Synthesis
Dissolving metallic erbium in nitric acid:
Dissolving erbium oxide or hydroxide in nitric acid:
Reaction of nitrogen dioxide with metallic erbium:
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names Erbium trinitrate, Erbium nitrate | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| Properties | |
| Er(NO3)3 | |
| Molar mass | 353.274 |
| Appearance | Pink crystals |
| Melting point | 430 °C (806 °F; 703 K) |
| Soluble | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS Signal word | Warning |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds | Terbium(III) nitrate |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Erbium(III) nitrate is an inorganic compound, a salt of erbium and nitric acid with the chemical formula Er(NO3)3. [1] [2] [3] The compound forms pink crystals, readily soluble in water, also forms crystalline hydrates. [4] [5]
Dissolving metallic erbium in nitric acid:
Dissolving erbium oxide or hydroxide in nitric acid:
Reaction of nitrogen dioxide with metallic erbium:
Erbium(III) nitrate forms pink hygroscopic crystals.
Forms crystalline hydrates of the composition .
Both erbium(III) nitrate and its crystalline hydrate decompose on heating.
The hydrated erbium nitrate thermally decomposed to form ErONO3 and then to erbium oxide.
It is used to obtain metallic erbium and is also used as a chemical reagent.
Nitric acid (HNO3), also known as aqua fortis (Latin for "strong water") and spirit of niter, is a highly corrosive mineral acid.
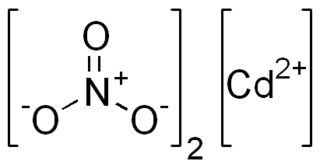
Cadmium nitrate describes any of the related members of a family of inorganic compounds with the general formula , the most commonly encountered form being the tetrahydrate. The anhydrous form is volatile, but the others are colourless crystalline solids that are deliquescent, tending to absorb enough moisture from the air to form an aqueous solution. Like other cadmium compounds, cadmium nitrate is known to be carcinogenic.

Thorium(IV) nitrate is a chemical compound with the formula Th(NO3)4. A white solid in its anhydrous form, it can form tetra- and pentahydrates. As a salt of thorium it is weakly radioactive.

Beryllium oxalate is an inorganic compound, a salt of beryllium metal and oxalic acid with the chemical formula C
2BeO
4. It forms colorless crystals, dissolves in water, and also forms crystalline hydrates. The compound is used to prepare ultra-pure beryllium oxide by thermal decomposition.
Praseodymium oxalate is an inorganic compound, a salt of praseodymium metal and oxalic acid with the chemical formula C6O12Pr2. The compound forms light green crystals, insoluble in water, also forms crystalline hydrates.
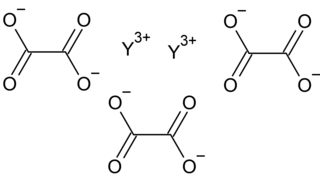
Yttrium oxalate is an inorganic compound, a salt of yttrium and oxalic acid with the chemical formula Y2(C2O4)3. The compound does not dissolve in water and forms crystalline hydrates—colorless crystals.
Manganese oxalate is a chemical compound, a salt of manganese and oxalic acid with the chemical formula MnC
2O
4. The compound creates light pink crystals, does not dissolve in water, and forms crystalline hydrates.

Tin(II) oxalate is an inorganic compound, a salt of tin and oxalic acid with the chemical formula SnC
2O
4. The compound looks like colorless crystals, does not dissolve in water, and forms crystalline hydrates.
Neptunium (IV) oxalate is an inorganic compound, a salt of neptunium and oxalic acid with the chemical formula Np(C2O4)2. The compound is slightly soluble in water, forms crystalline hydrates—green crystals.
Samarium(III) oxalate is an inorganic compound, a salt of samarium and oxalic acid with the formula Sm2(C2O4)3. The compound does not dissolve in water, forms a crystalline hydrate with yellow crystals.

Plutonium (IV) nitrate is an inorganic compound, a salt of plutonium and nitric acid with the chemical formula Pu(NO3)4. The compound dissolves in water and forms crystalline hydrates as dark green crystals.
Neptunium(IV) nitrate is an inorganic compound, a salt of neptunium and nitric acid with the chemical formula Np(NO3)4. The compound forms gray crystals, dissolves in water, and forms crystal hydrates.
Actinium (III) nitrate is an inorganic compound, actinium salt of nitric acid with the chemical formula Ac(NO3)3. The compound looks like white substance, readily soluble in water.

