A nuclear reactor, formerly known as an atomic pile, is a device used to initiate and control a self-sustained nuclear chain reaction. Nuclear reactors are used at nuclear power plants for electricity generation and in propulsion of ships. Heat from nuclear fission is passed to a working fluid, which in turn runs through steam turbines. These either drive a ship's propellers or turn electrical generators' shafts. Nuclear generated steam in principle can be used for industrial process heat or for district heating. Some reactors are used to produce isotopes for medical and industrial use, or for production of weapons-grade plutonium. Some are run only for research. As of early 2019, the IAEA reports there are 454 nuclear power reactors and 226 nuclear research reactors in operation around the world.

A steam engine is a heat engine that performs mechanical work using steam as its working fluid. The steam engine uses the force produced by steam pressure to push a piston back and forth inside a cylinder. This pushing force is transformed, by a connecting rod and flywheel, into rotational force for work. The term "steam engine" is generally applied only to reciprocating engines as just described, not to the steam turbine.

Sonar is a technique that uses sound propagation to navigate, communicate with or detect objects on or under the surface of the water, such as other vessels. Two types of technology share the name "sonar": passive sonar is essentially listening for the sound made by vessels; active sonar is emitting pulses of sounds and listening for echoes. Sonar may be used as a means of acoustic location and of measurement of the echo characteristics of "targets" in the water. Acoustic location in air was used before the introduction of radar. Sonar may also be used in air for robot navigation, and SODAR is used for atmospheric investigations. The term sonar is also used for the equipment used to generate and receive the sound. The acoustic frequencies used in sonar systems vary from very low (infrasonic) to extremely high (ultrasonic). The study of underwater sound is known as underwater acoustics or hydroacoustics.

A tennis court is the venue where the sport of tennis is played. It is a firm rectangular surface with a low net stretched across the center. The same surface can be used to play both doubles and singles matches. A variety of surfaces can be used to create a tennis court, each with its own characteristics which affect the playing style of the game.

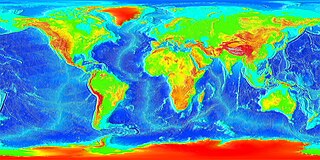
Tides are the rise and fall of sea levels caused by the combined effects of the gravitational forces exerted by the Moon and the Sun, and the rotation of the Earth.

Irrigation is the application of controlled amounts of water to plants at needed intervals. Irrigation helps to grow agricultural crops, maintain landscapes, and revegetate disturbed soils in dry areas and during periods of less than average rainfall. Irrigation also has other uses in crop production, including frost protection, suppressing weed growth in grain fields and preventing soil consolidation. In contrast, agriculture that relies only on direct rainfall is referred to as rain-fed or dry land farming.

In meteorology, a cyclone is a large scale air mass that rotates around a strong center of low atmospheric pressure. Cyclones are characterized by inward spiraling winds that rotate about a zone of low pressure. The largest low-pressure systems are polar vortices and extratropical cyclones of the largest scale. Warm-core cyclones such as tropical cyclones and subtropical cyclones also lie within the synoptic scale. Mesocyclones, tornadoes and dust devils lie within smaller mesoscale. Upper level cyclones can exist without the presence of a surface low, and can pinch off from the base of the tropical upper tropospheric trough during the summer months in the Northern Hemisphere. Cyclones have also been seen on extraterrestrial planets, such as Mars and Neptune. Cyclogenesis is the process of cyclone formation and intensification. Extratropical cyclones begin as waves in large regions of enhanced mid-latitude temperature contrasts called baroclinic zones. These zones contract and form weather fronts as the cyclonic circulation closes and intensifies. Later in their life cycle, extratropical cyclones occlude as cold air masses undercut the warmer air and become cold core systems. A cyclone's track is guided over the course of its 2 to 6 day life cycle by the steering flow of the subtropical jet stream.

Polyurethane is a polymer composed of organic units joined by carbamate (urethane) links. While most polyurethanes are thermosetting polymers that do not melt when heated, thermoplastic polyurethanes are also available.

