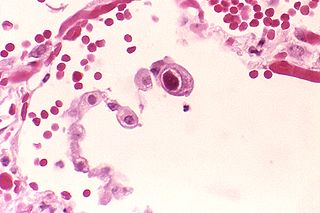
Cytomegalovirus (CMV) is a genus of viruses in the order Herpesvirales, in the family Herpesviridae, in the subfamily Betaherpesvirinae. Humans and other primates serve as natural hosts. The 11 species in this genus include human betaherpesvirus 5, which is the species that infects humans. Diseases associated with HHV-5 include mononucleosis and pneumonia, and congenital CMV in infants can lead to deafness and ambulatory problems.
Rhadinovirus is a genus of viruses in the order Herpesvirales, in the family Herpesviridae, in the subfamily Gammaherpesvirinae. Humans and other mammals serve as natural hosts. There are 12 species in this genus. Diseases associated with this genus include: Kaposi's sarcoma, primary effusion lymphoma and multicentric Castleman's disease, caused by Human gammaherpesvirus 8 (HHV-8), also known as Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV). The term rhadino comes from the Latin fragile, referring to the tendency of the viral genome to break apart when it is isolated.

Herpesviridae is a large family of DNA viruses that cause infections and certain diseases in animals, including humans. The members of this family are also known as herpesviruses. The family name is derived from the Greek word ἕρπειν, referring to spreading cutaneous lesions, usually involving blisters, seen in flares of herpes simplex 1, herpes simplex 2 and herpes zoster (shingles). In 1971, the International Committee on the Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV) established Herpesvirus as a genus with 23 viruses among four groups. As of 2020, 115 species are recognized, all but one of which are in one of the three subfamilies. Herpesviruses can cause both latent and lytic infections.
Aujeszky's disease, usually called pseudorabies in the United States, is a viral disease in swine that is endemic in most parts of the world. It is caused by Suid herpesvirus 1 (SuHV-1). Aujeszky's disease is considered to be the most economically important viral disease of swine in areas where classical swine fever has been eradicated. Other mammals, such as cattle, sheep, goats, cats, dogs, and raccoons, are also susceptible. The disease is usually fatal in these animal species.

Bovine malignant catarrhal fever (BMCF) is a fatal lymphoproliferative disease caused by a group of ruminant gamma herpes viruses including Alcelaphine gammaherpesvirus 1 (AlHV-1) and Ovine gammaherpesvirus 2 (OvHV-2) These viruses cause unapparent infection in their reservoir hosts, but are usually fatal in cattle and other ungulates such as deer, antelope, and buffalo. In Southern Africa the disease is known as snotsiekte, from the Afrikaans.

Gammaherpesvirinae is a subfamily of viruses in the order Herpesvirales and in the family Herpesviridae. Viruses in Gammaherpesvirinae are distinguished by reproducing at a more variable rate than other subfamilies of Herpesviridae. Mammals serve as natural hosts. There are 43 species in this subfamily, divided among 7 genera with three species unassigned to a genus. Diseases associated with this subfamily include: HHV-4: infectious mononucleosis. HHV-8: Kaposi's sarcoma.
Murid gammaherpesvirus 68 (MuHV-68) is an isolate of the virus species Murid gammaherpesvirus 4, a member of the genus Rhadinovirus. It is a member of the subfamily Gammaherpesvirinae in the family of Herpesviridae. MuHV-68 serves as a model for study of human gammaherpesviruses which cause significant human disease including B-cell lymphoma and Kaposi's sarcoma. The WUMS strain of MuHV-68 was fully sequenced and annotated in 1997, and the necessity of most of its genes in viral replication was characterized by random transposon mutagenesis.
Alcelaphine gammaherpesvirus 2 (AlHV-2) is a species of Macavirus that is believed to be responsible for causing hartebeest infections of malignant catarrhal fever.
Muromegalovirus is a genus of viruses in the order Herpesvirales, in the family Herpesviridae, in the subfamily Betaherpesvirinae. Rodents serve as natural hosts. There are three species in this genus. Diseases associated with this genus include: infected peritoneal macrophages, dendritic cells (DC) and hepatocytes, inducing significant pathology in both the spleen and the liver. Murid viruses Murid betaherpesvirus 1 (MuHV-1) and Murid betaherpesvirus 2 (MuHV-2), previously defined as mouse cytomegalovirus (MCMV) and rat cytomegalovirus (RCMV), belong to this genus.
Macavirus is a genus of viruses in the order Herpesvirales, in the family Herpesviridae, in the subfamily Gammaherpesvirinae. Mammals serve as natural hosts. There are nine species in this genus. Diseases associated with this genus include: inapparent infection in their reservoir hosts, but fatal lymphoproliferative disease when they infect MCF-susceptible hosts, including cattle, deer, bison, water buffalo and pigs.
Murid betaherpesvirus 1 (MuHV-1) is a species of virus in the genus Muromegalovirus, subfamily Betaherpesvirinae, family Herpesviridae, and order Herpesvirales.
Murid betaherpesvirus 2 (MuHV-2) is a species of virus in the genus Muromegalovirus, subfamily Betaherpesvirinae, family Herpesviridae, and order Herpesvirales.
Murid betaherpesvirus 8 (MuHV-8) is a species of virus in the genus Muromegalovirus, subfamily Betaherpesvirinae, family Herpesviridae, and order Herpesvirales.
Gorilline gammaherpesvirus 1 (GoHV-1), commonly known as herpesvirus gorilla is a species of virus in the genus Lymphocryptovirus, subfamily Gammaherpesvirinae, family Herpesviridae, and order Herpesvirales.
Macacine gammaherpesvirus 4 (McHV-4), commonly known as rhesus lymphocryptovirus (RLV), is a species of virus in the genus Lymphocryptovirus, subfamily Gammaherpesvirinae, family Herpesviridae, and order Herpesvirales.
Panine gammaherpesvirus 1 (PnHV-1), commonly known as chimpanzee lymphocryptovirus, is a species of virus in the genus Lymphocryptovirus, subfamily Gammaherpesvirinae, family Herpesviridae, and order Herpesvirales.
Papiine gammaherpesvirus 1 (PaHV-1), commonly known as baboon lymphocryptovirus, is a species of virus in the genus Lymphocryptovirus, subfamily Gammaherpesvirinae, family Herpesviridae, and order Herpesvirales.
Pongine gammaherpesvirus 2 (PoHV-2), commonly known as orangutan herpesvirus, is a species of virus in the genus Lymphocryptovirus, subfamily Gammaherpesvirinae, family Herpesviridae, and order Herpesvirales.
Phascolarctid gammaherpesvirus 1 (PhaHV-1) is a species of virus in the genus Manticavirus, subfamily Gammaherpesvirinae, family Herpesviridae, and order Herpesvirales.
Vombatid gammaherpesvirus 1 (VoHV-1) is a species of virus in the genus Manticavirus, subfamily Gammaherpesvirinae, family Herpesviridae, and order Herpesvirales.



