
Eosinophils, sometimes called eosinophiles or, less commonly, acidophils, are a variety of white blood cells and one of the immune system components responsible for combating multicellular parasites and certain infections in vertebrates. Along with mast cells and basophils, they also control mechanisms associated with allergy and asthma. They are granulocytes that develop during hematopoiesis in the bone marrow before migrating into blood, after which they are terminally differentiated and do not multiply. They form about 2 to 3% of white blood cells in the body.
Platelet-activating factor, also known as PAF, PAF-acether or AGEPC (acetyl-glyceryl-ether-phosphorylcholine), is a potent phospholipid activator and mediator of many leukocyte functions, platelet aggregation and degranulation, inflammation, and anaphylaxis. It is also involved in changes to vascular permeability, the oxidative burst, chemotaxis of leukocytes, as well as augmentation of arachidonic acid metabolism in phagocytes.
Interleukin 5 (IL-5) is an interleukin produced by type-2 T helper cells and mast cells.

Etizolam is a thienodiazepine derivative which is a benzodiazepine analog. The etizolam molecule differs from a benzodiazepine in that the benzene ring has been replaced by a thiophene ring and triazole ring has been fused, making the drug a thienotriazolodiazepine.

Rupatadine is a second generation antihistamine and platelet-activating factor antagonist used to treat allergies. It was discovered and developed by Uriach and is marketed as Rupafin and under several other trade names.

The platelet-activating factor receptor(PAF-R) is a G-protein coupled receptor which binds platelet-activating factor. It is encoded in the human by the PTAFR gene.

Platelet-derived growth factor receptor beta is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PDGFRB gene. Mutations in PDGFRB are mainly associated with the clonal eosinophilia class of malignancies.

Protease activated receptor 3 (PAR-3) also known as coagulation factor II receptor-like 2 (F2RL2) and thrombin receptor-like 2, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the F2RL2 gene.

Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(q) subunit alpha is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GNAQ gene. Together with GNA11, it functions as a Gq alpha subunit.

Ibudilast is an anti-inflammatory drug used mainly in Japan, which acts as a phosphodiesterase inhibitor, inhibiting the PDE4 subtype to the greatest extent, but also showing significant inhibition of other PDE subtypes.

Prostaglandin D2 receptor 2 (DP2 or CRTH2) is a human protein encoded by the PTGDR2 gene and GPR44. DP2 has also been designated as CD294 (cluster of differentiation 294). It is a member of the class of prostaglandin receptors which bind with and respond to various prostaglandins. DP2 along with Prostaglandin DP1 receptor are receptors for prostaglandin D2 (PGD2). Activation of DP2 by PGD2 or other cognate receptor ligands has been associated with certain physiological and pathological responses, particularly those associated with allergy and inflammation, in animal models and certain human diseases.

Cysteinyl leukotriene receptor 2, also termed CYSLTR2, is a receptor for cysteinyl leukotrienes (LT). CYSLTR2, by binding these cysteinyl LTs contributes to mediating various allergic and hypersensitivity reactions in humans. However, the first discovered receptor for these CsLTs, cysteinyl leukotriene receptor 1 (CysLTR1), appears to play the major role in mediating these reactions.
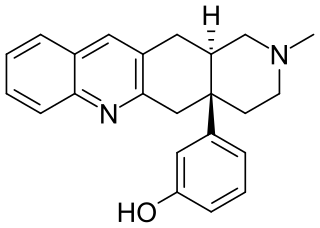
TAN-67 (SB-205,607) is an opioid drug used in scientific research that acts as a potent and selective δ-opioid agonist, selective for the δ1 subtype. It has analgesic properties and induces dopamine release in nucleus accumbens. It also protects both heart and brain tissue from hypoxic tissue damage through multiple mechanisms involving among others an interaction between δ receptors and mitochondrial K(ATP) channels.

Lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 (Lp-PLA2) also known as platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase (PAF-AH) is a phospholipase A2 enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PLA2G7 gene. Lp-PLA2 is a 45-kDa protein of 441 amino acids. It is one of several PAF acetylhydrolases.

DAA-1097 is a drug which acts as a potent and selective agonist at the peripheral benzodiazepine receptor, also known as the mitochondrial 18 kDa translocator protein or TSPO, but with no affinity at central benzodiazepine receptors. It has anxiolytic effects in animal studies.
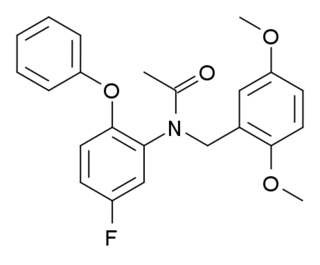
DAA-1106 is a drug which acts as a potent and selective agonist at the peripheral benzodiazepine receptor, also known as the mitochondrial 18 kDa translocator protein or TSPO, but with no affinity at the GABAA receptor. It has anxiolytic effects in animal studies. DAA-1106 has a sub-nanomolar binding affinity (Ki) of 0.28nM, and has been used extensively in its 3H or 11C radiolabelled form to map TSPO in the body and brain, which has proved especially helpful in monitoring the progress of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's disease.

5-Oxo-eicosatetraenoic acid is a Nonclassic eicosanoid metabolite of arachidonic acid and the most potent naturally occurring member of the 5-HETE family of cell signaling agents. Like other cell signaling agents, 5-oxo-ETE is made by a cell and then feeds back to stimulate its parent cell and/or exits this cell to stimulate nearby cells. 5-Oxo-ETE can stimulate various cell types particularly human leukocytes but possesses its highest potency and power in stimulating the human eosinophil type of leukocyte. It is therefore suggested to be formed during and to be an important contributor to the formation and progression of eosinophil-based allergic reactions; it is also suggested that 5-oxo-ETE contributes to the development of inflammation, cancer cell growth, and other pathological and physiological events.

A thienotriazolodiazepine is a heterocyclic compound containing a diazepine ring fused to thiophene and triazole rings. Thienotriazolodiazepine forms the central core of several pharmaceutical drugs including:

Clotizolam (Ro11-1465) is a thienotriazolodiazepine derivative first invented in the 1970s, which in more recent years has been sold as a designer drug. As with other related thienotriazolodiazepines, it produces sedative, anxiolytic, anticonvulsant and muscle relaxant effects, and also acts as an inhibitor of platelet-activating factor (PAF).

Apafant is a drug which acts as a potent and selective inhibitor of the phospholipid mediator platelet-activating factor (PAF). It was developed by structural modification of the thienotriazolodiazepine sedative drug brotizolam and demonstrated that PAF inhibitory actions could be separated from activity at the benzodiazepine receptor. Apafant was investigated for several applications involving inflammatory responses such as asthma and conjunctivitis but was never adopted for medical use, however it continues to be used in pharmacology research.


















