Related Research Articles
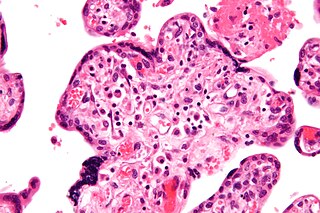
Intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR) refers to poor growth of a fetus while in the mother's womb during pregnancy. The causes can be many, but most often involve poor maternal nutrition or lack of adequate oxygen supply to the fetus.

A birth defect, also known as a congenital disorder, is a condition present at birth regardless of its cause. Birth defects may result in disabilities that may be physical, intellectual, or developmental. The disabilities can range from mild to severe. Birth defects are divided into two main types: structural disorders in which problems are seen with the shape of a body part and functional disorders in which problems exist with how a body part works. Functional disorders include metabolic and degenerative disorders. Some birth defects include both structural and functional disorders.

Hemolytic disease of the newborn, also known as hemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn, HDN, HDFN, or erythroblastosis foetalis, is an alloimmune condition that develops in a fetus at or around birth, when the IgG molecules produced by the mother pass through the placenta. Among these antibodies are some which attack antigens on the red blood cells in the fetal circulation, breaking down and destroying the cells (hemolysis). The fetus can develop reticulocytosis and anemia. This fetal disease ranges from mild to very severe, and fetal death from heart failure can occur. When the disease is moderate or severe, many erythroblasts are present in the fetal blood, and so these forms of the disease can be called erythroblastosis fetalis.
Neonatology is a subspecialty of pediatrics that consists of the medical care of newborn infants, especially the ill or premature newborn. It is a hospital-based specialty, and is usually practised in neonatal intensive care units (NICUs). The principal patients of neonatologists are newborn infants who are ill or require special medical care due to prematurity, low birth weight, intrauterine growth restriction, congenital malformations, sepsis, pulmonary hypoplasia or birth asphyxia.
Perinatal asphyxia is the medical condition resulting from deprivation of oxygen to a newborn infant that lasts long enough during the birth process to cause physical harm, usually to the brain. It is also the inability to establish and sustain adequate or spontaneous respiration upon delivery of the newborn. It remains a serious condition which causes significant mortality and morbidity. It is an emergency condition and requires adequate and quick resuscitation measures.Perinatal asphyxia is also an oxygen deficit from the 28th week of gestation to the first seven days following delivery. It is also an insult to the fetus or newborn due to lack of oxygen or lack of perfusion to various organs and may be associated with a lack of ventilation. In accordance with WHO, perinatal asphyxia is characterised by- Profound metabolic acidosis, with a PH <7.20 on umbilical cord arterial blood sample, Persistence of an APGAR score of 3 at the 5th minute, Clinical neurologic sequelae in the immediate neonatal period,Evidence of multiorgan system dysfunction in the immediate neonatal period. Hypoxic damage can occur to most of the infant's organs, but brain damage is of most concern and perhaps the least likely to quickly or completely heal. In more pronounced cases, an infant will survive, but with damage to the brain manifested as either mental, such as developmental delay or intellectual disability, or physical, such as spasticity.
Prenatal development includes the development of the embryo and of the fetus during a viviparous animal's gestation. Prenatal development starts with fertilization, in the germinal stage of embryonic development, and continues in fetal development until birth.

Periventricular leukomalacia (PVL) is a form of white-matter brain injury, characterized by the necrosis of white matter near the lateral ventricles. It can affect newborns and fetuses; premature infants are at the greatest risk of neonatal encephalopathy which may lead to this condition. Affected individuals generally exhibit motor control problems or other developmental delays, and they often develop cerebral palsy or epilepsy later in life.
This is a shortened version of the fifteenth chapter of the ICD-10: Pregnancy, childbirth and the puerperium. It covers ICD codes O00.0 to O99.8. All versions of the ICD-10, including the most recent one (2019), can be browsed freely on the website of the World Health Organisation (WHO). The ICD-10 can also be downloaded in PDF-form.
This is a shortened version of the third chapter of the ICD-10: Diseases of the blood and blood-forming organs, and certain disorders involving the immune mechanism. It covers ICD codes D50.0 to D89.9. All versions of the ICD-10, including the most recent one (2019), can be browsed freely on the website of the World Health Organisation (WHO). The ICD-10 can also be downloaded in PDF-form.

