Inorganic chemistry deals with synthesis and behavior of inorganic and organometallic compounds. This field covers chemical compounds that are not carbon-based, which are the subjects of organic chemistry. The distinction between the two disciplines is far from absolute, as there is much overlap in the subdiscipline of organometallic chemistry. It has applications in every aspect of the chemical industry, including catalysis, materials science, pigments, surfactants, coatings, medications, fuels, and agriculture.

A perovskite is any material with a crystal structure following the formula ABX3, which was first discovered as the mineral called perovskite, which consists of calcium titanium oxide (CaTiO3). The mineral was first discovered in the Ural mountains of Russia by Gustav Rose in 1839 and named after Russian mineralogist L. A. Perovski (1792–1856). 'A' and 'B' are two positively charged ions (i.e. cations), often of very different sizes, and X is a negatively charged ion (an anion, frequently oxide) that bonds to both cations. The 'A' atoms are generally larger than the 'B' atoms. The ideal cubic structure has the B cation in 6-fold coordination, surrounded by an octahedron of anions, and the A cation in 12-fold cuboctahedral coordination. Additional perovskite forms may exist where either/both the A and B sites have a configuration of A1x-1A2x and/or B1y-1B2y and the X may deviate from the ideal coordination configuration as ions within the A and B sites undergo changes in their oxidation states.

Titanium tetrachloride is the inorganic compound with the formula TiCl4. It is an important intermediate in the production of titanium metal and the pigment titanium dioxide. TiCl4 is a volatile liquid. Upon contact with humid air, it forms thick clouds of titanium dioxide and hydrochloric acid, a reaction that was formerly exploited for use in smoke machines. It is sometimes referred to as "tickle" or "tickle 4", as a phonetic representation of the symbols of its molecular formula.

Lead(II) chloride (PbCl2) is an inorganic compound which is a white solid under ambient conditions. It is poorly soluble in water. Lead(II) chloride is one of the most important lead-based reagents. It also occurs naturally in the form of the mineral cotunnite.

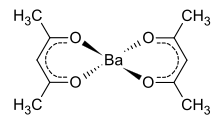
Acetylacetone is an organic compound with the chemical formula CH3−C(=O)−CH2−C(=O)−CH3. It is classified as a 1,3-diketone. It exists in equilibrium with a tautomer CH3−C(=O)−CH=C(−OH)−CH3. The mixture is a colorless liquid. These tautomers interconvert so rapidly under most conditions that they are treated as a single compound in most applications. Acetylacetone is a building block for the synthesis of many coordination complexes as well as heterocyclic compounds.
A salt metathesis reaction is a chemical process involving the exchange of bonds between two reacting chemical species which results in the creation of products with similar or identical bonding affiliations. This reaction is represented by the general scheme:

Barium titanate (BTO) is an inorganic compound with chemical formula BaTiO3. Barium titanate appears white as a powder and is transparent when prepared as large crystals. It is a ferroelectric, pyroelectric, and piezoelectric ceramic material that exhibits the photorefractive effect. It is used in capacitors, electromechanical transducers and nonlinear optics.
Titanium(III) chloride is the inorganic compound with the formula TiCl3. At least four distinct species have this formula; additionally hydrated derivatives are known. TiCl3 is one of the most common halides of titanium and is an important catalyst for the manufacture of polyolefins.

Titanium isopropoxide, also commonly referred to as titanium tetraisopropoxide or TTIP, is a chemical compound with the formula Ti{OCH(CH3)2}4. This alkoxide of titanium(IV) is used in organic synthesis and materials science. It is a diamagnetic tetrahedral molecule. Titanium isopropoxide is a component of the Sharpless epoxidation, a method for the synthesis of chiral epoxides.

EuFOD is the chemical compound with the formula Eu(OCC(CH3)3CHCOC3F7)3, also called Eu(fod)3. This coordination compound is used primarily as a shift reagent in NMR spectroscopy. It is the premier member of the lanthanide shift reagents and was popular in the 1970s and 1980s.

