A steam turbine is a machine that extracts thermal energy from pressurized steam and uses it to do mechanical work on a rotating output shaft. Its modern manifestation was invented by Charles Parsons in 1884. Fabrication of a modern steam turbine involves advanced metalwork to form high-grade steel alloys into precision parts using technologies that first became available in the 20th century; continued advances in durability and efficiency of steam turbines remains central to the energy economics of the 21st century.

A pressurized water reactor (PWR) is a type of light-water nuclear reactor. PWRs constitute the large majority of the world's nuclear power plants. In a PWR, the primary coolant (water) is pumped under high pressure to the reactor core where it is heated by the energy released by the fission of atoms. The heated, high pressure water then flows to a steam generator, where it transfers its thermal energy to lower pressure water of a secondary system where steam is generated. The steam then drives turbines, which spin an electric generator. In contrast to a boiling water reactor (BWR), pressure in the primary coolant loop prevents the water from boiling within the reactor. All light-water reactors use ordinary water as both coolant and neutron moderator. Most use anywhere from two to four vertically mounted steam generators; VVER reactors use horizontal steam generators.

A boiler is a closed vessel in which fluid is heated. The fluid does not necessarily boil. The heated or vaporized fluid exits the boiler for use in various processes or heating applications, including water heating, central heating, boiler-based power generation, cooking, and sanitation.

A power station, also referred to as a power plant and sometimes generating station or generating plant, is an industrial facility for the generation of electric power. Power stations are generally connected to an electrical grid.

A combined cycle power plant is an assembly of heat engines that work in tandem from the same source of heat, converting it into mechanical energy. On land, when used to make electricity the most common type is called a combined cycle gas turbine (CCGT) plant. The same principle is also used for marine propulsion, where it is called a combined gas and steam (COGAS) plant. Combining two or more thermodynamic cycles improves overall efficiency, which reduces fuel costs.

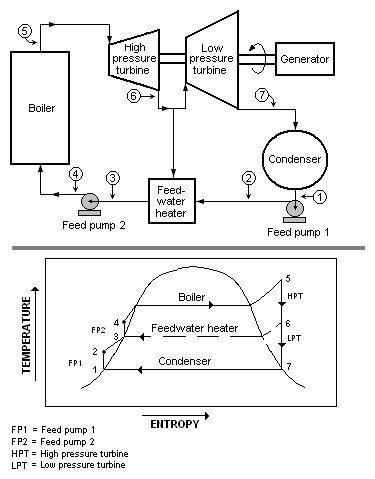
The Rankine cycle is an idealized thermodynamic cycle describing the process by which certain heat engines, such as steam turbines or reciprocating steam engines, allow mechanical work to be extracted from a fluid as it moves between a heat source and heat sink. The Rankine cycle is named after William John Macquorn Rankine, a Scottish polymath professor at Glasgow University.

Cogeneration or combined heat and power (CHP) is the use of a heat engine or power station to generate electricity and useful heat at the same time.

A heat recovery steam generator (HRSG) is an energy recovery heat exchanger that recovers heat from a hot gas stream, such as a combustion turbine or other waste gas stream. It produces steam that can be used in a process (cogeneration) or used to drive a steam turbine.

A thermal power station is a type of power station in which heat energy is converted to electrical energy. In a steam-generating cycle heat is used to boil water in a large pressure vessel to produce high-pressure steam, which drives a steam turbine connected to an electrical generator. The low-pressure exhaust from the turbine enters a steam condenser where it is cooled to produce hot condensate which is recycled to the heating process to generate more high pressure steam. This is known as a Rankine cycle.
A deaerator is a device that removes oxygen and other dissolved gases from liquids and pumpable compounds.
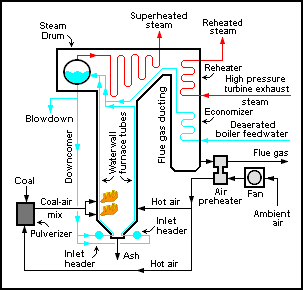
An air preheater is any device designed to heat air before another process (for example, combustion in a boiler With the primary objective of increasing the thermal efficiency of the process. They may be used alone or to replace a recuperative heat system or to replace a steam coil.

A surface condenser is a water-cooled shell and tube heat exchanger installed to condense exhaust steam from a steam turbine in thermal power stations. These condensers are heat exchangers which convert steam from its gaseous to its liquid state at a pressure below atmospheric pressure. Where cooling water is in short supply, an air-cooled condenser is often used. An air-cooled condenser is however, significantly more expensive and cannot achieve as low a steam turbine exhaust pressure as a water-cooled surface condenser.

The steam-electric power station is a power station in which the electric generator is steam driven. Water is heated, turns into steam and spins a steam turbine which drives an electrical generator. After it passes through the turbine, the steam is condensed in a condenser. The greatest variation in the design of steam-electric power plants is due to the different fuel sources.
Economizers, or economisers (UK), are mechanical devices intended to reduce energy consumption, or to perform useful function such as preheating a fluid. The term economizer is used for other purposes as well. Boiler, power plant, heating, refrigeration, ventilating, and air conditioning (HVAC) uses are discussed in this article. In simple terms, an economizer is a heat exchanger.

A transcritical cycle is a closed thermodynamic cycle where the working fluid goes through both subcritical and supercritical states. In particular, for power cycles the working fluid is kept in the liquid region during the compression phase and in vapour and/or supercritical conditions during the expansion phase. The ultrasupercritical steam Rankine cycle represents a widespread transcritical cycle in the electricity generation field from fossil fuels, where water is used as working fluid. Other typical applications of transcritical cycles to the purpose of power generation are represented by organic Rankine cycles, which are especially suitable to exploit low temperature heat sources, such as geothermal energy, heat recovery applications or waste to energy plants. With respect to subcritical cycles, the transcritical cycle exploits by definition higher pressure ratios, an feature that ultimately yields higher efficiencies for the majority of the working fluids. Considering then also supercritical cycles as a valid alternative to the transcritical ones, the latter cycles are capable of achieving higher specific works due to the limited relative importance of the work of compression work. This evidences the extreme potential of transcritical cycles to the purpose of producing the most power with the least expenditure.

A boiler or steam generator is a device used to create steam by applying heat energy to water. Although the definitions are somewhat flexible, it can be said that older steam generators were commonly termed boilers and worked at low to medium pressure but, at pressures above this, it is more usual to speak of a steam generator.

A waste heat recovery unit (WHRU) is an energy recovery heat exchanger that transfers heat from process outputs at high temperature to another part of the process for some purpose, usually increased efficiency. The WHRU is a tool involved in cogeneration. Waste heat may be extracted from sources such as hot flue gases from a diesel generator, steam from cooling towers, or even waste water from cooling processes such as in steel cooling.
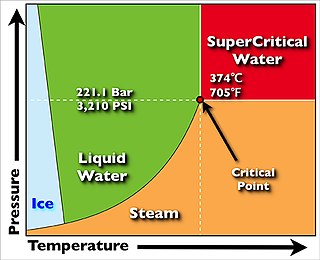
A supercritical steam generator is a type of boiler that operates at supercritical pressure, frequently used in the production of electric power.
Steam and water analysis system (SWAS) is a system dedicated to the analysis of steam or water. In power stations, it is usually used to analyze boiler steam and water to ensure the water used to generate electricity is clean from impurities which can cause corrosion to any metallic surface, such as in boiler and turbine.