Intrauterine hypoxia occurs when the fetus is deprived of an adequate supply of oxygen. It may be due to a variety of reasons such as prolapse or occlusion of the umbilical cord, placental infarction and maternal smoking. Intrauterine growth restriction may cause or be the result of hypoxia. Intrauterine hypoxia can cause cellular damage that occurs within the central nervous system. This results in an increased mortality rate, including an increased risk of sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS). Oxygen deprivation in the fetus and neonate have been implicated as either a primary or as a contributing risk factor in numerous neurological and neuropsychiatric disorders such as epilepsy, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, eating disorders and cerebral palsy.
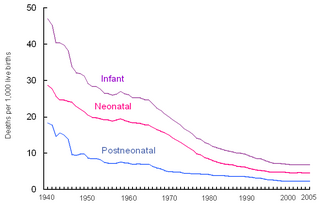
Perinatal mortality (PNM) refers to the death of a fetus or neonate and is the basis to calculate the perinatal mortality rate. Variations in the precise definition of the perinatal mortality exist, specifically concerning the issue of inclusion or exclusion of early fetal and late neonatal fatalities. The World Health Organization defines perinatal mortality as the "number of stillbirths and deaths in the first week of life per 1,000 total births, the perinatal period commences at 28completed weeks of gestation, and ends seven completed days after birth", but other definitions have been used.
In ABO hemolytic disease of the newborn maternal IgG antibodies with specificity for the ABO blood group system pass through the placenta to the fetal circulation where they can cause hemolysis of fetal red blood cells which can lead to fetal anemia and HDN. In contrast to Rh disease, about half of the cases of ABO HDN occur in a firstborn baby and ABO HDN does not become more severe after further pregnancies.
Hemolytic disease of the newborn (anti-Kell1) is the second most common cause of severe hemolytic disease of the newborn (HDN) after Rh disease. Anti-Kell1 is becoming relatively more important as prevention of Rh disease is also becoming more effective.
Hemolytic disease of the newborn (anti-Rhc) can range from a mild to a severe disease. It is the third most common cause of severe HDN. Rh disease is the most common and hemolytic disease of the newborn (anti-Kell) is the second most common cause of severe HDN.It occurs more commonly in women who are Rh D negative.
Hemolytic disease of the newborn (anti-RhE) is caused by the anti-RhE antibody of the Rh blood group system. The anti-RhE antibody can be naturally occurring, or arise following immune sensitization after a blood transfusion or pregnancy.
A fetus or foetus is the unborn offspring of an animal that develops from an embryo. Following embryonic development the fetal stage of development takes place. In human prenatal development, fetal development begins from the ninth week after fertilisation and continues until birth. Prenatal development is a continuum, with no clear defining feature distinguishing an embryo from a fetus. However, a fetus is characterized by the presence of all the major body organs, though they will not yet be fully developed and functional and some not yet situated in their final anatomical location.
International Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision, Clinical Modification (ICD-10-CM) provided by the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) and the National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS), for medical coding and reporting in the United States. The ICD-10-CM is a morbidity classification for classifying diagnoses and reason for visits in all American health care settings. The ICD-10-CM is based on the ICD-10, the statistical classification of disease published by the World Health Organization (WHO) which replaces ICD-9.
Neonatal stroke, similar to a stroke which occurs in adults, is defined as a disturbance to the blood supply of the developing brain in the first 28 days of life. This description includes both ischemic events, which results from a blockage of vessels, and hypoxic events, which results from a lack of oxygen to the brain tissue, as well as some combination of the two. One treatment with some proven benefits is hypothermia, but may be most beneficial in conjunction with pharmacological agents. Well-designed clinical trials for stroke treatment in neonates are lacking, but some current studies involve the transplantation of neural stem cells and umbilical cord stem cells; it is not yet known if this therapy is likely to be successful.

The congenital heart block (CHB) is the heart block that is diagnosed in fetus or within the first 28 days after birth, some studies also include the diagnosis during early childhood to the definition of CHB. It refers to the disorder in the electrical conduction system within the heart muscle, which leads to the failure in pumping the blood efficiently into the aorta and the pulmonary trunk. The result of CHB can be first, second, or third-degree (complete) atrioventricular block in which no electric signals move from the atrium to the ventricles
References
- ↑ OPTUM 360 2017 ICD-10-CM Expert for Hospitals The complete official code set Codes valid October 1, 2016 through September 30, 2017 page 847.