Processor design is a subfield of computer science and computer engineering (fabrication) that deals with creating a processor, a key component of computer hardware.

A microprocessor is a computer processor for which the data processing logic and control is included on a single integrated circuit (IC), or a small number of ICs. The microprocessor contains the arithmetic, logic, and control circuitry required to perform the functions of a computer's central processing unit (CPU). The IC is capable of interpreting and executing program instructions and performing arithmetic operations. The microprocessor is a multipurpose, clock-driven, register-based, digital integrated circuit that accepts binary data as input, processes it according to instructions stored in its memory, and provides results as output. Microprocessors contain both combinational logic and sequential digital logic, and operate on numbers and symbols represented in the binary number system.

AVR is a family of microcontrollers developed since 1996 by Atmel, acquired by Microchip Technology in 2016. These are modified Harvard architecture 8-bit RISC single-chip microcontrollers. AVR was one of the first microcontroller families to use on-chip flash memory for program storage, as opposed to one-time programmable ROM, EPROM, or EEPROM used by other microcontrollers at the time.
SuperH is a 32-bit reduced instruction set computing (RISC) instruction set architecture (ISA) developed by Hitachi and currently produced by Renesas. It is implemented by microcontrollers and microprocessors for embedded systems.
Atmel Corporation was a creator and manufacturer of semiconductors before being subsumed by Microchip Technology in 2016. Atmel was founded in 1984. The company focused on embedded systems built around microcontrollers. Its products included microcontrollers radio-frequency (RF) devices including Wi-Fi, EEPROM, and flash memory devices, symmetric and asymmetric security chips, touch sensors and controllers, and application-specific products. Atmel supplies its devices as standard products, application-specific integrated circuits (ASICs), or application-specific standard product (ASSPs) depending on the requirements of its customers.

The NXP ColdFire is a microprocessor that derives from the Motorola 68000 family architecture, manufactured for embedded systems development by NXP Semiconductors. It was formerly manufactured by Freescale Semiconductor which merged with NXP in 2015.

The Blackfin is a family of 16-/32-bit microprocessors developed, manufactured and marketed by Analog Devices. The processors have built-in, fixed-point digital signal processor (DSP) functionality performed by 16-bit multiply–accumulates (MACs), accompanied on-chip by a microcontroller. It was designed for a unified low-power processor architecture that can run operating systems while simultaneously handling complex numeric tasks such as real-time H.264 video encoding.
LEON is a radiation-tolerant 32-bit central processing unit (CPU) microprocessor core that implements the SPARC V8 instruction set architecture (ISA) developed by Sun Microsystems. It was originally designed by the European Space Research and Technology Centre (ESTEC), part of the European Space Agency (ESA), without any involvement by Sun. Later versions have been designed by Gaisler Research, under a variety of owners. It is described in synthesizable VHSIC Hardware Description Language (VHDL). LEON has a dual license model: An GNU Lesser General Public License (LGPL) and GNU General Public License (GPL) free and open-source software (FOSS) license that can be used without licensing fee, or a proprietary license that can be purchased for integration in a proprietary product. The core is configurable through VHDL generics, and is used in system on a chip (SOC) designs both in research and commercial settings.
V850 is a 32-bit RISC CPU architecture produced by Renesas Electronics for embedded microcontrollers. It was designed by NEC as a replacement for their earlier NEC V60 family, and was introduced shortly before NEC sold their designs to Renesas in the early 1990s. It has continued to be developed by Renesas as of 2018.
Atmel ARM-based processors are microcontrollers and microprocessors integrated circuits, by Microchip Technology, that are based on various 32-bit ARM processor cores, with in-house designed peripherals and tool support.

The Centre for Development of Advanced Computing (C-DAC) is an Indian autonomous scientific society, operating under the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology.
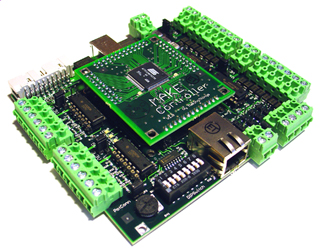
A single-board microcontroller is a microcontroller built onto a single printed circuit board. This board provides all of the circuitry necessary for a useful control task: a microprocessor, I/O circuits, a clock generator, RAM, stored program memory and any necessary support ICs. The intention is that the board is immediately useful to an application developer, without requiring them to spend time and effort to develop controller hardware.

Amlogic Inc. is a Fabless semiconductor company that was founded on March 14, 1995, in Santa Clara, California and is predominantly focused on designing and selling system on a chip integrated circuits. Like most Fabless companies in the industry, the company outsources the actual manufacturing of its chips to third-party independent chip manufacturers such as TSMC. Its main target applications as of 2021 are entertainment devices such as Android TV-based devices and IPTV/OTT set-top boxes, media dongles, smart TVs and tablets. It has offices in Shanghai, Shenzhen, Beijing, Xi'an, Chengdu, Hefei, Nanjing, Qingdao, Taipei, Hong Kong, Seoul, Mumbai, London, Munich, Indianapolis, Milan, Novi Sad and Santa Clara, California.
RISC-V is an open standard instruction set architecture (ISA) based on established reduced instruction set computer (RISC) principles. Unlike most other ISA designs, RISC-V is provided under royalty-free open-source licenses. Many companies are offering or have announced RISC-V hardware; open source operating systems with RISC-V support are available, and the instruction set is supported in several popular software toolchains.

The ESP8266 is a low-cost Wi-Fi microchip, with built-in TCP/IP networking software, and microcontroller capability, produced by Espressif Systems in Shanghai, China.
GigaDevice Semiconductor is a Chinese NOR flash memory designer. It also produces microcontrollers, some of them are based on the ARM architecture, and other on the RISC-V architecture. GD32 chips were introduced in 2015 and are compatible in pinout and periphery options to the STM32 line of microcontrollers.
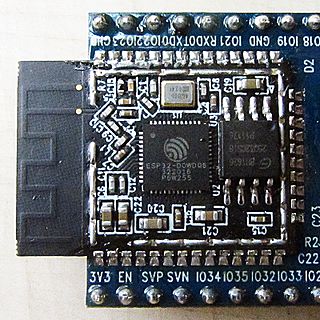
ESP32 is a series of low-cost, low-power system on a chip microcontrollers with integrated Wi-Fi and dual-mode Bluetooth. The ESP32 series employs either a Tensilica Xtensa LX6 microprocessor in both dual-core and single-core variations, Xtensa LX7 dual-core microprocessor or a single-core RISC-V microprocessor and includes built-in antenna switches, RF balun, power amplifier, low-noise receive amplifier, filters, and power-management modules. ESP32 is created and developed by Espressif Systems, a Chinese company based in Shanghai, and is manufactured by TSMC using their 40 nm process. It is a successor to the ESP8266 microcontroller.

SHAKTI is an open-source initiative by the Reconfigurable Intelligent Systems Engineering (RISE) group at Indian Institute of Technology, Madras to develop the first indigenous Indian industrial-grade processor. The aim of SHAKTI initiative includes building an opensource production-grade processor, complete system on chips (SoCs), development boards and SHAKTI based software platform. The primary focus of the team is architecture research to develop SoCs, which is competitive with commercial offerings in the market concerning area, power and performance. All the source codes for SHAKTI are open-sourced under the Modified BSD License. The project was funded by the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeITY), Government of India.










