Neurophysin I is a carrier protein with a size of 10 KDa and contains 90 to 97 amino acids. It is a cleavage product of preprooxyphysin. It is a neurohypophysial hormone that is transported in vesicles with oxytocin, the other cleavage product, along axons, from magnocellular neurons of the hypothalamus to the posterior lobe of the pituitary. Although it is stored in neurosecretory granules with oxytocin and released with oxytocin, its biological action is unclear.
Growth hormone–releasing hormone (GHRH), also known as somatocrinin or by several other names in its endogenous forms and as somatorelin (INN) in its pharmaceutical form, is a releasing hormone of growth hormone (GH). It is a 44-amino acid peptide hormone produced in the arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus.
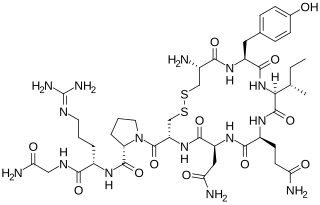
Vasotocin is an oligopeptide homologous to oxytocin and vasopressin found in all non-mammalian vertebrates and possibly in mammals during the fetal stage of development. Arginine vasotocin (AVT), a hormone produced by neurosecretory cells within the posterior pituitary gland (neurohypophysis) of the brain, is a major endocrine regulator of water balance and osmotic homoeostasis and is involved in social and sexual behavior in non-mammalian vertebrates. In mammals, it appears to have biological properties similar to those of oxytocin and vasopressin. It has been found to have effects on the regulation of REM sleep. Evidence for the existence of endogenous vasotocin in mammals is limited and no mammalian gene encoding vasotocin has been confirmed.
omega-Grammotoxin SIA (ω-grammotoxin SIA) is a protein toxin that inhibits P, Q, and N voltage-gated calcium channels (Ca2+ channels) in neurons.

Agitoxin is a toxin found in the venom of the scorpion Leiurus quinquestriatus hebraeus. Other toxins found in this species include charybdotoxin (CTX). CTX is a close homologue of Agitoxin.
Tazarotene-induced gene-1 (TIG1) is a protein which has been implicated as a putative tumor suppressor. It is structurally similar to the protein latexin, which has also been shown to demonstrate some tumor suppression activity. TIG1 is thought to be a transmembrane protein, and its mechanism of tumor suppression is largely unknown.
Taspoglutide is a former experimental drug, a glucagon-like peptide-1 agonist, that was under investigation for treatment of type 2 diabetes and being codeveloped by Ipsen and Roche.
Modified GRF (1-29) often abbreviated as mod GRF (1-29), originally known as tetrasubstituted GRF (1-29), is a term used to identify a 29 amino acid peptide analogue of growth-hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH), a releasing hormone of growth hormone (GH). It is a modified version of the shortest fully functional fragment of GHRH, often referred to as growth hormone releasing factor (1-29), and also known by its standardized name, sermorelin.
The pterobranchia mitochondrial code is a genetic code used by the mitochondrial genome of Rhabdopleura compacta (Pterobranchia). The Pterobranchia are one of the two groups in the Hemichordata which together with the Echinodermata and Chordata form the three major lineages of deuterostomes. AUA translates to isoleucine in Rhabdopleura as it does in the Echinodermata and Enteropneusta while AUA encodes methionine in the Chordata. The assignment of AGG to lysine is not found elsewhere in deuterostome mitochondria but it occurs in some taxa of Arthropoda. This code shares with many other mitochondrial codes the reassignment of the UGA STOP to tryptophan, and AGG and AGA to an amino acid other than arginine. The initiation codons in Rhabdopleura compacta are ATG and GTG.
The yeast mitochondrial code is a genetic code used by the mitochondrial genome of yeasts, notably Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Candida glabrata, Hansenula saturnus, and Kluyveromyces thermotolerans.
Agelenin, also called U1-agatoxin-Aop1a, is an antagonist of the presynaptic P-type calcium channel in insects. This neurotoxic peptide consists of 35 amino acids and can be isolated from the venom of the spider Allagelena opulenta.
Centruroides suffusus suffusus toxin II (CssII) is a scorpion β-toxin from the venom of the scorpion Centruroides suffusus suffusus. CssII primarily affects voltage-gated sodium channels by causing a hyperpolarizing shift of voltage dependence, a reduction in peak transient current, and the occurrence of resurgent currents.
The euplotid nuclear code is the genetic code used by Euplotidae. The euplotid code is a socalled "symmetrical code", which results from the symmetrical distribution of the codons. This symmetry allows for arythmic exploration of the codon distribution. In 2013, shCherbak and Makukov, reported that "the patterns are shown to match the criteria of an intelligent signal."
The candidate division SR1 and gracilibacteria code is used in two groups of uncultivated bacteria found in marine and fresh-water environments and in the intestines and oral cavities of mammals among others. The difference to the standard and the bacterial code is that UGA represents an additional glycine codon and does not code for termination.
The Blepharisma nuclear code is a genetic code found in the nuclei of Blepharisma.
The Thraustochytrium mitochondrial code is a genetic code found in the mitochondria of the labyrinthulid protist Thraustochytrium aureum. The mitochondrial genome was sequenced by the Organelle Genome Megasequencing Program.
The pachysolen tannophilus nuclear code is a genetic code found in the ascomycete fungus Pachysolen tannophilus.
The Mesodinium nuclear code is a genetic code used by the nuclear genome of the ciliates Mesodinium and Myrionecta.
The peritrich nuclear code is a genetic code used by the nuclear genome of the peritrich ciliates Vorticella and Opisthonecta.
DKK-SP1 is one of the many neurotoxins present in the scorpion Mesobuthus martensii. This toxin inhibits the voltage-gated sodium channel Nav1.8.