Dysprosium(III) nitrate is an inorganic compound, a salt of dysprosium and nitric acid with the chemical formula Dy(NO3)3. The compound forms yellowish crystals, dissolves in water, forms a crystalline hydrate.
Americium(III) nitrate is an inorganic compound, a salt of americium and nitric acid with the chemical formula Am(NO3)3. The compound is soluble in water and radioactive.

Holmium (III) nitrate is an inorganic compound, a salt of holmium and nitric acid with the chemical formula Ho(NO3)3. The compound forms yellowish crystals, dissolves in water, also forms crystalline hydrates.

Ytterbium (III) nitrate is an inorganic compound, a salt of ytterbium and nitric acid with the chemical formula Yb(NO3)3. The compound forms colorless crystals, dissolves in water, and also forms crystalline hydrates.
Lutetium(III) nitrate is an inorganic compound, a salt of lutetium and nitric acid with the chemical formula Lu(NO3)3. The compound forms colorless crystals, dissolves in water, and also forms crystalline hydrates. The compound is poisonous.
Curium(III) nitrate is an inorganic compound, a salt of curium and nitric acid with the chemical formula Cm(NO3)3.

Thulium(III) nitrate is an inorganic compound, a salt of curium and nitric acid with the chemical formula Tm(NO3)3. The compound forms dark-green crystals, readily soluble in water, also forms crystalline hydrates.
| HNO3 | He | ||||||||||||||||
| LiNO3 | Be(NO3)2 | B(NO 3)− 4 | RONO2 | NO− 3 NH4NO3 | HOONO2 | FNO3 | Ne | ||||||||||
| NaNO3 | Mg(NO3)2 | Al(NO3)3 | Si | P | S | ClONO2 | Ar | ||||||||||
| KNO3 | Ca(NO3)2 | Sc(NO3)3 | Ti(NO3)4 | VO(NO3)3 | Cr(NO3)3 | Mn(NO3)2 | Fe(NO3)2 Fe(NO3)3 | Co(NO3)2 Co(NO3)3 | Ni(NO3)2 | CuNO3 Cu(NO3)2 | Zn(NO3)2 | Ga(NO3)3 | Ge | As | Se | Br | Kr |
| RbNO3 | Sr(NO3)2 | Y(NO3)3 | Zr(NO3)4 | Nb | Mo | Tc | Ru(NO3)3 | Rh(NO3)3 | Pd(NO3)2 Pd(NO3)4 | AgNO3 Ag(NO3)2 | Cd(NO3)2 | In(NO3)3 | Sn(NO3)4 | Sb(NO3)3 | Te | INO3 | Xe(NO3)2 |
| CsNO3 | Ba(NO3)2 | Hf(NO3)4 | Ta | W | Re | Os | Ir | Pt(NO3)2 Pt(NO3)4 | Au(NO3)3 | Hg2(NO3)2 Hg(NO3)2 | TlNO3 Tl(NO3)3 | Pb(NO3)2 | Bi(NO3)3 BiO(NO3) | Po(NO3)4 | At | Rn | |
| FrNO3 | Ra(NO3)2 | Rf | Db | Sg | Bh | Hs | Mt | Ds | Rg | Cn | Nh | Fl | Mc | Lv | Ts | Og | |
| ↓ | |||||||||||||||||
| La(NO3)3 | Ce(NO3)3 Ce(NO3)4 | Pr(NO3)3 | Nd(NO3)3 | Pm(NO3)3 | Sm(NO3)3 | Eu(NO3)3 | Gd(NO3)3 | Tb(NO3)3 | Dy(NO3)3 | Ho(NO3)3 | Er(NO3)3 | Tm(NO3)3 | Yb(NO3)3 | Lu(NO3)3 | |||
| Ac(NO3)3 | Th(NO3)4 | PaO2(NO3)3 | UO2(NO3)2 | Np(NO3)4 | Pu(NO3)4 | Am(NO3)3 | Cm(NO3)3 | Bk | Cf | Es | Fm | Md | No | Lr | |||