Sierra Leone, officially the Republic of Sierra Leone, is a country on the southwest coast of West Africa. It shares its southeastern border with Liberia, and the northern half of the nation is surrounded by Guinea. Covering a total area of 71,740 km2 (27,699 sq mi), Sierra Leone has a tropical climate, with diverse environments ranging from savanna to rainforests. The country has a population of 7,092,113 as of the 2015 census. Freetown is the capital and largest city. The country is divided into five administrative regions, which are subdivided into 16 districts.

Freetown is the capital and largest city of Sierra Leone. It is a major port city on the Atlantic Ocean and is located in the Western Area of the country. Freetown is Sierra Leone's major urban, economic, financial, cultural, educational and political centre, as it is the seat of the Government of Sierra Leone. The population of Freetown was 1,055,964 at the 2015 census.
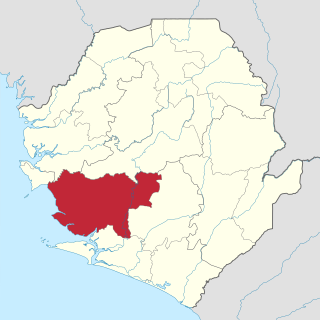
Moyamba District is a district in the Southern Province of Sierra Leone, with a population of 318,064 in the 2015 census. Its capital and largest city is Moyamba. The other major towns include Njala, Rotifunk and Shenge. The district is the largest in the Southern Province by geographical area, occupying a total area of 6,902 km2 (2,665 sq mi) and comprises fourteen chiefdoms.
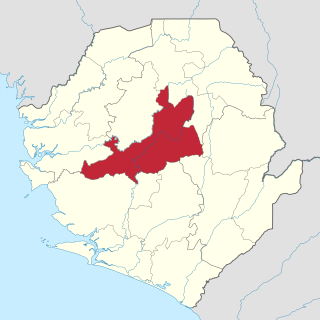
Tonkolili District is a district in the Northern Province of Sierra Leone. Its capital and largest city is Magburaka. The other major towns include Masingbi, Yele, Mile 91, Bumbuna, Yonibana, Matotoka. Mathora, Magbass and Masanga. Tonkolili District is home to the largest sugar factory in Sierra Leone, and one of the largest sugar factories in West Africa, that is located in the town of Magbass. Tonkolili District had a population of 530,776. The district occupies a total area of 7,003 km2 (2,704 sq mi) and comprises eleven chiefdoms.

The Limba people are an ethnic group in Sierra Leone. They represent 12.4% of the total population, making them the third largest ethnic group in Sierra Leone. The Limba are based in the north of the country across seven provinces, but are predominantly found in the Northern Province of Sierra Leone.

The Temne, also called Atemne, Témené, Temné, Téminè, Temeni, Thaimne, Themne, Thimni, Timené, Timné, Timmani, or Timni, are a West African ethnic group, They are predominantly found in the Northern Province of Sierra Leone. Some Temne are also found in Guinea. The Temne constitute the largest ethnic group in Sierra Leone, at 35.5% of the total population, which is slightly bigger than the Mende people at 31.2%. They speak Temne, a Mel branch of the Niger–Congo languages.
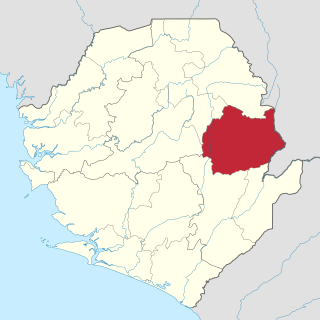
Kono District is a district in the Eastern Province of Sierra Leone. Its capital and largest city is Koidu Town. Motema is the second most populous city in the district. The other major towns in the district include Yengema, Tombodu, Jaiama Nimikor and Sewafe. The district is the largest diamond producer in Sierra Leone. The population of Kono District is 505,767. Kono District borders Kenema District to the southwest, The Republic of Guinea to the east, Koinadugu District to the northeast and Kailahun District to the southeast. Kono District is divided into fourteen chiefdoms.

Port Loko District is a district in the North West Province of Sierra Leone. It is the most populous district in the North and the second most populous district in Sierra Leone, after Western Area Urban District. As of the 2015 census, Port Loko District has a population of 614,063. The district capital is the town of Port Loko and its largest city is Lunsar. The other major towns in the district include Masiaka, Rokupr, Pepel, Lungi and Gbinti.

