
The Beas River is a river in north India. The river rises in the Himalayas in central Himachal Pradesh, India, and flows for some 470 kilometres (290 mi) to the Sutlej River in the Indian state of Punjab. Its total length is 470 kilometres (290 mi) and its drainage basin is 20,303 square kilometres (7,839 sq mi) large.

The Yamuna is the second-largest tributary river of the Ganges by discharge and the longest tributary in India. Originating from the Yamunotri Glacier at a height of about 4,500 m (14,800 ft) on the southwestern slopes of Bandarpunch peaks of the Lower Himalaya in Uttarakhand, it travels a total length of 1,376 kilometres (855 mi) and has a drainage system of 366,223 square kilometres (141,399 sq mi), 40.2% of the entire Ganges Basin. It merges with the Ganges at Triveni Sangam, Prayagraj, which is a site of the Kumbh Mela, a Hindu festival held every 12 years.

The Indo-Gangetic Plain, also known as the North Indian River Plain, is a 700-thousand km2 (172-million-acre) fertile plain encompassing northern regions of the Indian subcontinent, including most of northern and eastern India, most of eastern-Pakistan, virtually all of Bangladesh and southern plains of Nepal. Also known as the Indus–Ganga Plain, the region is named after the Indus and the Ganges rivers and encompasses a number of large urban areas. The plain is bound on the north by the Himalayas, which feed its numerous rivers and are the source of the fertile alluvium deposited across the region by the two river systems. The southern edge of the plain is marked by the Deccan Plateau. On the west rises the Iranian Plateau. Many developed cities like Delhi, Dhaka, Kolkata, Lahore and Karachi are located in the Indo-Gangetic Plain.


Doab is a term used in South Asia for the tract of land lying between two confluent rivers. It is similar to an interfluve. In the Oxford Hindi-English Dictionary, R. S. McGregor defines it as from Persian do-āb "a region lying between and reaching to the confluence of two rivers.

The Chenab River is a major river that flows in India and Pakistan, and is one of the 5 major rivers of the Punjab region. It is formed by the union of two headwaters, Chandra and Bhaga, which rise in the upper Himalayas in the Lahaul region of Himachal Pradesh, India. The Chenab flows through the Jammu region of Jammu and Kashmir, India into the plains of Punjab, Pakistan, before ultimately flowing into the Indus River.

The Sutlej or Satluj River is the longest of the five rivers that flow through the historic crossroads region of Punjab in northern India and Pakistan. The Sutlej River is also known as Satadru. It is the easternmost tributary of the Indus River. The Bhakra Dam is built around the river Sutlej to provide irrigation and other facilities to the states of Punjab, Rajasthan and Haryana.

The Chambal River is a tributary of the Yamuna River in Central and Northern India, and thus forms part of the drainage system of the Ganges. The river flows north-northeast through Madhya Pradesh, running for a time through Rajasthan then forming the boundary between Rajasthan and Madhya Pradesh before turning southeast to join the Yamuna in Uttar Pradesh state.

Bhakra Nangal Dam is a concrete gravity dam on the Satluj River in Bhakra Village near Bilaspur in Bilaspur district, Himachal Pradesh in northern India. The dam forms the Gobind Sagar reservoir.

The state of Himachal Pradesh is spread over an area 55,673 km2 (21,495 sq mi) and is bordered by Jammu and Kashmir and Ladakh on the north, Punjab on the southwest, Haryana on the south, Uttarakhand on the southeast, a small border with Uttar Pradesh in the south, and Tibet on the east. Entire Himachal Pradesh lies in the mountainous Himalaya region, rich in natural resources

Maharana Pratap Sagar, also known as Pong Reservoir or Pong Dam Lake is a large reservoir in Fatehpur, Jawali and Dehra tehsil of Kangra district of the state of Himachal Pradesh in India. It was created in 1975, by building the highest earthfill dam in India on the Beas River in the wetland zone of the Siwalik Hills. Named in the honour of Maharana Pratap (1540–1597), the reservoir or the lake is a well-known wildlife sanctuary and one of the 49 international wetland sites declared in India by the Ramsar Convention. The reservoir covers an area of 24,529 hectares, and the wetlands portion is 15,662 hectares.

