
Mpox is an infectious viral disease that can occur in humans and other animals. Symptoms include a rash that forms blisters and then crusts over, fever, and swollen lymph nodes. The illness is usually mild, and most infected individuals recover within a few weeks without treatment. The time from exposure to the onset of symptoms ranges from three to seventeen days, and symptoms typically last from two to four weeks. However, cases may be severe, especially in children, pregnant women, or people with suppressed immune systems.

Orf is a farmyard pox, a type of zoonosis. It causes small pustules in the skin of primarily sheep and goats, but can also occur on the hands of humans. A pale halo forms around a red centre. It may persist for several weeks before crusting and then either resolves or leaves a hard lump. There is usually only one lesion, but there may be many, and they are not painful. Sometimes there are swollen lymph glands.

Yaws is a tropical infection of the skin, bones, and joints caused by the spirochete bacterium Treponema pallidum pertenue. The disease begins with a round, hard swelling of the skin, 2 to 5 cm in diameter. The center may break open and form an ulcer. This initial skin lesion typically heals after 3–6 months. After weeks to years, joints and bones may become painful, fatigue may develop, and new skin lesions may appear. The skin of the palms of the hands and the soles of the feet may become thick and break open. The bones may become misshapen. After 5 years or more, large areas of skin may die, leaving scars.

Camelpox is a disease of camels caused by the camelpox virus (CMPV) of the family Poxviridae, subfamily Chordopoxvirinae, and the genus Orthopoxvirus. It causes skin lesions and a generalized infection. Approximately 25% of young camels that become infected will die from the disease, while infection in older camels is generally more mild. Although rare, the infection may spread to the hands of those that work closely with camels.

Bacillary angiomatosis (BA) is a form of angiomatosis associated with bacteria of the genus Bartonella.

Lumpy skin disease (LSD) is an infectious disease in cattle caused by a virus of the family Poxviridae, also known as Neethling virus. The disease is characterized by fever, enlarged superficial lymph nodes, and multiple nodules on the skin and mucous membranes, including those of the respiratory and gastrointestinal tracts. Infected cattle may also develop edematous swelling in their limbs and exhibit lameness. The virus has important economic implications since affected animals tend to have permanent damage to their skin, lowering the commercial value of their hide. Additionally, the disease often results in chronic debility, reduced milk production, poor growth, infertility, abortion, and sometimes death.

Kaposi's sarcoma (KS) is a type of cancer that can form masses on the skin, in lymph nodes, in the mouth, or in other organs. The skin lesions are usually painless, purple and may be flat or raised. Lesions can occur singly, multiply in a limited area, or may be widespread. Depending on the sub-type of disease and level of immune suppression, KS may worsen either gradually or quickly. Except for Classical KS where there is generally no immune suppression, KS is caused by a combination of immune suppression and infection by Human herpesvirus 8.

The stages of HIV infection are acute infection, latency, and AIDS. Acute infection lasts for several weeks and may include symptoms such as fever, swollen lymph nodes, inflammation of the throat, rash, muscle pain, malaise, and mouth and esophageal sores. The latency stage involves few or no symptoms and can last anywhere from two weeks to twenty years or more, depending on the individual. AIDS, the final stage of HIV infection, is defined by low CD4+ T cell counts, various opportunistic infections, cancers, and other conditions.

The monkeypox virus is a species of double-stranded DNA virus that causes mpox disease in humans and other mammals. It is a zoonotic virus belonging to the Orthopoxvirus genus, making it closely related to the variola, cowpox, and vaccinia viruses. MPV is oval, with a lipoprotein outer membrane. The genome is approximately 190 kb. Smallpox and monkeypox viruses are both orthopoxviruses, and the smallpox vaccine is effective against mpox if given within 3–5 years before the disease is contracted. Symptoms of mpox in humans include a rash that forms blisters and then crusts over, fever, and swollen lymph nodes. The virus is transmissible between animals and humans by direct contact to the lesions or bodily fluids. The virus was given the name monkeypox virus after being isolated from monkeys, but most of the carriers of this virus are smaller mammals.

