Related Research Articles

The Ajanta Caves are 29 rock-cut Buddhist cave monuments dating from the second century BCE to about 480 CE in the Aurangabad District of Maharashtra state in India. Ajanta Caves are a UNESCO World Heritage Site. Universally regarded as masterpieces of Buddhist religious art, the caves include paintings and rock-cut sculptures described as among the finest surviving examples of ancient Indian art, particularly expressive paintings that present emotions through gesture, pose and form.

In archaeology, cave paintings are a type of parietal art, found on the wall or ceilings of caves. The term usually implies prehistoric origin, and the oldest known are more than 40,000 years old and found in the caves in the district of Maros. The oldest are often constructed from hand stencils and simple geometric shapes. More recently, in 2021, cave art of a pig found in Sulawesi, Indonesia, and dated to over 45,500 years ago, has been reported.

In the history of art, prehistoric art is all art produced in preliterate, prehistorical cultures beginning somewhere in very late geological history, and generally continuing until that culture either develops writing or other methods of record-keeping, or makes significant contact with another culture that has, and that makes some record of major historical events. At this point ancient art begins, for the older literate cultures. The end-date for what is covered by the term thus varies greatly between different parts of the world.

The Bhimbetka rock shelters are an archaeological site in central India that spans the Paleolithic and Mesolithic periods, as well as the historic period. It exhibits the earliest traces of human life in India and evidence of the Stone Age starting at the site in Acheulian times. It is located in the Raisen District in the Indian state of Madhya Pradesh, about 45 kilometres (28 mi) south-east of Bhopal. It is a UNESCO World Heritage Site that consists of seven hills and over 750 rock shelters distributed over 10 km (6.2 mi). At least some of the shelters were inhabited more than 100,000 years ago. The rock shelters and caves provide evidence of human settlement and the cultural evolution from hunter-gatherers to agriculture, and expressions of prehistoric spirituality.

In archaeology, rock art is human-made markings placed on natural surfaces, typically vertical stone surfaces. A high proportion of surviving historic and prehistoric rock art is found in caves or partly enclosed rock shelters; this type also may be called cave art or parietal art. A global phenomenon, rock art is found in many culturally diverse regions of the world. It has been produced in many contexts throughout human history. In terms of technique, the four main groups are:
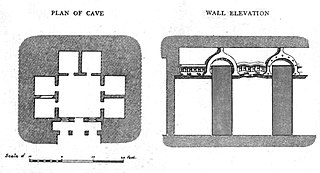
Vihāra generally refers to a Buddhist monastery for Buddhist renunciates, mostly in the Indian subcontinent. The concept is ancient and in early Sanskrit and Pali texts, it meant any arrangement of space or facilities for dwellings. The term evolved into an architectural concept wherein it refers to living quarters for monks with an open shared space or courtyard, particularly in Buddhism. The term is also found in Ajivika, Hindu and Jain monastic literature, usually referring to temporary refuge for wandering monks or nuns during the annual Indian monsoons. In modern Jainism, the monks continue to wander from town to town except during the rainy season (Chaturmas), and the term "vihara" refers to their wanderings.

Indian art consists of a variety of art forms, including painting, sculpture, pottery, and textile arts such as woven silk. Geographically, it spans the entire Indian subcontinent, including what is now India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Sri Lanka, Nepal, and at times eastern Afghanistan. A strong sense of design is characteristic of Indian art and can be observed in its modern and traditional forms.

Rock-cut architecture is the creation of structures, buildings, and sculptures by excavating solid rock where it naturally occurs. Intensely laborious when using ancient tools and methods, rock-cut architecture was presumably combined with quarrying the rock for use elsewhere. Though, in India and China, the terms cave and cavern are often applied to this form of man-made architecture, caves and caverns that began in natural form are not considered to be rock-cut architecture even if extensively modified. Although rock-cut structures differ from traditionally built structures in many ways, many rock-cut structures are made to replicate the facade or interior of traditional architectural forms. Interiors were usually carved out by starting at the roof of the planned space and then working downward. This technique prevents stones falling on workers below. The three main uses of rock-cut architecture were temples, tombs, and cave dwellings.

The South Asian Stone Age covers the Palaeolithic, Mesolithic and Neolithic periods in South Asia. Evidence for the most ancient Homo sapiens in South Asia has been found in the cave sites of Cudappah of India, Batadombalena and Belilena in Sri Lanka. In Mehrgarh, in what is today western Pakistan, the Neolithic began c. 7000 BCE and lasted until 3300 BCE and the first beginnings of the Bronze Age. In South India, the Mesolithic lasted until 3000 BCE, and the Neolithic until 1400 BCE, followed by a Megalithic transitional period mostly skipping the Bronze Age. The Iron Age began roughly simultaneously in North and South India, around c. 1200 to 1000 BCE.

