ene-3,17-dione, is a synthetic anabolic-androgenic steroid (AAS) and a derivative of 19-nortestosterone (nandrolone). It may act as a prohormone of trestolone. MENT dione has been sold on the Internet under the name Mentabolan as a "dietary supplement".

19-Nor-5-androstenediol, also known as estr-5-ene-3β,17β-diol, is a synthetic, orally active anabolic-androgenic steroid (AAS) and a derivative of 19-nortestosterone (nandrolone) that was never introduced for medical use. It is an androgen prohormone of nandrolone and of other 19-norandrostanes.

19-Nor-5-androstenedione, also known as estr-5-ene-3,17-dione, is a synthetic, orally active anabolic-androgenic steroid (AAS) and a derivative of 19-nortestosterone (nandrolone) that was never introduced for medical use. It is an androgen prohormone of nandrolone and of other 19-norandrostanes.

1-Androsterone is a synthetic, orally active anabolic-androgenic steroid (AAS). It is an androgen prohormone of 1-testosterone (dihydroboldenone), 1-androstenedione, and other 1-dehydrogenated androstanes. The drug has been sold on the Internet as a designer steroid and "dietary supplement". It is a positional isomer of dehydroepiandrosterone.
The structure–activity relationships (SAR) of anabolic steroids (AAS) have been extensively studied.

Etiocholanedione, also known as 5β-androstanedione or as etiocholane-3,17-dione, is a naturally occurring etiocholane (5β-androstane) steroid and an endogenous metabolite of androgens like testosterone, dihydrotestosterone, dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA), and androstenedione. It is the C5 epimer of androstanedione (5α-androstanedione). Although devoid of androgenic activity like other 5β-reduced steroids, etiocholanedione has some biological activity of its own. The compound has been found to possess potent haematopoietic effects in a variety of models. In addition, it has been found to promote weight loss in animals and in a double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical study in humans conducted in 1993. These effects are said to be similar to those of DHEA. Unlike DHEA however, etiocholanedione cannot be metabolized further into steroid hormones like androgens and estrogens.















