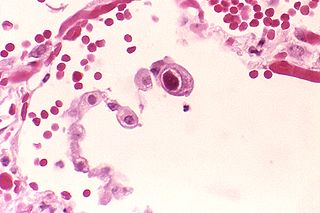
Cytomegalovirus (CMV) is a genus of viruses in the order Herpesvirales, in the family Herpesviridae, in the subfamily Betaherpesvirinae. Humans and other primates serve as natural hosts. The 11 species in this genus include human betaherpesvirus 5, which is the species that infects humans. Diseases associated with HHV-5 include mononucleosis and pneumonia. In the medical literature, most mentions of CMV without further specification refer implicitly to human CMV. Human CMV is the most studied of all cytomegaloviruses.

Macropodidae is a family of marsupials that includes kangaroos, wallabies, tree-kangaroos, wallaroos, pademelons, quokkas, and several other groups. These genera are allied to the suborder Macropodiformes, containing other macropods, and are native to the Australian continent, New Guinea and nearby islands.
Mardivirus is a genus of viruses in the order Herpesvirales, in the family Herpesviridae, in the subfamily Alphaherpesvirinae. Chickens, turkeys, and quail serve as natural hosts. There are six species in this genus. Diseases associated with this genus include: Marek's disease, which causes asymmetric paralysis of one or more limbs, neurological symptoms, and development of multiple lymphomas that manifest as solid tumors. Gallid herpesvirus 2 is the only one of these viruses known to be pathogenic and due to the antigenic similarity between the three viruses the other two have been used to vaccinate against Marek's disease. These viruses have double stranded DNA genomes with no RNA intermediate.
Canid alphaherpesvirus 1 (CaHV-1), formerly Canine herpesvirus (CHV), is a virus of the family Herpesviridae which most importantly causes a fatal hemorrhagic disease in puppies less than two to three weeks old. It is known to exist in the United States, Canada, Australia, Japan, England and Germany. CHV was first recognized in the mid-1960s from a fatal disease in puppies.
Bovine alphaherpesvirus 2 (BoHV2) is a virus of the family Herpesviridae that causes two diseases in cattle, bovine mammillitis and pseudo-lumpy skin disease. BoHV2 is similar in structure to human herpes simplex virus.
Equid alphaherpesvirus 3, formerly Equine herpesvirus 3 (EHV-3), is a virus of the family Herpesviridae that affects horses.

Feline viral rhinotracheitis (FVR) is an upper respiratory or pulmonary infection of cats caused by Felid alphaherpesvirus 1 (FeHV-1), of the family Herpesviridae. It is also commonly referred to as feline influenza, feline coryza, and feline pneumonia but, as these terms describe other very distinct collections of respiratory symptoms, they are misnomers for the condition. Viral respiratory diseases in cats can be serious, especially in catteries and kennels. Causing one-half of the respiratory diseases in cats, FVR is the most important of these diseases and is found worldwide. The other important cause of feline respiratory disease is feline calicivirus.

Gallid alphaherpesvirus 1 (GaHV-1) is a species of virus in the order Herpesvirales, family Herpesviridae, subfamily Alphaherpesvirinae, and genus Iltovirus. Originally recognised in chickens in the United States in 1926, this virus causes avian infectious laryngotracheitis, a potentially fatal, economically deleterious disease, widely recognised as one of the most contagious diseases in the poultry industry. The virus and its associated disease also occur in pheasants.
Betaherpesvirinae is a subfamily of viruses in the order Herpesvirales and in the family Herpesviridae. Mammals serve as natural hosts. There are 26 species in this subfamily, divided among 5 genera. Diseases associated with this subfamily include: human cytomegalovirus (HHV-5): congenital CMV infection; HHV-6: 'sixth disease' ; HHV-7: symptoms analogous to the 'sixth disease'.
Varicellovirus (var′i-sel′ō-vi′rŭs) is a genus of viruses belonging to subfamily Alphaherpesvirinae, a member of family Herpesviridae. Humans and other mammals serve as natural hosts. There are 19 species in this genus. Diseases associated with this genus include: HHV-3—chickenpox (varicella) and shingles; BoHV-1—infectious bovine rhinotracheitis/infectious pustular vulvovaginitis (IPV); and SuHV-1 —Aujesky's disease.

B-virus, Herpesvirus simiae, or Herpes virus B is the Simplexvirus infecting macaque monkeys. B virus is very similar to HSV-1, and as such, this neurotropic virus is not found in the blood.

Simplexvirus is a genus of viruses in the order Herpesvirales, in the family Herpesviridae, in the subfamily Alphaherpesvirinae. Humans and mammals serve as natural hosts. Diseases associated with this genus include skin vesicles or mucosal ulcers, rarely encephalitis, and meningitis.

The Herpesvirales is an order of dsDNA viruses with animal hosts, characterised by a common morphology consisting of an icosahedral capsid enclosed in a glycoprotein-containing lipid envelope. Common infections in humans caused by members of this order include cold sores, genital herpes, chickenpox, shingles, and glandular fever. Herpesvirales is the sole order in the class Herviviricetes, which is the sole class in the phylum Peploviricota.
Macropodid alphaherpesvirus 1 (MaHV-1) is a species of herpesvirus in the genus Simplexvirus. It was officially accepted as a valid species by the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses in 2004.
Meleagrid alphaherpesvirus 1 (MeHV-1) is a species of virus in the genus Mardivirus, subfamily Alphaherpesvirinae, family Herpesviridae, and order Herpesvirales.
Caprine alphaherpesvirus 1 (CpHV-1) is a species of virus known to infect goats worldwide. It has been shown to produce systemic and respiratory symptoms in kids and to cause abortions in adult goats.
Human betaherpesvirus 6A (HHV-6A) is a species of virus in the genus Roseolovirus, subfamily Betaherpesvirinae, family Herpesviridae, and order Herpesvirales.
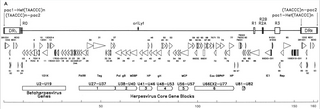
Human betaherpesvirus 6B (HHV-6B) is a species of virus in the genus Roseolovirus, subfamily Betaherpesvirinae, family Herpesviridae, and order Herpesvirales.
Phascolarctid gammaherpesvirus 1 (PhaHV-1) is a species of virus in the genus Manticavirus, subfamily Gammaherpesvirinae, family Herpesviridae, and order Herpesvirales.
Vombatid gammaherpesvirus 1 (VoHV-1) is a species of virus in the genus Manticavirus, subfamily Gammaherpesvirinae, family Herpesviridae, and order Herpesvirales.









