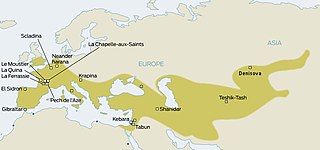
The Mousterian is an archaeological industry of stone tools, associated primarily with the Neanderthals in Europe, and to the earliest anatomically modern humans in North Africa and West Asia. The Mousterian largely defines the latter part of the Middle Paleolithic, the middle of the West Eurasian Old Stone Age. It lasted roughly from 160,000 to 40,000 BP. If its predecessor, known as Levallois or Levallois-Mousterian, is included, the range is extended to as early as c. 300,000–200,000 BP. The main following period is the Aurignacian of Homo sapiens.

The Levallois technique is a name given by archaeologists to a distinctive type of stone knapping developed around 250,000 to 300,000 years ago during the Middle Palaeolithic period. It is part of the Mousterian stone tool industry, and was used by the Neanderthals in Europe and by modern humans in other regions such as the Levant.

The Tabun Cave is an excavated site located at Nahal Me'arot Nature Reserve, Israel and is one of the Human Evolution sites at Mount Carmel, which were proclaimed as having universal value by UNESCO in 2012.

The Quina Mousterian is a variety of the Mousterian industry of the European Middle Palaeolithic, associated with Neanderthals and described by François Bordes. The Quina strategy emphasizes the production of thick and wide flakes, often bearing cortex, with the characteristic feature being scaled stepped retouch. The Quina Mousterian is usually dominated by transverse scrapers and typically has a Levallois index of less than 10%.
Harold Lewis Dibble was an American Paleolithic archaeologist. His main research concerned the lithic reduction during which he conducted fieldwork in France, Egypt, and Morocco. He was a professor of Anthropology at the University of Pennsylvania and Curator-in-Charge of the European Section of the University of Pennsylvania Museum of Archaeology and Anthropology.

The Grotte du Renne is one of the many caves at Arcy-sur-Cure in France, an archaeological site of the Middle/Upper Paleolithic period in the Yonne departement, Bourgogne-Franche-Comté. It contains Châtelperronian lithic industry and Neanderthal remains. Grotte du Renne has been argued to provide the best evidence that Neanderthals developed aspects of modern behaviour before contact with modern humans, but this has been challenged by radiological dates, which suggest mixing of later human artifacts with Neanderthal remains. However, it has also been argued that the radiometric dates have been affected by post-recovery contamination, and statistical testing suggests the association between Neanderthal remains, Châtelperronian artefacts and personal ornaments is genuine, not the result of post-depositional processes.

Shuqba cave is an archaeological site near the town of Shuqba in the western Judaean Mountains in the Ramallah and al-Bireh Governorate of the West Bank.

Roca dels Bous is an archaeological site located in Sant Llorenç de Montgai, in the Catalan Pyrenees, Spain. Since 1988 the Autonomous University of Barcelona and the UCL Institute of Archaeology study and record the fossil sequence of southern European Neanderthals who inhabited the area during the Middle Paleolithic approximately 50,000 years ago. The excavation team utilizes a worldwide unique digital system and various innovative technologies that significantly improve the quality of the classification of the recovered objects. Roca dels Bous has as one of the first Paleolithic excavation sites in Spain established a visitor centre, that focuses on displaying the Prehistory research of the prepyrenees area.

Scladina, or Sclayn Cave, is an archaeological site located in Wallonia in the town of Sclayn, in the Andenne hills in Belgium, where excavations since 1978 have provided the material for an exhaustive collection of over thirteen thousand Mousterian stone artifacts and the fossilized remains of an especially ancient Neanderthal, called the Scladina child were discovered in 1993.
The Obi-Rakhmat Grotto is a Middle Paleolithic prehistoric site that yielded Neanderthal fossils. It is a shallow karst cave near the junction of the Chatkal and Pskem Rivers at the southwestern end of the Talassky Alatau Range in the Tien Shan Mountains, 100 km (62 mi) northeast of Tashkent, Uzbekistan.

Trou de l’Abîme also known as La caverne de l'Abîme and Couvin Cave is a karst cave located in Wallonia on the right bank of the Eau Noire river in the center of Couvin, Belgium, in Namur province. During various archaeological excavations of sediment deposits, Mousterian artefacts and a Neanderthal molar were discovered.

Okladnikov Cave is a paleoanthropological site located in the foothills of the Altai Mountains in Soloneshensky District, Altai Krai in southern Siberia, Russia. The cave faces south and is located on a Devonian karst escarpment, lying about 14 metres (46 ft) above the left bank of the Sibiryachikha River valley below; the river itself is a tributary of the Anuy River.

The Noisetier Cave, owing its popular name to the Hazel trees that grow in front of its entrance, is located in a mountainside 145 m (476 ft) atop the Vallée d'Aure in the Ardengost commune, Hautes-Pyrénées department in the region Occitania, Southern France. During systematic excavations since 1992 Middle Paleolithic stone tools and artifacts attributed to the Neanderthal Mousterian culture were discovered among numerous faunal remains.

Pešturina is a cave in the municipality of Niška Banja in southeast Serbia. It is located southwest of Jelašnica and 20 km (12 mi) southeast of Niš. Artifacts from the Middle and Upper Paleolithic periods were discovered since the archaeological excavations began in 2006. The remains, identified as the Mousterian culture, were dated from 111,000 BP+ 5,000 to 39,000 BP + 3,000, which makes Pešturina one of the latest surviving Neanderthal habitats. The cave has been nicknamed the "Serbian Atapuerca".
Qafzeh Cave, also known by other names, is a prehistoric archaeological site located at the bottom of Mount Precipice in the Jezreel Valley of Lower Galilee south of Nazareth. Important remains of prehistoric people were discovered on the site - some of the oldest examples in the world, outside of Africa, of virtually anatomically modern human beings. These were discovered on the ledge just outside the cave, where 18 layers from the Middle Paleolithic era were identified. The interior of the cave contains layers ranging from the Neolithic era to the Bronze Age.

Cueva de Bolomor, or Bolomor Cave, is an archaeological site near Tavernes de la Valldigna in the Valencian Community, Spain. It was occupied over a long period of time, between 350,000 and 120,000 years ago.

Fumane Cave is a dolomite cave in the Fumane Valley, which was formed in the Neogene period. The cave contains rich evidence of three prehistoric hominid cultures: Mousterian, Uluzzian and Aurignacian. Additionally, the cave has some of the oldest cave art that has been discovered in Europe.

The Nesher RamlaHomo group are an extinct population of archaic humans who lived during the Middle Pleistocene in what is now modern-day Israel. In 2010, evidence of a tool industry had been discovered during a year of archaeological excavations at the Nesher Ramla site. In 2021, the first Nesher Ramla Homo individual was identified from remains discovered during further excavations.
Darai Rockshelter is an archaeological site in the southwest of Kurdistan Province, in west Iran. It is located in the Sirwan River valley, between Naw and Asparez villages, in the Hawraman region. It faces NNW at an altitude of 760m a.s.l.The shelter was discovered during Darian Dam Archaeological Salvage Program in 2015, excavated in 2015–2016, and it was subsequently submerged in 2016.
















