
Cerium nitrate refers to a family of nitrates of cerium in the +3 or +4 oxidation state. Often these compounds contain water, hydroxide, or hydronium ions in addition to cerium and nitrate. Double nitrates of cerium also exist.

Beryllium oxalate is an inorganic compound, a salt of beryllium metal and oxalic acid with the chemical formula C
2BeO
4. It forms colorless crystals, dissolves in water, and also forms crystalline hydrates. The compound is used to prepare ultra-pure beryllium oxide by thermal decomposition.
Praseodymium(III) oxalate is an inorganic compound, a salt of praseodymium metal and oxalic acid with the chemical formula C6O12Pr2. The compound forms light green crystals, insoluble in water, also forms crystalline hydrates.
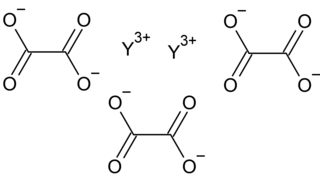
Yttrium oxalate is an inorganic compound, a salt of yttrium and oxalic acid with the chemical formula Y2(C2O4)3. The compound does not dissolve in water and forms crystalline hydrates—colorless crystals.
Manganese oxalate is a chemical compound, a salt of manganese and oxalic acid with the chemical formula MnC
2O
4. The compound creates light pink crystals, does not dissolve in water, and forms crystalline hydrates. It occurs naturally as the mineral Lindbergite.
Neptunium (IV) oxalate is an inorganic compound, a salt of neptunium and oxalic acid with the chemical formula Np(C2O4)2. The compound is slightly soluble in water, forms crystalline hydrates—green crystals.
Samarium(III) oxalate is an inorganic compound, a salt of samarium and oxalic acid with the formula Sm2(C2O4)3. The compound does not dissolve in water, forms a crystalline hydrate with yellow crystals.

Plutonium (IV) nitrate is an inorganic compound, a salt of plutonium and nitric acid with the chemical formula Pu(NO3)4. The compound dissolves in water and forms crystalline hydrates as dark green crystals.
Neptunium(IV) nitrate is an inorganic compound, a salt of neptunium and nitric acid with the chemical formula Np(NO3)4. The compound forms gray crystals, dissolves in water, and forms crystal hydrates.

Actinium (III) nitrate is an inorganic compound, actinium salt of nitric acid with the chemical formula Ac(NO3)3. The compound looks like white substance, readily soluble in water.
Dysprosium(III) nitrate is an inorganic compound, a salt of dysprosium and nitric acid with the chemical formula Dy(NO3)3. The compound forms yellowish crystals, dissolves in water, forms a crystalline hydrate.
Americium(III) nitrate is an inorganic compound, a salt of americium and nitric acid with the chemical formula Am(NO3)3. The compound is soluble in water and radioactive.

Holmium (III) nitrate is an inorganic compound, a salt of holmium and nitric acid with the chemical formula Ho(NO3)3. The compound forms yellowish crystals, dissolves in water, also forms crystalline hydrates.

Ytterbium(III) nitrate is an inorganic compound, a salt of ytterbium and nitric acid with the chemical formula Yb(NO3)3. The compound forms colorless crystals, dissolves in water, and also forms crystalline hydrates.
Erbium(III) nitrate is an inorganic compound, a salt of erbium and nitric acid with the chemical formula Er(NO3)3. The compound forms pink crystals, readily soluble in water, also forms crystalline hydrates.

Thulium(III) nitrate is an inorganic compound, a salt of thulium and nitric acid with the chemical formula Tm(NO3)3. The compound forms dark-green crystals, readily soluble in water, also forms crystalline hydrates.
Polonium tetranitrate is an inorganic compound, a salt of polonium and nitric acid with the chemical formula Po(NO3)4. The compound is radioactive, forms white crystals.

Praseodymium(III) acetate is an inorganic salt composed of a Praseodymium atom trication and three acetate groups as anions. This compound commonly forms the dihydrate, Pr(O2C2H3)3·2H2O.
Ytterbium compounds are chemical compounds that contain the element ytterbium (Yb). The chemical behavior of ytterbium is similar to that of the rest of the lanthanides. Most ytterbium compounds are found in the +3 oxidation state, and its salts in this oxidation state are nearly colorless. Like europium, samarium, and thulium, the trihalides of ytterbium can be reduced to the dihalides by hydrogen, zinc dust, or by the addition of metallic ytterbium. The +2 oxidation state occurs only in solid compounds and reacts in some ways similarly to the alkaline earth metal compounds; for example, ytterbium(II) oxide (YbO) shows the same structure as calcium oxide (CaO).
Lutetium compounds are compounds formed by the lanthanide metal lutetium (Lu). In these compounds, lutetium generally exhibits the +3 oxidation state, such as LuCl3, Lu2O3 and Lu2(SO4)3. Aqueous solutions of most lutetium salts are colorless and form white crystalline solids upon drying, with the common exception of the iodide. The soluble salts, such as nitrate, sulfate and acetate form hydrates upon crystallization. The oxide, hydroxide, fluoride, carbonate, phosphate and oxalate are insoluble in water.












