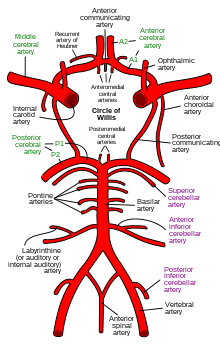
The circle of Willis is a circulatory anastomosis that supplies blood to the brain and surrounding structures in reptiles, birds and mammals, including humans. It is named after Thomas Willis (1621–1675), an English physician.
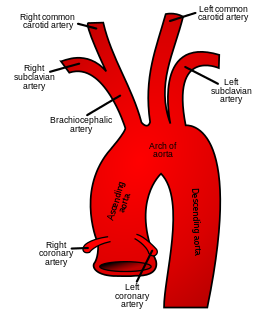
In human anatomy, the subclavian arteries are paired major arteries of the upper thorax, below the clavicle. They receive blood from the aortic arch. The left subclavian artery supplies blood to the left arm and the right subclavian artery supplies blood to the right arm, with some branches supplying the head and thorax. On the left side of the body, the subclavian comes directly off the aortic arch, while on the right side it arises from the relatively short brachiocephalic artery when it bifurcates into the subclavian and the right common carotid artery.

The internal carotid artery is an artery in the neck which supplies the anterior circulation of the brain. In human anatomy, the internal and external carotids arise from the common carotid arteries, where these bifurcate at cervical vertebrae C3 or C4. The internal carotid artery supplies the brain, including the eyes, while the external carotid nourishes other portions of the head, such as the face, scalp, skull, and meninges.

The internal capsule is a white matter structure situated in the inferomedial part of each cerebral hemisphere of the brain. It carries information past the basal ganglia, separating the caudate nucleus and the thalamus from the putamen and the globus pallidus. The internal capsule contains both ascending and descending axons, going to and coming from the cerebral cortex. It also separates the caudate nucleus and the putamen in the dorsal striatum, a brain region involved in motor and reward pathways.

Cerebral circulation is the movement of blood through a network of cerebral arteries and veins supplying the brain. The rate of cerebral blood flow in an adult human is typically 750 milliliters per minute, or about 15% of cardiac output. Arteries deliver oxygenated blood, glucose and other nutrients to the brain. Veins carry "used or spent" blood back to the heart, to remove carbon dioxide, lactic acid, and other metabolic products. Because the brain would quickly suffer damage from any stoppage in blood supply, the cerebral circulatory system has safeguards including autoregulation of the blood vessels. The failure of these safeguards may result in a stroke. The volume of blood in circulation is called the cerebral blood flow. Sudden intense accelerations change the gravitational forces perceived by bodies and can severely impair cerebral circulation and normal functions to the point of becoming serious life-threatening conditions.

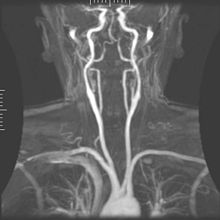
Cerebral angiography is a form of angiography which provides images of blood vessels in and around the brain, thereby allowing detection of abnormalities such as arteriovenous malformations and aneurysms. It was pioneered in 1927 by the Portuguese neurologist Egas Moniz at the University of Lisbon, who also helped develop thorotrast for use in the procedure.

Moyamoya disease is a disease in which certain arteries in the brain are constricted. Blood flow is blocked by constriction and blood clots (thrombosis). A collateral circulation develops around the blocked vessels to compensate for the blockage, but the collateral vessels are small, weak, and prone to bleeding, aneurysm and thrombosis. On conventional angiography, these collateral vessels have the appearance of a "puff of smoke".

The anterior cerebral artery (ACA) is one of a pair of cerebral arteries that supplies oxygenated blood to most midline portions of the frontal lobes and superior medial parietal lobes of the brain. The two anterior cerebral arteries arise from the internal carotid artery and are part of the circle of Willis. The left and right anterior cerebral arteries are connected by the anterior communicating artery.

The ophthalmic artery (OA) is an artery of the head. It is the first branch of the internal carotid artery distal to the cavernous sinus. Branches of the ophthalmic artery supply all the structures in the orbit around the eye, as well as some structures in the nose, face, and meninges. Occlusion of the ophthalmic artery or its branches can produce sight-threatening conditions.

