
The aorta is the main and largest artery in the human body, originating from the left ventricle of the heart, branching upwards immediately after, and extending down to the abdomen, where it splits at the aortic bifurcation into two smaller arteries. The aorta distributes oxygenated blood to all parts of the body through the systemic circulation.

The heart is a muscular organ in most animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels of the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the body, while carrying metabolic waste such as carbon dioxide to the lungs. In humans, the heart is approximately the size of a closed fist and is located between the lungs, in the middle compartment of the chest, called the mediastinum.

Veins are blood vessels in the circulatory system of humans and most other animals that carry blood towards the heart. Most veins carry deoxygenated blood from the tissues back to the heart; exceptions are those of the pulmonary and fetal circulations which carry oxygenated blood to the heart. In the systemic circulation, arteries carry oxygenated blood away from the heart, and veins return deoxygenated blood to the heart, in the deep veins.
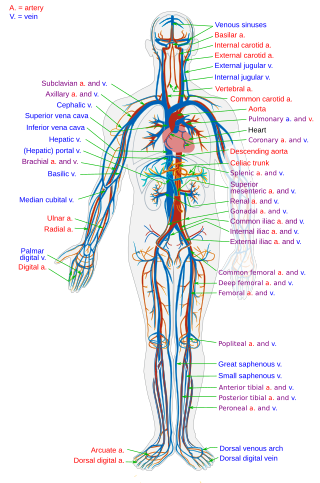
The blood circulatory system is a system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the entire body of a human or other vertebrate. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, that consists of the heart and blood vessels. The circulatory system has two divisions, a systemic circulation or circuit, and a pulmonary circulation or circuit. Some sources use the terms cardiovascular system and vascular system interchangeably with the circulatory system.

Coronary artery bypass surgery, also known as coronary artery bypass graft, is a surgical procedure to treat coronary artery disease (CAD), the buildup of plaques in the arteries of the heart. It can relieve chest pain caused by CAD, slow the progression of CAD, and increase life expectancy. It aims to bypass narrowings in heart arteries by using arteries or veins harvested from other parts of the body, thus restoring adequate blood supply to the previously ischemic heart.
Articles related to anatomy include:

Cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) is a technique in which a machine temporarily takes over the function of the heart and lungs during cardiac surgery, maintaining the circulation of blood and oxygen to the body. The CPB pump itself is often referred to as a heart-lung machine or "the pump". Cardiopulmonary bypass pumps are operated by perfusionists. CPB is a form of extracorporeal circulation. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) is generally used for longer-term treatment.
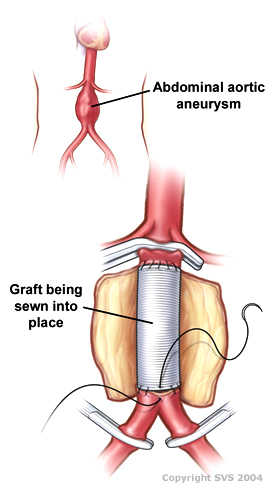
Vascular surgery is a surgical subspecialty in which vascular diseases involving the arteries, veins, or lymphatic vessels, are managed by medical therapy, minimally-invasive catheter procedures and surgical reconstruction. The specialty evolved from general and cardiovascular surgery where it refined the management of just the vessels, no longer treating the heart or other organs. Modern vascular surgery includes open surgery techniques, endovascular techniques and medical management of vascular diseases - unlike the parent specialities. The vascular surgeon is trained in the diagnosis and management of diseases affecting all parts of the vascular system excluding the coronaries and intracranial vasculature. Vascular surgeons also are called to assist other physicians to carry out surgery near vessels, or to salvage vascular injuries that include hemorrhage control, dissection, occlusion or simply for safe exposure of vascular structures.

Amaurosis fugax is a painless temporary loss of vision in one or both eyes.

An arteriovenous fistula is an abnormal connection or passageway between an artery and a vein. It may be congenital, surgically created for hemodialysis treatments, or acquired due to pathologic process, such as trauma or erosion of an arterial aneurysm.

The cavernous sinus within the human head is one of the dural venous sinuses creating a cavity called the lateral sellar compartment bordered by the temporal bone of the skull and the sphenoid bone, lateral to the sella turcica.

A Hollenhorst plaque is a cholesterol embolus that is seen in a blood vessel of the retina. It is usually found when a physician performs ophthalmoscopy, during which a plaque will appear as a small, bright crystal that is refractile and yellow. This is a medical exam finding, and is not a medical condition, though it may be related to cardiovascular conditions such as atherosclerosis of the internal carotid artery. It was first described by American ophthalmologist Robert Hollenhorst in 1961.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to human anatomy:
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to cardiology, the branch of medicine dealing with disorders of the human heart. The field includes medical diagnosis and treatment of congenital heart defects, coronary artery disease, heart failure, valvular heart disease and electrophysiology. Physicians who specialize in cardiology are called cardiologists.
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.










