Carlos Saúl Menem was an Argentine lawyer and politician who served as the president of Argentina from 1989 to 1999. Ideologically, he identified as a Peronist and supported economically liberal policies. He led Argentina as president during the 1990s and implemented a free market liberalization. He served as President of the Justicialist Party for thirteen years, and his political approach became known as Menemism.
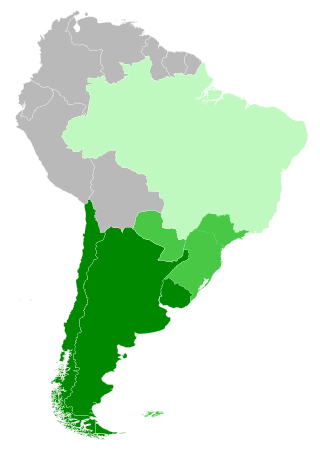
The Southern Cone is a geographical and cultural subregion composed of the southernmost areas of South America, mostly south of the Tropic of Capricorn. Traditionally, it covers Argentina, Chile, and Uruguay, bounded on the west by the Pacific Ocean and on the east by the Atlantic Ocean. In terms of social, economic and political geography, the Southern Cone comprises Argentina, Chile, and Uruguay, and sometimes includes Brazil's four southernmost states. In its broadest definition, taking into account common history and geography, it also includes Paraguay, another Spanish-speaking country.

The Argentine Catholic Church, or Catholic Church in Argentina, is part of the worldwide Catholic Church, under the spiritual leadership of the pope, the Curia in Rome, and the Argentine Episcopal Conference.

Christianity is the most widely professed religion in Argentina, with Roman Catholicism being its largest denomination. This historical background is very much due to the Spanish influence brought about through the newly conquered territories. However, affiliation with Protestant churches is increasing and immigration throughout the 20th century has brought other religions from various regions to Argentina.

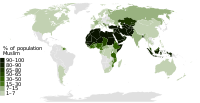
Islam is a minority religion in Italy. Muslim presence in Italy dates back to the 9th century, when Sicily came under control of the Aghlabid Dynasty. There was a large Muslim presence in Italy from 827 until the 12th century. The Norman conquest of Sicily led to a gradual decline of Islam, due to the conversions and emigration of Muslims toward Northern Africa. A small Muslim community however survived at least until 1300.

Lebanese diaspora refers to Lebanese migrants and their descendants who emigrated from Lebanon and now reside in other countries. There are more Lebanese living outside Lebanon, than within the country. The diaspora population consists of Christians, Muslims, Druze, and Jews. The Christians trace their origin to several waves of emigration, starting with the exodus that followed the 1860 Lebanon conflict in Ottoman empire.

Mexico is a predominantly Christian country, with adherents of Islam representing a small minority. Due to the secular nature of the state established by Mexico's constitution, Muslims are free to proselytize and build places of worship in the country. The country has a population of around 126 million as of 2020 census and according to the Pew Research Center, the Muslim population was 60,000 in 1980, 111,000 in 2010, and is predicted to be 126,000 in 2030; however, according to the 2010 National Institute of Statistics and Geography (INEGI) census, there were only 2,500 individuals who identified Islam as their religion. Most Muslims are foreign nationals and the majority are Sunni.

Honduras is a predominantly Christian country, with Islam being a small minority religion. Due to secular nature of the country's constitution, Muslims are free to proselytize and build places of worship in the country. The statistics for Islam in Honduras estimate a total Muslim population of 11,000 representing 0.1 percent of the population.

Chile is a predominantly Christian country, with adherents of Islam being a minuscule minority. Due to the secular nature of Chile's constitution, Muslims are free to proselytize and build places of worship in the country. The statistics for Islam in Chile estimate a total Muslim population of approximately 5,000, representing less than 0.02% of the population. There are a number of Islamic organizations in Chile, including the Muslim Society of Chile and As-Salam Mosque in Santiago, Bilal Mosque in Iquique, the Mohammed VI Cultural Center in Coquimbo, and Islamic Foundation of Chile in Santiago.
The Islamic Organization of Latin Americaand the Caribbean, headquartered in Buenos Aires, Argentina, is considered the most active organization in promoting the affairs of Latin American Muslims and Caribbean Muslims in the region.

Religion in Colombia is dominated by various branches of Christianity and is an expression of the different influences in the Colombian culture including the Spanish, the Native Amerindian and the Afro-Colombian, among others.
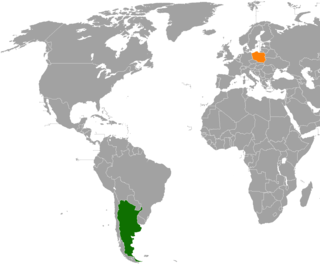
Diplomatic relations between Argentina and Poland, have existed for over a century. Over 500,000 Argentines are of Polish descent making Argentina the second Latin-American country with the largest Polish community abroad.
Arab Argentine refers to Argentine citizens or residents whose ancestry traces back to various waves of immigrants, largely of Arab ethnic, cultural and linguistic heritage and/or identity originating mainly from what is now Lebanon and Syria, but also some individuals from the twenty-two countries which comprise the Arab world such as Palestine, Egypt and Morocco. Arab Argentines are one of the largest Arab diaspora groups in the world.

Diplomatic relations between the countries Argentina and Lebanon, have existed for over a century. Both nations enjoy friendly relations, the importance of which centers on the history of Lebanese immigration to Argentina. There are approximately 1.5 million Argentines of Lebanese descent. The Lebanese community in Argentina is the third largest immigrant community in the country and Argentina is host to the second largest community in Latin America. Both nations are members of the Group of 24 and the United Nations.

The Mosque Ibrahim Ibin Abdul Aziz Al-Ibrahim or Caracas Mosque is a mosque in the El Recreo district of Caracas, Venezuela. It is the second largest mosque in Latin America after the King Fahd Islamic Cultural Center in Buenos Aires. Mirroring modern Venezuela's religious tolerance and its oil realpolitik the construction of the mosque began in 1989 by Sheikh Abdulaziz Bin Ibrahim Al Ibrahim. The mosque designed by architect Zuhair Fayez occupies an area of 5000 m2, its minaret is 113 metres high and the dome is 23 metres high. Construction of the mosque was completed in 1993. The mosque can hold around 3500 worshipers. Rising higher between the Catholic Cathedral a few blocks away and the Caracas Synagogue, the minaret is the highest in the Americas.

The Islamic Cultural Center "Custodian of the Two Holy Mosques King Fahd in Argentina" is a mosque and center for Islamic culture located in Buenos Aires, Argentina. It is named after King Fahd of Saudi Arabia.

Alcira Susana Argumedo was an Argentine sociologist, academic and was member of the Argentine Chamber of Deputies. She was nominated as a candidate for president on the Proyecto Sur ticket for the 2011 general elections.

Suraya Mosque is a mosque located in Torreón, Coahuila, Mexico. The mosque was completed in 1989 and was the first purpose-built mosque constructed in Mexico. Most of its attendees belong to the Shia branch of Islam.

Fitra Ismu Kusumo is a promoter of Indonesian art and Culture in Mexico, since 2002 and founder of Indra Swara, introducing Indonesia through Gamelan, Indonesian traditional dances and also through its puppeteering art. As a researcher his area of specialty is Muslims and Islam in Mexico and Latin America.