A tornado is a violently rotating column of air that is in contact with both the surface of the Earth and a cumulonimbus cloud or, in rare cases, the base of a cumulus cloud. It is often referred to as a twister, whirlwind or cyclone, although the word cyclone is used in meteorology to name a weather system with a low-pressure area in the center around which, from an observer looking down toward the surface of the Earth, winds blow counterclockwise in the Northern Hemisphere and clockwise in the Southern. Tornadoes come in many shapes and sizes, and they are often visible in the form of a condensation funnel originating from the base of a cumulonimbus cloud, with a cloud of rotating debris and dust beneath it. Most tornadoes have wind speeds less than 180 kilometers per hour, are about 80 meters across, and travel several kilometers before dissipating. The most extreme tornadoes can attain wind speeds of more than 480 kilometers per hour (300 mph), are more than 3 kilometers (2 mi) in diameter, and stay on the ground for more than 100 km (62 mi).

St. Croix County is a county in the U.S. state of Wisconsin. As of the 2020 census, the population was 93,536. Its county seat is Hudson. The county was created in 1840 and organized in 1849. St. Croix County is part of the Minneapolis-St. Paul-Bloomington, MN-WI Metropolitan Statistical Area. Between 2000 and 2010, it was the fastest-growing county in Wisconsin.

Adel is a city in and the county seat of Cook County, Georgia, United States, located fifty-two miles (84 km) southeast of Albany. As of the 2020 census, the city had a population of 5,571.

Delhi, originally called Deerfield, is a town in Richland Parish, Louisiana, United States. As of the 2020 census, the town population was 2,622.

La Plata is a town in Charles County, Maryland, United States. The population was 10,159 at the 2020 census. It is the county seat of Charles County.

Lancaster is a city in Dallas County, Texas, United States. Its population was 41,275 according to the 2020 census. Founded in 1852 as a frontier post, Lancaster is one of Dallas County's earliest settlements. Today, it is a suburban community located in the Dallas–Fort Worth metroplex, about 15 mi (24 km) south of downtown Dallas.

On March 18, 1925, one of the deadliest tornado outbreaks in recorded history generated at least twelve significant tornadoes and spanned a large portion of the midwestern and southern United States. In all, at least 751 people were killed and more than 2,298 were injured, making the outbreak the deadliest tornado outbreak, March 18 the deadliest tornado day, and 1925 the deadliest tornado year in U.S. history. The outbreak generated several destructive tornadoes in Missouri, Illinois, and Indiana on the same day, as well as significant tornadoes in Alabama and Kansas. In addition to confirmed tornadoes, there were undoubtedly others with lesser impacts, the occurrences of which have been lost to history.

The 1974 Super Outbreak was the second-largest tornado outbreak on record for a single 24-hour period, just behind the 2011 Super Outbreak. It was also the most violent tornado outbreak ever recorded, with 30 F4/F5 tornadoes confirmed. From April 3–4, 1974, there were 148 tornadoes confirmed in 13 U.S. states and the Canadian province of Ontario. In the United States, tornadoes struck Illinois, Indiana, Michigan, Ohio, Kentucky, Tennessee, Alabama, Mississippi, Georgia, North Carolina, Virginia, West Virginia, and New York. The outbreak caused roughly $843 million USD in damage, with more than $600 million occurring in the United States. The outbreak extensively damaged approximately 900 sq mi (2,331 km2) along a total combined path length of 2,600 mi (4,184 km). At one point, as many as 15 separate tornadoes were occurring simultaneously.
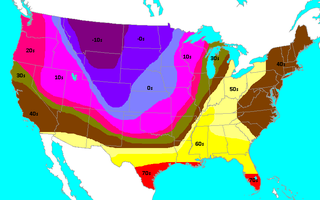
On Saturday, November 11, 1911, a cold snap, known as the Great Blue Norther or 11/11/11, affected the Central United States. Many cities broke record highs, going into the 70s and 80s early that afternoon. By nightfall, cities were dealing with temperatures in the teens and single-digits on the Fahrenheit scale. This is the only day in many midwest cities' weather bureau jurisdictions where the record highs and lows were broken for the same day. Some cities experienced tornadoes on Saturday and a blizzard on Sunday. A blizzard even occurred within one hour after an F4 tornado hit Rock County, Wisconsin.

Tornado Alley is a loosely defined location of the central United States and Canada where tornadoes are most frequent. The term was first used in 1952 as the title of a research project to study severe weather in areas of Texas, Louisiana, Oklahoma, Kansas, South Dakota, Iowa and Nebraska. Tornado climatologists distinguish peaks in activity in certain areas and storm chasers have long recognized the Great Plains tornado belt.