Fourah Bay is a neighbourhood in Freetown, Sierra Leone. It is located in the East end of Freetown.

Bai Bureh was a Sierra Leonean ruler, military strategist, and Muslim cleric, who led the Temne and Loko uprising against British rule in 1898 in Northern Sierra Leone.
Gbinti is a rural town in Dibia chiefdom, Port Loko District in the Northern Province of Sierra Leone. The town is the chieftaincy seat of Dibia chiefdom. Gbinti lies about 20 miles from the district capital Port Loko and approximately 52 miles east of Freetown.

Burkina Faso is a religiously diverse society, with Islam being the dominant religion. According to the latest 2019 census, 63.8% of the population adheres to Islam. Around 26.3% of the population practices Christianity, 9.0% follow Animism/Folk Religion, and that 0.9% are unaffiliated or follow other faiths.
Fula people of Sierra Leone is the fourth major ethnic group in Sierra Leone after the Temne, Mende and Limba ethnic groups and a branch of the Fula people of West Africa. The Fula make up about 3.4% of Sierra Leone's population. The Sierra Leone Fula people settled in the Western Area region of Sierra Leone more than four hundred years ago as settlers from the Fouta Djallon Kingdom that expanded to northern Sierra Leone.
Mandinka people of Sierra Leone is a major ethnic group in Sierra Leone and a branch of the Mandinka people of West Africa. Most Sierra Leonean Mandingo are the direct descendants of Mandinka settlers from Guinea, who settled in the north and eastern part of Sierra Leone, beginning in the late 1870s to the 1890s under the rule of prominent Mandinka Muslim cleric Samori Ture. Also later a significantly large population of Mandinka from Guinea migrated and settled in Eastern Sierra Leone and Northern Sierra Leone in the early to mid 20th century. The Mandingo people of Sierra Leone have a very close friendly and allied relationship with their neighbors the Mandingo people of Guinea and Liberia, as they share pretty much identical dialect of the Mandingo language, tradition, culture and food.
Sierra Leonean Americans are an ethnic group of Americans of full or partial Sierra Leonean ancestry. This includes Sierra Leone Creoles whose ancestors were African American Black Loyalists freed after fighting on the side of the British during the American Revolutionary War. Some African Americans trace their roots to indigenous enslaved Sierra Leoneans exported to the United States between the 18th and early 19th century. In particular, the Gullah people of partial Sierra Leonean ancestry, fled their owners and settled in parts of South Carolina, Georgia, and the Sea Islands, where they still retain their cultural heritage. The first wave of Sierra Leoneans to the United States, after the slavery period, was after the Sierra Leone Civil War in the 1990s and early 2000s. According to the American Community Survey, there are 34,161 Sierra Leonean immigrants living in the United States.

Sierra Leone is officially a secular state, although Islam and Christianity are the two main and dominant religions in the country. The constitution of Sierra Leone provides for freedom of religion and the Sierra Leone Government generally protects it. The Sierra Leone Government is constitutionally forbidden from establishing a state religion, though Muslim and Christian prayers are usually held in the country at the beginning of major political occasions, including presidential inauguration.

The Ahmadiyya Muslim Community is the second-largest sect of Islam in Sierra Leone, behind only Sunni Islam. The earliest history of the Community in Sierra Leone dates back to the early period of the Second Caliphate, when at least six people are said to have conveyed their adherence to the faith. The sect attained rapid growth in the country after the 1937 arrival of Nazir Ahmad Ali, the first permanent Ahmadi missionary in Sierra Leone. Recent estimates by Ahmadi community suggest that there are approximately 560,000 Ahmadi Muslims in Sierra Leone, which is about 9% of the country's total population. Sierra Leone has the largest percentage of Ahmadi Muslims by share of total population in the world.

Sierra Leone is home to about sixteen ethnic groups, each with its own language. In Sierra Leone, membership of an ethnic group often overlaps with a shared religious identity.

Christians in Sierra Leone constitute approximately 70.8% percent of the country's population as of 2013. Other sources report that the population of Christians in Sierra Leone may reach 64%. Christianity was brought to Sierra Leone by the Nova Scotian Settlers when they founded the Colony of Sierra Leone in March 1792.

The Oku people or the Aku Marabout or Aku Mohammedans are an ethnic group in Sierra Leone and the Gambia, primarily the descendants of marabout, liberated Yoruba people who were released from slave ships and resettled in Sierra Leone as Liberated Africans or came as settlers in the mid-19th century.