The falx cerebri is a large, crescent-shaped fold of dura mater that descends vertically into the longitudinal fissure between the cerebral hemispheres of the human brain, separating the two hemispheres and supporting dural sinuses that provide venous and CSF drainage to the brain.
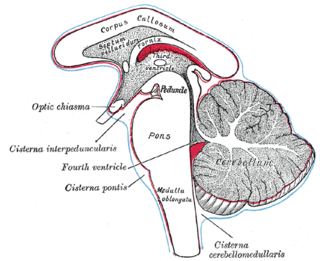
The subarachnoid cisterns are spaces formed by openings in the subarachnoid space, an anatomic space in the meninges of the brain. The space is situated between the two meninges, the arachnoid mater and the pia mater. These cisterns are filled with cerebrospinal fluid.

The middle cerebral artery (MCA) is one of the three major paired arteries that supply blood to the cerebrum. The MCA arises from the internal carotid and continues into the lateral sulcus where it then branches and projects to many parts of the lateral cerebral cortex. It also supplies blood to the anterior temporal lobes and the insular cortices.

The posterior cerebral artery (PCA) is one of a pair of cerebral arteries that supply oxygenated blood to the occipital lobe, part of the back of the human brain. The two arteries originate from the distal end of the basilar artery, where it bifurcates into the left and right posterior cerebral arteries. These anastomose with the middle cerebral arteries and internal carotid arteries via the posterior communicating arteries.

In human anatomy, the left and right posterior communicating arteries are arteries at the base of the brain that form part of the circle of Willis. Each posterior communicating artery connects the three cerebral arteries of the same side. Anteriorly, it connects to the internal carotid artery (ICA) prior to the terminal bifurcation of the ICA into the anterior cerebral artery and middle cerebral artery. Posteriorly, it communicates with the posterior cerebral artery.

In human anatomy, the anterior communicating artery is a blood vessel of the brain that connects the left and right anterior cerebral arteries.

Transcranial Doppler (TCD) and transcranial color Doppler (TCCD) are types of Doppler ultrasonography that measure the velocity of blood flow through the brain's blood vessels by measuring the echoes of ultrasound waves moving transcranially. These modes of medical imaging conduct a spectral analysis of the acoustic signals they receive and can therefore be classified as methods of active acoustocerebrography. They are used as tests to help diagnose emboli, stenosis, vasospasm from a subarachnoid hemorrhage, and other problems. These relatively quick and inexpensive tests are growing in popularity. The tests are effective for detecting sickle cell disease, ischemic cerebrovascular disease, subarachnoid hemorrhage, arteriovenous malformations, and cerebral circulatory arrest. The tests are possibly useful for perioperative monitoring and meningeal infection. The equipment used for these tests is becoming increasingly portable, making it possible for a clinician to travel to a hospital, to a doctor's office, or to a nursing home for both inpatient and outpatient studies. The tests are often used in conjunction with other tests such as MRI, MRA, carotid duplex ultrasound and CT scans. The tests are also used for research in cognitive neuroscience.

A watershed stroke is defined as a brain ischemia that is localized to the vulnerable border zones between the tissues supplied by the anterior, posterior and middle cerebral arteries. The actual blood stream blockage/restriction site can be located far away from the infarcts. Watershed locations are those border-zone regions in the brain supplied by the major cerebral arteries where blood supply is decreased. Watershed strokes are a concern because they comprise approximately 10% of all ischemic stroke cases. The watershed zones themselves are particularly susceptible to infarction from global ischemia as the distal nature of the vasculature predisposes these areas to be most sensitive to profound hypoperfusion.

Posterior cerebral artery syndrome is a condition whereby the blood supply from the posterior cerebral artery (PCA) is restricted, leading to a reduction of the function of the portions of the brain supplied by that vessel: the occipital lobe, the inferomedial temporal lobe, a large portion of the thalamus, and the upper brainstem and midbrain.

Anterior cerebral artery syndrome is a condition whereby the blood supply from the anterior cerebral artery (ACA) is restricted, leading to a reduction of the function of the portions of the brain supplied by that vessel: the medial aspects of the frontal and parietal lobes, basal ganglia, anterior fornix and anterior corpus callosum.

The leptomeningeal collateral circulation is a network of small blood vessels in the brain that connects branches of the middle, anterior and posterior cerebral arteries, with variation in its precise anatomy between individuals. During a stroke, leptomeningeal collateral vessels allow limited blood flow when other, larger blood vessels provide inadequate blood supply to a part of the brain.