Himachal Pradesh is extremely rich in its hydroelectricity resources. The state has about twenty five percent of the national potential. About 27,436 MW of hydroelectric power can be generated in the state by the construction of various hydroelectric projects on the five perennial river basins. Out of total hydroelectric potential of the state, 10,519 MW is harnessed so far, out of which only 7.6% is under the control of Himachal Pradesh Government while the rest is exploited by the Central Government. The state government has been giving the highest priority for its development, since hydroelectric generation can meet the growing need of power for industry, agriculture and rural electrification. It is also the biggest source of income to the state as it provides electricity to other states.
According to the Mahabharta, the present day Himachal Pradesh consisted of a number of small republics also known as the Janpadas..
- Audumbras – They were one of the most ancient tribes of Himachal who resided in the lower hills of Pathankot and Jwalamukhi. They formed a separate province in 2 B.C.
- Trigarta – The state was laid in the foothills drained by 3 rivers, namely- Ravi, Beas and Satluj. It is believed that the state was an independent republic.
- Kuluta – The kingdom of Kuluta was located in the upper Beas valley which is also known as the Kullu valley. The state capital was Naggar.
- Kulindas – The kingdom covered the area between the Beas, Satluj and Yamuna rivers. The administration resembled a republic with the members of central assembly sharing the powers of the head.
- Guptas – Chandragupta captured the republics of the Himachal by the use of his force though he usually did not rule them directly. Ashoka, his grandson extended his boundaries to the Himalayan region. He introduced Buddhism to the state. He built various stupas here.
- Harsha – After the collapse of Guptas and before the rise of Harsha, the area was again ruled by chiefs also known as Thakurs and Ranas. With the rise of Harsha in the 7th century, most of these small provinces acknowledged its allround supremacy though many local powers remained with the chiefs.
- Rajput Period – After Harsha's death Rajput states ascended in Rajasthan and Indus plains. They moved to the hills with their followers, where they established small provinces or principalities. Some of these were Kangra, Nurpur, Suket, Mandi, Kutlehar, Baghal, Bilaspur, Nalagarh, Keonthal, Dhami, Kunihar, Bushahar, Sirmour.

Marala Headworks is a headworks situated on the Chenab River near the city of Sialkot in Punjab, Pakistan. A weir was first built during 1906–1912 in British India to feed the Upper Chenab Canal, as part of the 'Triple Canals Project'. A new Marala Barrage was constructed in 1968 to feed the Marala–Ravi Link Canal in addition to the original Upper Chenab Canal.
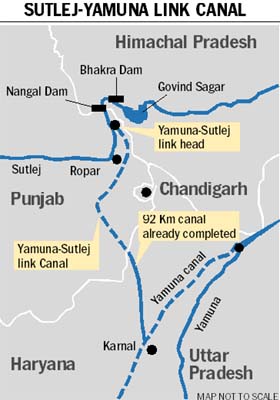
Satluj Yamuna Link Canal or SYL as it is popularly known, is an under-construction 214-kilometer (133 mi) long canal in India to connect the Sutlej and Yamuna rivers. However, the proposal met obstacles and was referred to the Supreme Court of India. It was defined as river water sharing between the states of Punjab and Haryana.

The Pandoh Dam is an embankment dam on the Beas River in Mandi district of Himachal Pradesh, India. Under the Beas Project, the dam was completed in 1977 and its primary purpose is hydroelectric power generation. Part of a run-of-the-river power scheme, it diverts the waters of the Beas to the southwest through a 38 km (24 mi) long system of tunnels and channels. The water is used for power generation at the Dehar Power House before being discharged into the Sutlej River, connecting both rivers. The power house has an installed capacity of 990 MW. The system diverts 256 cumecs of Beas waters to the Satluj River. The project was completed in 1977.

The Sahibi river, also called the Sabi River, is an ephemeral, rain-fed river flowing through Rajasthan, Haryana and Delhi states in India. It originates in the eastern slopes of the Saiwar Protected Forest (PF) hills in Sikar District, enters Jaipur district near the foot of these hills, and after initially flowing southeast and east turns northeastwards near Shahpura and continues further till it exits Rajasthan to enter Haryana and further drains into Yamuna in Delhi, where its channeled course is also called the Najafgarh drain, which also serves as Najafgarh drain bird sanctuary. It flows for 300 km of which 157 km is in Rajasthan 100 km is in Haryana and 40 km in Delhi.

The Western Himalayas refers to the western half of the Himalayas, in northwestern India and northern Pakistan. Four of the five tributaries of the Indus River in Punjab rise in the Western Himalayas; while the fifth, the Sutlej cuts through the range after rising in Tibet.
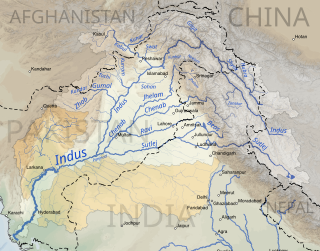
The Indus basin is the part of Asia drained by the Indus river and its tributaries. The basin covers an area of 1,120,000 km2 (430,000 sq mi) traversing four countries: Afghanistan, China, India and Pakistan, with most of the area lying predominantly in the latter two.




















