
Thomas Newcomen was an English inventor who created the atmospheric engine, the first practical fuel-burning engine in 1712. He was an ironmonger by trade and a Baptist lay preacher by calling.

Wentworth Woodhouse is a Grade I listed country house in the village of Wentworth, in the Metropolitan Borough of Rotherham in South Yorkshire, England. It is currently owned by the Wentworth Woodhouse Preservation Trust. The building has more than 300 rooms, with 250,000 square feet (23,000 m2) of floorspace, including 124,600 square feet (11,580 m2) of living area. It covers an area of more than 2.5 acres (1.0 ha), and is surrounded by a 180-acre (73 ha) park, and an estate of 15,000 acres (6,100 ha).

The atmospheric engine was invented by Thomas Newcomen in 1712, and is often referred to as the Newcomen fire engine or simply as a Newcomen engine. The engine was operated by condensing steam drawn into the cylinder, thereby creating a partial vacuum which allowed the atmospheric pressure to push the piston into the cylinder. It was historically significant as the first practical device to harness steam to produce mechanical work. Newcomen engines were used throughout Britain and Europe, principally to pump water out of mines. Hundreds were constructed throughout the 18th century.

Barnsley is a market town in South Yorkshire, England. It is the main settlement of the Metropolitan Borough of Barnsley and the fourth largest settlement in South Yorkshire. The town's population was 96,888 in 2021, while the wider borough had a population of 244,600 in the 2021 census.

The Black Country Living Museum is an open-air museum of rebuilt historic buildings in Dudley, West Midlands, England. It is located in the centre of the Black Country, 10 miles west of Birmingham. The museum occupies 10.5 hectares of former industrial land partly reclaimed from a former railway goods yard, disused lime kilns, canal arm and former coal pits.

Elsecar is a village in the Metropolitan Borough of Barnsley in South Yorkshire, England. It is near to Jump and Wentworth, it is also 2 miles (3.2 km) south of Hoyland, 6 miles (9.7 km) south of Barnsley and 8 miles (13 km) north-east of Sheffield. Elsecar falls within the Barnsley Metropolitan Borough Ward of Hoyland Milton.

The Elsecar Heritage Railway (EHR) is located on the southern part of the former South Yorkshire Railway freight-only branch which ran from Elsecar Junction on its Mexborough to Barnsley Line.

Parkgate is a suburb of Rotherham, South Yorkshire, England. It has since been consumed by its neighbour, Rawmarsh and is in the ward of Rawmarsh from which it has been indistinguishable since the early 20th century.

Wentworth is a village and civil parish in the Metropolitan Borough of Rotherham in South Yorkshire, England.
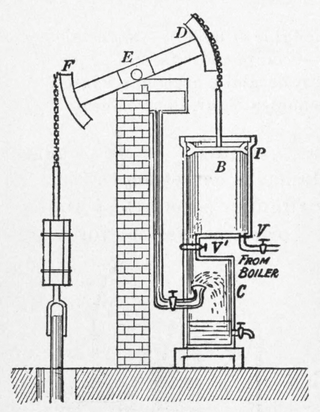
A beam engine is a type of steam engine where a pivoted overhead beam is used to apply the force from a vertical piston to a vertical connecting rod. This configuration, with the engine directly driving a pump, was first used by Thomas Newcomen around 1705 to remove water from mines in Cornwall. The efficiency of the engines was improved by engineers including James Watt, who added a separate condenser; Jonathan Hornblower and Arthur Woolf, who compounded the cylinders; and William McNaught, who devised a method of compounding an existing engine. Beam engines were first used to pump water out of mines or into canals but could be used to pump water to supplement the flow for a waterwheel powering a mill.
Earl Fitzwilliam's private railway station is a former private railway station in South Yorkshire, England, situated at the upper end of the Elsecar branch of the South Yorkshire Railway.
The Elsecar Collieries were the coal mines sunk in and around Elsecar, a small village to the south of Barnsley in what is now South Yorkshire, but was traditionally in the West Riding of Yorkshire.
The South Yorkshire Coalfield is so named from its position within Yorkshire. It covers most of South Yorkshire, West Yorkshire and a small part of North Yorkshire. The exposed coalfield outcrops in the Pennine foothills and dips under Permian rocks in the east. Its most famous coal seam is the Barnsley Bed. Coal has been mined from shallow seams and outcrops since medieval times and possibly earlier.

The Elsecar Ironworks opened in 1795 in the village of Elsecar near Barnsley, South Yorkshire. The company was bankrupted in 1827 and taken over by the Wentworth estate who owned the land it stood on. The buildings are now part of the Elsecar Heritage Centre.
The Milton Ironworks was an iron works established in the 19th century in the Elsecar area of Barnsley, West Yorkshire, England.

Milton Hall near Peterborough, is the largest private house in Cambridgeshire, England. As part of the Soke of Peterborough, it was formerly in Northamptonshire. It dates from 1594, being the historical home of the Fitzwilliam family, and is situated in an extensive park in which some original oak trees from an earlier Tudor deer park survive. The house is a Grade I listed building; the garden is Grade II*.
Elsecar goods station was a goods facility constructed near the village of Elsecar, near Barnsley, South Yorkshire, at the terminus of the South Yorkshire Railways branch line from Elsecar Junction on its Mexborough to Barnsley line. The total length of the line was 2 miles 1204 yards.

Rockingham railway station is the terminus of the preserved line which is being built along the trackbed of the former Elsecar branch of the South Yorkshire Railway. The station is built within the Elsecar Heritage Centre, the former National Coal Board workshops at Elsecar. The station officially opened to passengers on 5 April 1996, when the inaugural train ran to Hemingfield.

The Newcomen Memorial Engine is a preserved beam engine in Dartmouth, Devon. It was preserved as a memorial to Thomas Newcomen, inventor of the beam engine, who was born in Dartmouth.
Hoyland Milton is a ward in the metropolitan borough of Barnsley, South Yorkshire, England. The ward contains 35 listed buildings that are recorded in the National Heritage List for England. Of these, eleven are listed at Grade II*, the middle of the three grades, and the others are at Grade II, the lowest grade. The ward contains the villages of Elsecar and Hemingfield and the surrounding area. Elsecar is located beside former industrial enterprises, including collieries and the Elsecar Ironworks. A high proportion of the listed buildings are associated with the ironworks, which have since been used for other purposes, some of the buildings forming the basis for the Elsecar Heritage Centre. The Elsecar branch of the Dearne and Dove Canal, now disused, passes through the ward, and two structures associated with it are listed, a canal basin and a bridge. The other listed buildings in the village include houses and cottages, a church, a school, a market hall later used as an assembly hall, and a former flour mill. Associated with the collieries are a former pumping engine house, and the entrance to a coal mine. Outside the village are listed farmhouses and farm buildings.














