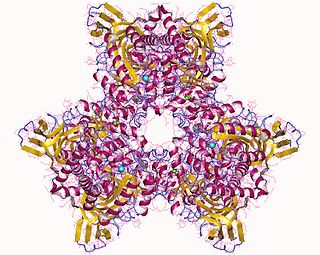
Atrazine Chlorohydrolase (AtzA) is an enzyme (E.C.3.8.1.8), which catalyzes the conversion of atrazine to hydroxyatrazine. Bacterial degradation determines the environmental impact and efficacy of an herbicide or pesticide. Initially, most pesticides are highly effective and show minimal bacterial degradation; however, bacteria can rapidly evolve and gain the ability to metabolize potential nutrients in the environment. Despite a remarkable structural similarity, degradation of atrazine by bacteria capable of melamine degradation was rare; however, since its introduction as a pesticide in the United States, bacteria capable of atrazine degradation have evolved. Currently, Pseudomonas sp. strain ADP seems to be the optimal bacterial strain for atrazine degradations, which appears to be the sole nitrogen source for the bacteria.
The crotonase family comprises mechanistically diverse proteins that share a conserved trimeric quaternary structure, the core of which consists of 4 turns of a (beta/beta/alpha)n superhelix.
In enzymology, a galactose 1-dehydrogenase (NADP+) (EC 1.1.1.120) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a 5,6-dihydroxy-3-methyl-2-oxo-1,2,5,6-tetrahydroquinoline dehydrogenase (EC 1.3.1.65) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a quinaldate 4-oxidoreductase (EC 1.3.99.18) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a quinoline 2-oxidoreductase (EC 1.3.99.17) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a 2-chlorobenzoate 1,2-dioxygenase (EC 1.14.12.13) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a 4-hydroxyquinoline 3-monooxygenase (EC 1.14.13.62) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, juglone 3-monooxygenase (EC 1.14.99.27) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
Chloridazon-catechol dioxygenase (EC 1.13.11.36) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a 4-chlorobenzoate dehalogenase (EC 3.8.1.6) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
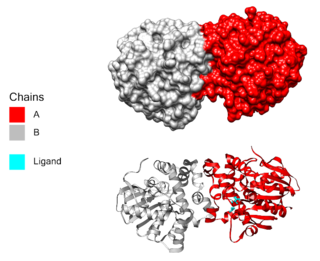
In enzymology, a haloacetate dehalogenase (EC 3.8.1.3) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
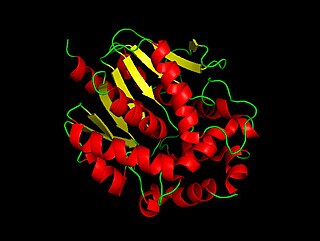
In enzymology, a haloalkane dehalogenase (EC 3.8.1.5) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a (R)-2-haloacid dehalogenase(EC 3.8.1.9), DL-2-haloacid halidohydrolase (inversion of configuration), DL-DEXi, (R,S)-2-haloacid dehalogenase (configuration-inverting)) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a 4-chlorobenzoate—CoA ligase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an ubiquitin-calmodulin ligase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme poly(3-hydroxyoctanoate) depolymerase (EC 3.1.1.76) catalyzes the hydrolysis of the polyester poly{oxycarbonyl[(R)-2-pentylethylene] to oligomers
2-haloacid dehalogenase (configuration-inverting) (EC 3.8.1.10, 2-haloalkanoic acid dehalogenase, 2-haloalkanoid acid halidohydrolase, DL-2-haloacid dehalogenase, DL-2-haloacid dehalogenase (inversion of configuration), DL-2-haloacid halidohydrolase (inversion of configuration), DL-DEXi, (R,S)-2-haloacid dehalogenase (configuration-inverting)) is an enzyme with systematic name (S)-2-haloacid dehalogenase (configuration-inverting). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
2-haloacid dehalogenase (configuration-retaining) (EC 3.8.1.11, 2-haloalkanoic acid dehalogenase, 2-haloalkanoid acid halidohydrolase, DL-2-haloacid dehalogenase, DL-DEXr) is an enzyme with systematic name (S)-2-haloacid dehalogenase (configuration-retaining). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Adsorbable organic halides (AOX) is a measure of the organic halogen load at a sampling site such as soil from a land fill, water, or sewage waste. The procedure measures chlorine, bromine, and iodine as equivalent halogens, but does not measure fluorine levels in the sample.