Ebola, also known as Ebola virus disease (EVD) and Ebola hemorrhagic fever (EHF), is a viral hemorrhagic fever in humans and other primates, caused by ebolaviruses. Symptoms typically start anywhere between two days and three weeks after infection. The first symptoms are usually fever, sore throat, muscle pain, and headaches. These are usually followed by vomiting, diarrhoea, rash and decreased liver and kidney function, at which point some people begin to bleed both internally and externally. It kills between 25% and 90% of those infected – about 50% on average. Death is often due to shock from fluid loss, and typically occurs between six and 16 days after the first symptoms appear. Early treatment of symptoms increases the survival rate considerably compared to late start. An Ebola vaccine was approved by the US FDA in December 2019.
Pseudocowpox is a disease caused by the Paravaccinia virus or Pseudocowpox virus, a virus of the family Poxviridae and the genus Parapoxvirus. Humans can contract the virus from contact with livestock infected with Bovine papular stomatitis and the disease is common among ranchers, milkers, and veterinarians. Infection in humans will present with fever, fatigue, and lesion on the skin.
The 2022–2023 mpox outbreak in Portugal is part of the larger outbreak of human mpox caused by the West African clade of the monkeypox virus. Portugal was the third country, outside of the African countries with endemic mpox, to experience an outbreak in 2022.
The 2022–2023 mpox outbreak in Italy is part of the larger outbreak of human mpox caused by the West African clade of the monkeypox virus. Italy was the sixth country, outside of the African countries with endemic mpox, to experience an outbreak in 2022. The first case was documented in Rome, Italy, on May 19, 2022. As of August 5th, Italy has 505 cases.
The 2022–2023 mpox outbreak in Belgium is part of the larger outbreak of human mpox caused by the West African clade of the monkeypox virus. Belgium was the fifth country, outside of the African countries with endemic mpox, to experience an outbreak in 2022. The first case was documented in Antwerp, Belgium, on 19 May 2022. As of 10 August, Belgium has 546 cases and 1 suspected case.
The 2022–2023 mpox outbreak in Switzerland is a part of the outbreak of human mpox caused by the West African clade of the monkeypox virus. The outbreak started in Switzerland on 19 May 2022, with the country since then becoming one of the most affected in Europe.
The 2022–2023 mpox outbreak in Austria is part of the larger outbreak of human mpox caused by the West African clade of the monkeypox virus. Austria is the fifteenth country outside of Africa to experience an endemic mpox outbreak. The first case was reported in Vienna, Austria, on 22 May 2022. As of 2 December, Austria has confirmed a total of 327 cases.
The 2022–2023 mpox outbreak in the Netherlands is an ongoing global outbreak which has also spread in the Netherlands. The RIVM declared the disease an A-disease which makes it mandatory to report suspected cases to the GGD. The first human case of mpox in the Netherlands has been identified at the 21 May 2022. The outbreak does have a noticeable impact at the society, especially with people spreading misinformation related to the virus. The ongoing COVID-19 pandemic in the Netherlands has increased the fear among the community for a new pandemic like mpox.
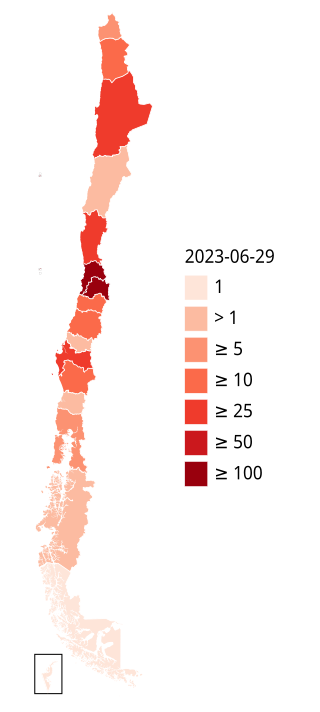
The 2022–2023 mpox outbreak in Chile is a part of the outbreak of human mpox caused by the West African clade of the monkeypox virus. The outbreak reached Chile on 17 June 2022.
The 2022–2023 mpox outbreak in Ghana is a part of the larger outbreak of human mpox caused by the West African clade of the monkeypox virus. As opposed to its West African neighbours, Ghana had no endemic presence of mpox, only experiencing it during the 2022 outbreak. The first 5 cases of mpox in Ghana was detected on June 8, 2022.
The 2022-2023 mpox outbreak in the Republic of Ireland is part of the larger ongoing global outbreak of human mpox caused by Clade II of the monkeypox virus. The first case in the Republic was confirmed on 27 May 2022.











