Nitric acid is the inorganic compound with the formula HNO3. It is a highly corrosive mineral acid. The compound is colorless, but older samples tend to be yellow cast due to decomposition into oxides of nitrogen. Most commercially available nitric acid has a concentration of 68% in water. When the solution contains more than 86% HNO3, it is referred to as fuming nitric acid. Depending on the amount of nitrogen dioxide present, fuming nitric acid is further characterized as red fuming nitric acid at concentrations above 86%, or white fuming nitric acid at concentrations above 95%.

Copper(II) nitrate describes any member of the family of inorganic compounds with the formula Cu(NO3)2(H2O)x. The hydrates are blue solids. Anhydrous copper nitrate forms blue-green crystals and sublimes in a vacuum at 150-200 °C. Common hydrates are the hemipentahydrate and trihydrate.
In chemistry, water(s) of crystallization or water(s) of hydration are water molecules that are present inside crystals. Water is often incorporated in the formation of crystals from aqueous solutions. In some contexts, water of crystallization is the total mass of water in a substance at a given temperature and is mostly present in a definite (stoichiometric) ratio. Classically, "water of crystallization" refers to water that is found in the crystalline framework of a metal complex or a salt, which is not directly bonded to the metal cation.
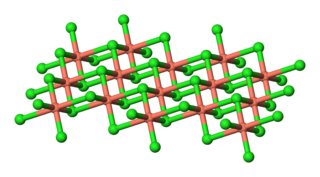
Copper(II) chloride is the chemical compound with the chemical formula CuCl2. The anhydrous form is yellowish brown but slowly absorbs moisture to form a blue-green dihydrate.

Uranium trioxide (UO3), also called uranyl oxide, uranium(VI) oxide, and uranic oxide, is the hexavalent oxide of uranium. The solid may be obtained by heating uranyl nitrate to 400 °C. Its most commonly encountered polymorph, γ-UO3, is a yellow-orange powder.

Zinc nitrate is an inorganic chemical compound with the formula Zn(NO3)2. This colorless, crystalline salt is highly deliquescent. It is typically encountered as a hexahydrate Zn(NO3)2·6H2O. It is soluble in both water and alcohol.

Palladium(II) oxide is the inorganic compound of formula PdO. It is the only well characterised oxide of palladium. It is prepared by treating the metal with oxygen. Above about 900 °C, the oxide reverts to palladium metal and oxygen gas. It is not attacked by acids.
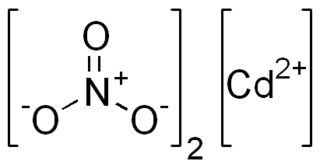
Cadmium nitrate describes any of the related members of a family of inorganic compounds with the general formula , the most commonly encountered form being the tetrahydrate. The anhydrous form is volatile, but the others are colourless crystalline solids that are deliquescent, tending to absorb enough moisture from the air to form an aqueous solution. Like other cadmium compounds, cadmium nitrate is known to be carcinogenic.

Iron(III) nitrate, or ferric nitrate, is the name used for a series of inorganic compounds with the formula Fe(NO3)3.(H2O)n. Most common is the nonahydrate Fe(NO3)3.(H2O)9. The hydrates are all pale colored, water-soluble paramagnetic salts.

Nickel nitrate is the inorganic compound Ni(NO3)2 or any hydrate thereof. The anhydrous form is not commonly encountered, thus "nickel nitrate" usually refers to nickel(II) nitrate hexahydrate. The formula for this species is written in two ways: Ni(NO3)2.6H2O and, more descriptively [Ni(H2O)6](NO3)2. The latter formula indicates that the nickel(II) center is surrounded by six water molecules in this hydrated salt. In the hexahydrate, the nitrate anions are not bonded to nickel. Also known are three other hydrates: Ni(NO3)2.9H2O, Ni(NO3)2.4H2O, and Ni(NO3)2.2H2O. Anhydrous Ni(NO3)2 is also known.

Cobalt nitrate is the inorganic compound with the formula Co(NO3)2.xH2O. It is cobalt(II)'s salt. The most common form is the hexahydrate Co(NO3)2·6H2O, which is a red-brown deliquescent salt that is soluble in water and other polar solvents.
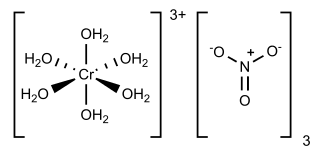
Chromium(III) nitrate describes several inorganic compounds consisting of chromium, nitrate and varying amounts of water. Most common is the dark violet hygrosscopic solid. An anhydrous green form is also known. Chromium(III) nitrate compounds are of a limited commercial importance, finding some applications in the dyeing industry. It is common in academic laboratories for the synthesis of chromium coordination complexes.

Metal halides are compounds between metals and halogens. Some, such as sodium chloride are ionic, while others are covalently bonded. A few metal halides are discrete molecules, such as uranium hexafluoride, but most adopt polymeric structures, such as palladium chloride.

Cerium nitrate refers to a family of nitrates of cerium in the +3 or +4 oxidation state. Often these compounds contain water, hydroxide, or hydronium ions in addition to cerium and nitrate. Double nitrates of cerium also exist.

Titanium nitrate is the inorganic compound with formula Ti(NO3)4. It is a colorless, diamagnetic solid that sublimes readily. It is an unusual example of a volatile binary transition metal nitrate. Ill defined species called titanium nitrate are produced upon dissolution of titanium or its oxides in nitric acid.

Thorium(IV) nitrate is a chemical compound with the formula Th(NO3)4. A white solid in its anhydrous form, it can form tetra- and pentahydrates. As a salt of thorium it is weakly radioactive.

Terbium(III) nitrate is an inorganic chemical compound, a salt of terbium and nitric acid, with the formula Tb(NO3)3. The hexahydrate crystallizes as triclinic colorless crystals with the formula [Tb(NO3)3(H2O)4]·2H2O. It can be used to synthesize materials with green emission.

A transition metal nitrate complex is a coordination compound containing one or more nitrate ligands. Such complexes are common starting reagents for the preparation of other compounds.

Europium compounds are compounds formed by the lanthanide metal europium (Eu). In these compounds, europium generally exhibits the +3 oxidation state, such as EuCl3, Eu(NO3)3 and Eu(CH3COO)3. Compounds with europium in the +2 oxidation state are also known. The +2 ion of europium is the most stable divalent ion of lanthanide metals in aqueous solution. Lipophilic europium complexes often feature acetylacetonate-like ligands, e.g., Eufod.
Cobalt compounds are chemical compounds formed by cobalt with other elements. In the compound, the most stable oxidation state of cobalt is the +2 oxidation state, and in the presence of specific ligands, there are also stable compounds with +3 valence. In addition, there are cobalt compounds in high oxidation states +4, +5 and low oxidation states -1, 0, +1.


