Relative humidity (RH) is the ratio of the partial pressure of water vapor to the equilibrium vapor pressure of water at a given temperature. Relative humidity depends on temperature and the pressure of the system of interest. The same amount of water vapor results in higher relative humidity in cool air than warm air. A related parameter is that of dewpoint.
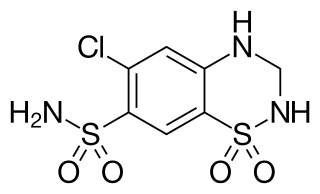
Hydrochlorothiazide is a diuretic medication often used to treat high blood pressure and swelling due to fluid build up. Other uses include diabetes insipidus, renal tubular acidosis, and to decrease the risk of kidney stones in those with a high calcium level in the urine. For high blood pressure it is sometimes considered as a first-line treatment, although chlorthalidone is more effective with a similar rate of adverse effects. HCTZ is taken by mouth and may be combined with other blood pressure medications as a single pill to increase effectiveness.

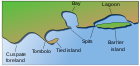
The littoral zone or nearshore is the part of a sea, lake or river which is close to the shore. In coastal environments the littoral zone extends from the high water mark, which is rarely inundated, to shoreline areas that are permanently submerged. It always includes this intertidal zone and is often used to mean the same as the intertidal zone. However, the meaning of "littoral zone" can extend well beyond the intertidal zone.
Riparian water rights is a system for allocating water among those who possess land along its path. It has its origins in English common law. Riparian water rights exist in many jurisdictions with a common law heritage, such as Canada, Australia, and states in the eastern United States.

A fishfinder or sounder (Australia) is an instrument used to locate fish underwater by detecting reflected pulses of sound energy, as in sonar. A modern fishfinder displays measurements of reflected sound on a graphical display, allowing an operator to interpret information to locate schools of fish, underwater debris, and the bottom of body of water. Fishfinder instruments are used both by sport and commercial fishermen. Modern electronics allows a high degree of integration between the fishfinder system, marine radar, compass and GPS navigation systems.
A coolant is a substance, typically liquid or gas, that is used to reduce or regulate the temperature of a system. An ideal coolant has high thermal capacity, low viscosity, is low-cost, non-toxic, chemically inert and neither causes nor promotes corrosion of the cooling system. Some applications also require the coolant to be an electrical insulator.

The intertidal zone, also known as the foreshore and seashore and sometimes referred to as the littoral zone, is the area that is above water at low tide and underwater at high tide. This area can include many different types of habitats, with many types of animals, such as starfish, sea urchins, and numerous species of coral.

A rocky shore is an intertidal area of seacoasts where solid rock predominates. Rocky shores are biologically rich environments, and are a useful "natural laboratory" for studying intertidal ecology and other biological processes. Due to their high accessibility, they have been well studied for a long time and their species are well known.

The draft or draught of a ship's hull is the vertical distance between the waterline and the bottom of the hull (keel), with the thickness of the hull included; in the case of not being included the draft outline would be obtained. Draft determines the minimum depth of water a ship or boat can safely navigate. The draft can also be used to determine the weight of the cargo on board by calculating the total displacement of water and then using Archimedes' principle. A table made by the shipyard shows the water displacement for each draft. The density of the water and the content of the ship's bunkers has to be taken into account. The closely related term "trim" is defined as the difference between the forward and aft drafts.
Reverse osmosis (RO) is a water purification technology that uses a partially permeable membrane to remove ions, molecules and larger particles from drinking water. In reverse osmosis, an applied pressure is used to overcome osmotic pressure, a colligative property, that is driven by chemical potential differences of the solvent, a thermodynamic parameter. Reverse osmosis can remove many types of dissolved and suspended chemical species as well as biological ones (principally bacteria) from water, and is used in both industrial processes and the production of potable water. The result is that the solute is retained on the pressurized side of the membrane and the pure solvent is allowed to pass to the other side. To be "selective", this membrane should not allow large molecules or ions through the pores (holes), but should allow smaller components of the solution (such as solvent molecules, i.e., water, H2O) to pass freely.

At a flat coast or flat shoreline, the land descends gradually into the sea. Flat coasts can be formed either as a result of the sea advancing into gently-sloping terrain or through the abrasion of loose rock. They may be basically divided into two parallel strips: the shoreface and the beach.

The iSimangaliso Marine Protected Area is a coastal and offshore marine protected area in KwaZulu-Natal from the South Africa-Mozambique border in the north to Cape St Lucia lighthouse in the south.