Vishnu Shridhar Wakankar was an Indian archeologist. Wakankar is credited with the discovery of the Bhimbetka rock caves in 1957 and the Kayatha culture in 1964, among others. In 2003, UNESCO inscribed the Bhimbetka rock caves as a World Heritage Site. The Bhimbetka rock caves exhibit one of the earliest traces of human life in India.
Kailaras is a town and a nagar panchayat in Morena district in the Indian state of Madhya Pradesh.The name of the town is related to Kailash mountain due to the Temple of God Shankar,Alopi Shankar Temple which is situated on a hill 490 meters above sea level. The Behara Mata Temple is located near Kailaras. The idol of Goddess Bahrara is present in this temple. Bahara is also known as Pasar Devi and Bharkhandi Sarkar Temple. The city called Pahargarh which was the center of the princely state of Pahargarh is located at a distance of 12 km from Kailaras where the fort of Ishwar and Ishwara Mahadev Temple and Stone Age cave images are present. on the mountain situated in the middle of it

The Edakkal caves are two natural caves at a remote location at Edakkal, 25 km (15.5 mi) from Kalpetta in the Wayanad district of Kerala in India. It connects the Western Ghats and the Eastern Ghats. They lie 1,200 m (3,900 ft) above sea level on Ambukutty Mala, near an ancient trade route connecting the high mountains of Mysore to the ports of the Malabar Coast. Inside the caves are pictorial writings believed to date to at least 6,000 BCE, from the Neolithic man, indicating the presence of a prehistoric settlement in this region. The Stone Age carvings of Edakkal are rare and are the only known examples from South India besides those of Shenthurini, Kollam, also in Kerala. The cave paintings of Shenthurini (Shendurney) forests in Kerala are of the Mesolithic era.

The art of the Upper Paleolithic represents the oldest form of prehistoric art. Figurative art is present in Europe and Southeast Asia, beginning between about 40,000 to 35,000 years ago. Non-figurative cave paintings, consisting of hand stencils and simple geometric shapes, are somewhat older, at least 40,000 years old, and possibly as old as 64,000 years. This latter estimate is due to a controversial 2018 study based on uranium-thorium dating, which would imply Neanderthal authorship and qualify as art of the Middle Paleolithic.

The history of cave paintings in India or rock art range from drawings and paintings from prehistoric times, beginning in the caves of Central India, typified by those at the Bhimbetka rock shelters from around 10,000 BP, to elaborate frescoes at sites such as the rock-cut artificial caves at Ajanta and Ellora, extending as late as 6th–10th century CE.

The Ambadevi rock shelters are part of an extensive cave site, where the oldest yet known traces of human life in the central province of the Indian subcontinent were discovered. The site is located in the Satpura Range of the Gawilgarh Hills in Betul District of the Indian state of Madhya Pradesh, north of Dharul village in Amravati district of Maharashtra. Studies of various rock paintings and petroglyphs present in the caves suggest, that the Ambadevi rock shelters were inhabited by prehistoric human settlers since around 25,000 years ago. First discoveries of clusters of numerous rock shelters and caves were made by Vijay Ingole and his team beginning on 27 January 2007. Named after the nearby ancient Ambadevi Cave Temple, the site has also been referred to as the Satpura-Tapti valley caves and the Gavilgarh-Betul rock shelters. The Ambadevi rock shelters rank among the most important archaeological discoveries of the early 21st Century in India, on par with the 20th Century discovery of the Bhimbetka rock shelters.
Mangar Bani, a paleolithic archaeological site and sacred grove hill forest next to the Mangar village on Delhi-Haryana border,which is dominated by Gurjar community;is in the South Delhi Ridge of Aravalli mountain range in Faridabad tehsil of Faridabad district in the Indian state of Haryana. It lies, immediate south of India's national capital Delhi, within NCR.This whole area is dominated by Gurjar Community.

Tikla, or Tikula, is an archeological site and ancient rock shelter in Madhya Pradesh, India, known for its petroglyphs. Tikla is situated around 170 km (110 mi) south of Mathura and 50 km (31 mi) southwest of Gwalior on the Agra to Mumbai road near the town of Mohana on the right bank of the Parvati river.

Anangpur is a historical village located near Faridabad in Haryana, India. Anangpur forms a geographical triangle along with Mehrauli and Tugluqabad. It was the earliest settlement of the Tomara dynasty. Anangpur was the capital of the Tomar king, Anangpal Tomar I.

Indo-Scythian art developed under the various dynasties of Indo-Scythian rulers in northwestern India, from the 1st century BCE to the early 5th century CE, encompassing the productions of the early Indo-Scythians, the Northern Satraps and the Western Satraps. It follows the development of Indo-Greek art in northwestern India. The Scythians in India were ultimately replaced by the Kushan Empire and the Gupta Empire, whose art form appear in Kushan art and Gupta art.
References
- ↑ "Cave paintings in the cave shelters". The Worth Visiting Places of District. Morena District. Retrieved 11 July 2017.
- 1 2 "India cave project gets preliminary grant OK". Western News. Vol. 7, no. 14. 4 December 1980.
- 1 2 3 Bobb, Dilip (15 October 1981). "Pahargarh caves: A wealth of archaeological treasure". India Today. Retrieved 2017-07-11.
- ↑ "History of pahargarh | पहाड़गढ़ का इतिहास". YouTube .