This article needs more medical references for verification or relies too heavily on primary sources .(September 2019) |
This is a list of types of inflammation in the body when organised by location.
This article needs more medical references for verification or relies too heavily on primary sources .(September 2019) |
This is a list of types of inflammation in the body when organised by location.
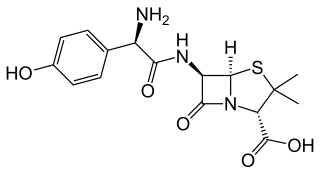
Amoxicillin is an antibiotic used to treat a number of bacterial infections. These include middle ear infection, strep throat, pneumonia, skin infections, and urinary tract infections among others. It is taken by mouth, or less commonly by injection.

Hepatitis is inflammation of the liver tissue. Some people or animals with hepatitis have no symptoms, whereas others develop yellow discoloration of the skin and whites of the eyes (jaundice), poor appetite, vomiting, tiredness, abdominal pain, and diarrhea. Hepatitis is acute if it resolves within six months, and chronic if it lasts longer than six months. Acute hepatitis can resolve on its own, progress to chronic hepatitis, or (rarely) result in acute liver failure. Chronic hepatitis may progress to scarring of the liver (cirrhosis), liver failure, and liver cancer.
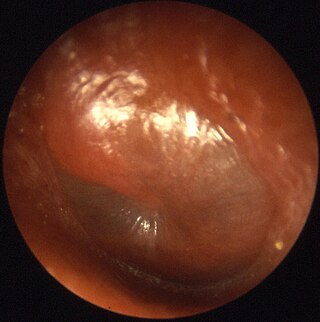
Otitis media is a group of inflammatory diseases of the middle ear. One of the two main types is acute otitis media (AOM), an infection of rapid onset that usually presents with ear pain. In young children this may result in pulling at the ear, increased crying, and poor sleep. Decreased eating and a fever may also be present. The other main type is otitis media with effusion (OME), typically not associated with symptoms, although occasionally a feeling of fullness is described; it is defined as the presence of non-infectious fluid in the middle ear which may persist for weeks or months often after an episode of acute otitis media. Chronic suppurative otitis media (CSOM) is middle ear inflammation that results in a perforated tympanic membrane with discharge from the ear for more than six weeks. It may be a complication of acute otitis media. Pain is rarely present. All three types of otitis media may be associated with hearing loss. If children with hearing loss due to OME do not learn sign language, it may affect their ability to learn.

Nephritis is inflammation of the kidneys and may involve the glomeruli, tubules, or interstitial tissue surrounding the glomeruli and tubules. It is one of several different types of nephropathy.

Lupus nephritis is an inflammation of the kidneys caused by systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), an autoimmune disease. It is a type of glomerulonephritis in which the glomeruli become inflamed. Since it is a result of SLE, this type of glomerulonephritis is said to be secondary, and has a different pattern and outcome from conditions with a primary cause originating in the kidney. The diagnosis of lupus nephritis depends on blood tests, urinalysis, X-rays, ultrasound scans of the kidneys, and a kidney biopsy. On urinalysis, a nephritic picture is found and red blood cell casts, red blood cells and proteinuria is found.

Ear pain, also known as earache, is pain in the ear. Primary ear pain is pain that originates from the ear. Secondary ear pain is a type of referred pain, meaning that the source of the pain differs from the location where the pain is felt.

Cefaclor, sold under the trade name Ceclor among others, is a second-generation cephalosporin antibiotic used to treat certain bacterial infections such as pneumonia and infections of the ear, lung, skin, throat, and urinary tract. It is also available from other manufacturers as a generic.

Otitis is a general term for inflammation or infection of the ear, in both humans and other animals. When infection is present, it may be viral or bacterial. When inflammation is present due to fluid build up in the middle ear and infection is not present it is considered Otitis media with effusion. It is subdivided into the following:
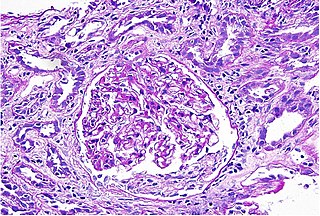
Interstitial nephritis, also known as tubulointerstitial nephritis, is inflammation of the area of the kidney known as the renal interstitium, which consists of a collection of cells, extracellular matrix, and fluid surrounding the renal tubules. In addition to providing a scaffolding support for the tubular architecture, the interstitium has been shown to participate in the fluid and electrolyte exchange as well as endocrine functions of the kidney.

Astroviruses are a type of virus that was first discovered in 1975 using electron microscopes following an outbreak of diarrhea in humans. In addition to humans, astroviruses have now been isolated from numerous mammalian animal species and from avian species such as ducks, chickens, and turkey poults. Astroviruses are 28–35 nm diameter, icosahedral viruses that have a characteristic five- or six-pointed star-like surface structure when viewed by electron microscopy. Along with the Picornaviridae and the Caliciviridae, the Astroviridae comprise a third family of nonenveloped viruses whose genome is composed of plus-sense, single-stranded RNA. Astrovirus has a non-segmented, single stranded, positive sense RNA genome within a non-enveloped icosahedral capsid. Human astroviruses have been shown in numerous studies to be an important cause of gastroenteritis in young children worldwide. In animals, Astroviruses also cause infection of the gastrointestinal tract but may also result in encephalitis, hepatitis (avian) and nephritis (avian).

Cambuquira is a Brazilian municipality in the State of Minas Gerais, Brazil. It has approximately 12,812 inhabitants, and the city is part of the Circuito das Águas of Minas Gerais.
Urhobo is a South-Western Edoid language spoken by the Urhobo people of southern Nigeria.
Cerebral vasculitis is vasculitis involving the brain and occasionally the spinal cord. It affects all of the vessels: very small blood vessels (capillaries), medium-size blood vessels, or large blood vessels. If blood flow in a vessel with vasculitis is reduced or stopped, the parts of the body that receive blood from that vessel begins to die. It may produce a wide range of neurological symptoms, such as headache, skin rashes, feeling very tired, joint pains, difficulty moving or coordinating part of the body, changes in sensation, and alterations in perception, thought or behavior, as well as the phenomena of a mass lesion in the brain leading to coma and herniation. Some of its signs and symptoms may resemble multiple sclerosis. 10% have associated bleeding in the brain.

Otitis externa, also called swimmer's ear, is inflammation of the ear canal. It often presents with ear pain, swelling of the ear canal, and occasionally decreased hearing. Typically there is pain with movement of the outer ear. A high fever is typically not present except in severe cases.

Government Nizamia General Hospital popularly known as Government Unani Hospital is a public hospital located in Hyderabad, Telangana, India. It is a hospital for general medicine and Unani medicine. It was established during the reign of Nizams. It is located near the historic building of Charminar.
Ianalumab is a monoclonal antibody that is being investigated for autoimmune hepatitis, multiple sclerosis, pemphigus vulgaris, rheumatoid arthritis, Sjogren's syndrome, and systemic lupus erythematosus.

Astroviridae is a family of non-enveloped ssRNA viruses that cause infections in different animals. The family name is derived from the Greek word astron ("star") referring to the star-like appearance of spikes projecting from the surface of these small unenveloped viruses. Astroviruses were initially identified in humans but have since been isolated from other mammals and birds. This family of viruses consists of two genera, Avastrovirus (AAstV) and Mamastrovirus (MAstV). Astroviruses most frequently cause infection of the gastrointestinal tract but in some animals they may result in encephalitis, hepatitis (avian) and nephritis (avian).