Barium borate is an inorganic compound, a borate of barium with a chemical formula BaB2O4 or Ba(BO2)2. It is available as a hydrate or dehydrated form, as white powder or colorless crystals. The crystals exist in the high-temperature α phase and low-temperature β phase, abbreviated as BBO; both phases are birefringent, and BBO is a common nonlinear optical material.

Nickel(II) bis(acetylacetonate) is a coordination complex with the formula [Ni(acac)2]3, where acac is the anion C5H7O2− derived from deprotonation of acetylacetone. It is a dark green paramagnetic solid that is soluble in organic solvents such as toluene. It reacts with water to give the blue-green diaquo complex Ni(acac)2(H2O)2.
Metal acetylacetonates are coordination complexes derived from the acetylacetonate anion (CH
3COCHCOCH−
3) and metal ions, usually transition metals. The bidentate ligand acetylacetonate is often abbreviated acac. Typically both oxygen atoms bind to the metal to form a six-membered chelate ring. The simplest complexes have the formula M(acac)3 and M(acac)2. Mixed-ligand complexes, e.g. VO(acac)2, are also numerous. Variations of acetylacetonate have also been developed with myriad substituents in place of methyl (RCOCHCOR′−). Many such complexes are soluble in organic solvents, in contrast to the related metal halides. Because of these properties, acac complexes are sometimes used as catalyst precursors and reagents. Applications include their use as NMR "shift reagents" and as catalysts for organic synthesis, and precursors to industrial hydroformylation catalysts. C
5H
7O−
2 in some cases also binds to metals through the central carbon atom; this bonding mode is more common for the third-row transition metals such as platinum(II) and iridium(III).
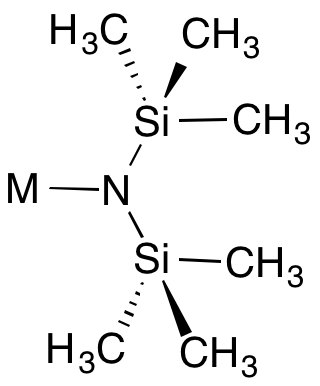
Metal bis(trimethylsilyl)amides are coordination complexes composed of a cationic metal M with anionic bis(trimethylsilyl)amide ligands (the −N 2 monovalent anion, or −N 2 monovalent group, and are part of a broader category of metal amides.

Tantalum(V) ethoxide is a metalorganic compound with formula Ta2(OC2H5)10, often abbreviated as Ta2(OEt)10. It is a colorless solid that dissolves in some organic solvents but hydrolyzes readily. It is used to prepare films of tantalum(V) oxide.

Aluminium acetylacetonate, also referred to as Al(acac)3, is a coordination complex with formula Al(C5H7O2)3. This aluminium complex with three acetylacetone ligands is used in research on Al-containing materials. The molecule has D3 symmetry, being isomorphous with other octahedral tris(acetylacetonate)s.
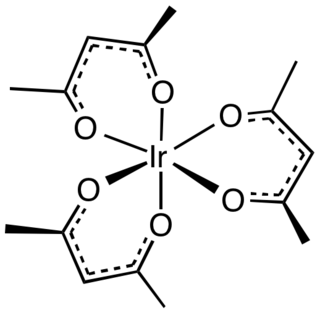
Iridium acetylacetonate is the iridium coordination complex with the formula Ir(O2C5H7)3, which is sometimes known as Ir(acac)3. The molecule has D3-symmetry. It is a yellow-orange solid that is soluble in organic solvents.
Copper(II) chlorate is a chemical compound of the transition metal copper and the chlorate anion with basic formula Cu(ClO3)2. Copper chlorate is an oxidiser. It commonly forms the tetrahydrate, Cu(ClO3)2·4H2O.
The +4 oxidation state dominates titanium chemistry, but compounds in the +3 oxidation state are also numerous. Commonly, titanium adopts an octahedral coordination geometry in its complexes, but tetrahedral TiCl4 is a notable exception. Because of its high oxidation state, titanium(IV) compounds exhibit a high degree of covalent bonding.