The 1993 Storm of the Century was a cyclonic storm that formed over the Gulf of Mexico on March 12, 1993. The cold weather, heavy snowfall, high winds and storm surges that the storm brought affected a very large area; at its height, it stretched from Canada to Honduras. The cyclone moved through the Gulf of Mexico and then through the eastern United States before moving on to eastern Canada. It eventually dissipated in the North Atlantic Ocean on March 15.
The Tornado outbreak of June 1881 was a tornado outbreak that occurred on June 11–12, 1881. It affected the West North Central States of the Midwestern United States and produced numerous strong tornadoes, killing at least 20 people, primarily in parts of Kansas and Missouri. One of the strongest tornadoes in the outbreak was an F4—possibly an F5—that hit near Hopkins, Missouri, in Nodaway County. In all, the outbreak killed at least 20 people and injured at least 141.
On February 19–20, 1884, one of the largest and most widespread tornado outbreaks in American history occurred over the Southeastern United States, known as the Enigma tornado outbreak due to the uncertain number of total tornadoes and fatalities. Nonetheless, an inspection of newspaper reports and governmental studies published in the aftermath reveals successive, long-tracked tornado families striking Alabama, Georgia, Illinois, Indiana, Kentucky, Mississippi, North Carolina, South Carolina, Tennessee and Virginia, with an estimation of at least 52—and possibly 60 or more—tornadoes.
On April 23–25, 1908, a destructive tornado outbreak affected portions of the Midwestern and Southern United States, including the Great Plains. The outbreak produced at least 31 tornadoes in 13 states, with a total of at least 324 tornado-related deaths. Of these deaths, most were caused by three long-tracked, violent tornadoes—each rated F4 on the Fujita scale and considered to be a tornado family—that occurred on April 24. Most of the deaths were in rural areas, often consisted of African Americans, and consequently may have been undercounted. One of the tornadoes killed 143 people along its path, 73 of them in the U.S. state of Mississippi, making the tornado the third deadliest in Mississippi history, following the 1936 Tupelo F5, with 216 deaths, and the 1840 Natchez tornado, with 317 deaths.
On March 16–17, 1942, a deadly late-winter tornado outbreak struck a large area of the Central and Southern United States. The tornado outbreak killed 149 people and injured at least 1,312. At least five states reported violent tornadoes, from Illinois and Indiana south to Mississippi, beginning with an F4 tornado in the morning in Illinois. Intense activity spread south to the Gulf Coast and north to the Michigan–Indiana border as the day went on. Seven violent tornadoes were reported, one of which was a powerful F5 in Illinois. A long-tracked F4 tornado family in Mississippi claimed 63 lives as well, becoming the deadliest tornado of the outbreak. Another long-lived F4 in Tennessee killed 15 more people, and a series of intense tornadoes caused 23 other deaths in Kentucky. The outbreak also produced 18 tornadoes that caused at least one death, one of the highest such totals for a single outbreak.

The 2010 New Year's Eve tornado outbreak was a three-day-long tornado outbreak that impacted the central and lower Mississippi Valley from December 30, 2010 to January 1, 2011. Associated with a low pressure system and a strong cold front, 37 tornadoes tracked across five states over the length of the severe event, killing nine and injuring several others. Activity was centered in the states of Missouri and later Mississippi on December 31. Seven tornadoes were rated EF3 on the Enhanced Fujita Scale; these were the strongest during the outbreak. Non-tornadic winds were recorded to have reached as high as 80 mph (130 km/h) at eight locations on December 31, while hail as large as 2.75 in (7.0 cm) was documented north-northeast of Mansfield, Missouri. Overall, damage from the outbreak totaled US$123.3 million, most of which was related to tornadoes. This is the most prolific tornado outbreak in Missouri in the month of December.

The tornado outbreak of June 16–18, 2014, was a tornado outbreak concentrated in the Great Plains and the Midwestern United States. Two tornadoes also occurred in Ontario. The severe weather event most significantly affected the state of Nebraska, where twin EF4 tornadoes killed two and critically injured twenty others in and around the town of Pilger on the evening of June 16. The two Pilger tornadoes were part of a violent tornado family that produced four EF4 tornadoes and was broadcast live on television. The outbreak went on to produce multiple other strong tornadoes across the northern Great Plains states throughout the next two days.
On November 7–8, 1957, a significant tornado outbreak affected portions of the Southern United States, particularly the Golden Triangle of Southeast Texas and parts of Acadiana in Louisiana. The severe weather event inflicted 12 deaths and more than 200 injuries, especially in the vicinity of Beaumont and Port Arthur, Texas. The most intense tornado of the outbreak, retrospectively rated F4 on the Fujita scale, struck the town of Orange, Texas, killing one person, injuring 81 others, and causing $11⁄2 million in losses. The deadliest tornado of the outbreak was an F3 that killed four people northwest of Carencro, Louisiana. The costliest tornado of the outbreak, also rated F3, caused $2.3 million in losses in the town of Groves, Texas, killing a few people there. Other intense tornadoes occurred as far east as Mississippi and North Carolina. In all, at least 28 tornadoes were confirmed, yet others were likely present as well.
Several destructive tornadoes struck the Southeastern United States, primarily along and east of the Lower Mississippi Valley, on February 13, 1952. Multiple intense tornadoes touched down throughout the day, three of which were killers. The deadliest and most destructive tornado of the outbreak was a violent F4 that touched down in south-central Tennessee, killing three people and injuring 44 others. A similarly destructive tornado—albeit of weaker, F2 intensity—formed from the same storm as the preceding F4 and became the second costliest of the outbreak. Another intense tornado affected the Mississippi embayment near Manila, Arkansas, injuring five people, and a pair of deadly F3s in Alabama claimed a combined two lives. In all, the outbreak killed five people and injured 102 others.