
Lead(II) nitrate is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Pb(NO3)2. It commonly occurs as a colourless crystal or white powder and, unlike most other lead(II) salts, is soluble in water.

Copper(II) nitrate describes any member of the family of inorganic compounds with the formula Cu(NO3)2(H2O)x. The hydrates are blue solids. Anhydrous copper nitrate forms blue-green crystals and sublimes in a vacuum at 150-200 °C. Common hydrates are the hemipentahydrate and trihydrate.

Dinitrogen pentoxide is the chemical compound with the formula N2O5. It is one of the binary nitrogen oxides, a family of compounds that only contain nitrogen and oxygen. It exists as colourless crystals that sublime slightly above room temperature, yielding a colorless gas.

Iron(III) nitrate, or ferric nitrate, is the name used for a series of inorganic compounds with the formula Fe(NO3)3.(H2O)n. Most common is the nonahydrate Fe(NO3)3.(H2O)9. The hydrates are all pale colored, water-soluble paramagnetic salts.
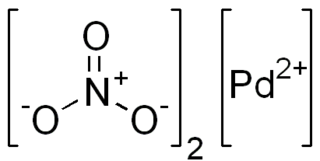
Palladium(II) nitrate is the inorganic compound with the formula Pd(NO3)2.(H2O)x where x = 0 or 2. The anhydrous and dihydrate are deliquescent solids. According to X-ray crystallography, both compounds feature square planar Pd(II) with unidentate nitrate ligands. The anhydrous compound, which is a coordination polymer, is yellow.

Cobalt nitrate is the inorganic compound with the formula Co(NO3)2.xH2O. It is cobalt(II)'s salt. The most common form is the hexahydrate Co(NO3)2·6H2O, which is a red-brown deliquescent salt that is soluble in water and other polar solvents.

Cerium nitrate refers to a family of nitrates of cerium in the +3 or +4 oxidation state. Often these compounds contain water, hydroxide, or hydronium ions in addition to cerium and nitrate. Double nitrates of cerium also exist.

Titanium nitrate is the inorganic compound with formula Ti(NO3)4. It is a colorless, diamagnetic solid that sublimes readily. It is an unusual example of a volatile binary transition metal nitrate. Ill defined species called titanium nitrate are produced upon dissolution of titanium or its oxides in nitric acid.

Yttrium(III) nitrate is an inorganic compound, a salt with the formula Y(NO3)3. The hexahydrate is the most common form commercially available.

Terbium(III) nitrate is an inorganic chemical compound, a salt of terbium and nitric acid, with the formula Tb(NO3)3. The hexahydrate crystallizes as triclinic colorless crystals with the formula [Tb(NO3)3(H2O)4]·2H2O. It can be used to synthesize materials with green emission.
Indium(III) nitrate is a nitrate salt of indium which forms various hydrates. Only the pentahydrate has been crystallographically verified. Other hydrates are also reported in literature, such as the trihydrate.

Nitratoauric acid, hydrogen tetranitratoaurate, or simply called gold(III) nitrate is a crystalline gold compound that forms the trihydrate, HAu(NO3)4·3H2O or more correctly H5O2Au(NO3)4·H2O. This compound is an intermediate in the process of extracting gold. In older literature it is also known as aurinitric acid.

Iron(II) nitrate is the nitrate salt of iron(II). It is commonly encountered as the green hexahydrate, Fe(NO3)2·6H2O, which is a metal aquo complex, however it is not commercially available unlike iron(III) nitrate due to its instability to air. The salt is soluble in water serves as a ready source of ferrous ions.

Praseodymium(III) nitrate is any inorganic compound with the chemical formula Pr(NO3)3·xH2O. They are used in the extraction and purification of praseodymium from its ores. The hexahydrate has been characterized by X-ray crystallography.
Rhodium(III) nitrate is a inorganic compound, a salt of rhodium and nitric acid with the formula Rh(NO3)3. This anhydrous complex has been the subject of theoretical analysis but has not been isolated. However, a dihydrate and an aqueous solution are known with similar stoichiometry; they contain various hexacoordinated rhodium(III) aqua and nitrate complexes. A number of other rhodium nitrates have been characterized by X-ray crystallography: Rb4[trans-[Rh(H2O)2(NO3)4][Rh(NO3)6] and Cs2[-[Rh(NO3)5]. Rhodium nitrates are of interest because nuclear wastes, which contain rhodium, are recycled by dissolution in nitric acid.

Americium(III) nitrate is an inorganic compound, a salt of americium and nitric acid with the chemical formula Am(NO3)3. The compound is soluble in water and radioactive.

Ytterbium(III) nitrate is an inorganic compound, a salt of ytterbium and nitric acid with the chemical formula Yb(NO3)3. The compound forms colorless crystals, dissolves in water, and also forms crystalline hydrates.
Lutetium(III) nitrate is an inorganic compound, a salt of lutetium and nitric acid with the chemical formula Lu(NO3)3. The compound forms colorless crystals, dissolves in water, and also forms crystalline hydrates. The compound is poisonous.
Curium(III) nitrate is an inorganic compound, a salt of curium and nitric acid with the chemical formula Cm(NO3)3.

A transition metal nitrate complex is a coordination compound containing one or more nitrate ligands. Such complexes are common starting reagents for the preparation of other compounds.




















