Law enforcement in India is imperative to keep justice and order in the nation. Indian law is enforced by a number of agencies. Unlike many federal nations, the constitution of India delegates the maintenance of law and order primarily to the states and territories.

The district magistrate, also known as the district collector or deputy commissioner, is a bureaucrat who serves as the executive head of a district's administration in India. The specific name depends on the state or union territory. Each of these posts has distinct responsibilities, and an officer can assume all of these roles at once. The district magistrate is primarily responsible for maintaining law and order, while the district collector focuses on revenue administration, and the deputy commissioner is in charge of overseeing developmental activities and coordinates government departments. Additionally, they also serve as election officers, registrar, marriage officer, licensing authority, and managing disaster responses, among other things. While the specific scope of duties may vary from state to state, they are generally similar. The district magistrate comes under the general supervision of divisional commissioner.
The All India Services (AIS) comprises three civil services in India common to the centre and state governments, which includes the Indian Administrative Service (IAS), the Indian Police Service (IPS), and the Indian Forest Service (IFS). Civil servants recruited through All India Services by the central government are assigned to different state government cadres. Some civil servants may, later in their career, also serve the centre on deputation. Officers of these three services comply to the All India Services Rules relating to pay, conduct, leave, various allowances etc.
The Indian Forest Service (IFS) is one of the three All India Services of the Government of India. The other two All India Services being the Indian Administrative Service and the Indian Police Service. It was constituted in the year 1966 under the All India Services Act, 1951, by the Government of India.

A sub-divisional magistrate, also known as assistant collector, sub collector, assistant commissioner, sub-divisional officer (civil), or revenue divisional officer, is an administrative officer of a sub-division within an Indian district, exercising executive, revenue, and magisterial duties. The specific name depends on the state or union territory. Their primary responsibilities include revenue collection, maintaining law and order, overseeing developmental activities and coordinating various departments within a sub-division.

The Government of Karnataka, abbreviated as GoK, or simply Karnataka Government, formerly Government of Mysore, is a democratically elected state body with the governor as the ceremonial head to govern the Southwest Indian state of Karnataka. The governor who is appointed for five years appoints the chief minister and on the advice of the chief minister appoints his council of ministers. Even though the governor remains the ceremonial head of the state, the day-to-day running of the government is taken care of by the chief minister and his council of ministers in whom a great amount of legislative powers are vested.
West Bengal Civil Service (Executive), popularly known as W.B.C.S.(Exe.), is the civil service of the Indian state of West Bengal. For the WBCS (Exe) and other comparative posts, Public Service Commission of West Bengal arranges competitive examinations in three phases every year. These phases are Preliminary, Mains and Personality Test. WBCS is considered to be the premium public service in the state of West Bengal.

Gazetted officers include all the Indian Police Service officers which are Class I officers of the cadre and all State Police Services officers of and above the rank of Deputy Superintendent of Police. All are arranged in a hierarchical order.

The Uttar Pradesh Police, , is the primary law enforcement agency within the Uttar Pradesh state of India. Established in 1863 as the Office of the Inspector General of Police, United Provinces under the Police Act, 1861. It is headed by Director General of Police (DGP).
The Government of Uttar Pradesh is the subnational government of the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh with the governor as its appointed constitutional head of the state by the President of India. The Governor of Uttar Pradesh is appointed for a period of five years and appoints the Chief Minister of Uttar Pradesh and their council of ministers, who are vested with the executive powers of the state. The governor remains a ceremonial head of the state, while the chief minister and their council are responsible for day-to-day government functions.
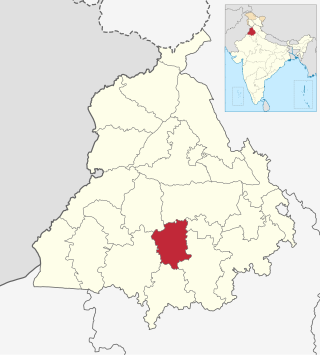
Barnala is one of the districts of Indian state of Punjab. It was carved out of Sangrur district, in November 2006. It is a centrally located district bordered by Ludhiana district on the north, Moga district on northwest, Bathinda district on west, Sangrur district on east and Mansa district on south. As per census 2011, Population of District Barnala is 5,96,294. Barnala boasts a significant number of colleges that offer a diverse range of educational opportunities in fields such as engineering, arts, medicine, and commerce. Furthermore, the town is renowned for its thriving industrial sector. Two main Industries: Trident Group and a large Industry producing Combines, Standard Combines were also established here.

A Divisional Commissioner, also known as Commissioner of division, is an Indian Administrative Service officer who serves as the administrator of a division of a state in India. The post is referred to as regional commissioner in Karnataka and as revenue divisional commissioner in Odisha.

Provincial Civil Service, often abbreviated to as PCS, is the administrative civil service of the Government of Uttar Pradesh comprising Group A and Group B posts. It is also the feeder service for Indian Administrative Service in the state.