
In organic chemistry, a diene ; also diolefin, dy-OH-lə-fin) or alkadiene) is a covalent compound that contains two double bonds, usually among carbon atoms. They thus contain two alkene units, with the standard prefix di of systematic nomenclature. As a subunit of more complex molecules, dienes occur in naturally occurring and synthetic chemicals and are used in organic synthesis. Conjugated dienes are widely used as monomers in the polymer industry. Polyunsaturated fats are of interest to nutrition.
The Cope rearrangement is an extensively studied organic reaction involving the [3,3]-sigmatropic rearrangement of 1,5-dienes. It was developed by Arthur C. Cope and Elizabeth Hardy. For example, 3-methyl-hexa-1,5-diene heated to 300 °C yields hepta-1,5-diene.
Organopalladium chemistry is a branch of organometallic chemistry that deals with organic palladium compounds and their reactions. Palladium is often used as a catalyst in the reduction of alkenes and alkynes with hydrogen. This process involves the formation of a palladium-carbon covalent bond. Palladium is also prominent in carbon-carbon coupling reactions, as demonstrated in tandem reactions.
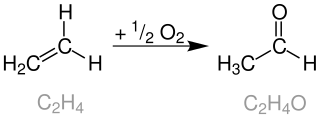
The Wacker process or the Hoechst-Wacker process refers to the oxidation of ethylene to acetaldehyde in the presence of palladium(II) chloride and copper(II) chloride as the catalyst. This chemical reaction was one of the first homogeneous catalysis with organopalladium chemistry applied on an industrial scale.

A cyclooctadiene (sometimes abbreviated COD) is any of several cyclic diene with the formula (CH2)4(C2H2)2. Focusing only on cis derivatives, four isomers are possible: 1,2-, which is an allene, 1,3-, 1,4-, and 1,5-. Commonly encountered isomers are the conjugated isomer 1,3-cyclooctadiene and 1,5-cyclooctadiene, which is used as a ligand for transition metals. These dienes are colorless volatile liquids.
Cycloocta-1,5-diene is a cyclic hydrocarbon with the chemical formula C8H12, specifically [−(CH2)2−CH=CH−]2.

Platinum(II) chloride is the chemical compound PtCl2. It is an important precursor used in the preparation of other platinum compounds. It exists in two crystalline forms, but the main properties are somewhat similar: dark brown, insoluble in water, diamagnetic, and odorless.
Acyclic diene metathesis or 'ADMET' is a special type of olefin metathesis used to polymerize terminal dienes to polyenes:
In organic chemistry, the di-π-methane rearrangement is the photochemical rearrangement of a molecule that contains two π-systems separated by a saturated carbon atom. In the aliphatic case, this molecules is a 1,4-diene; in the aromatic case, an allyl-substituted arene. The reaction forms (respectively) an ene- or aryl-substituted cyclopropane. Formally, it amounts to a 1,2 shift of one ene group or the aryl group, followed by bond formation between the lateral carbons of the non-migrating moiety:

Larry E. Overman is Distinguished Professor of Chemistry at the University of California, Irvine. He was born in Chicago in 1943. Overman obtained a B.A. degree from Earlham College in 1965, and he completed his Ph.D. in chemistry from the University of Wisconsin–Madison in 1969, under Howard Whitlock Jr. Professor Overman is a member of the United States National Academy of Sciences and the American Academy of Arts and Sciences. He was the recipient of the Arthur C. Cope Award in 2003, and he was awarded the Tetrahedron Prize for Creativity in Organic Chemistry for 2008.
In enzymology, a (3S,4R)-3,4-dihydroxycyclohexa-1,5-diene-1,4-dicarboxylate dehydrogenase (EC 1.3.1.53) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
1,5-Pentanediol is the organic compound with the formula HO(CH2)5OH. Like other diols, this viscous colourless liquid is used as plasticizer and also forms polyesters that are used as emulsifying agents and resin intermediates.

Atamestane, also known as metandroden, as well as 1-methylandrosta-1,4-diene-3,17-dione, is a steroidal aromatase inhibitor that was studied in the treatment of cancer. It blocks the production of estrogen in the body. The drug is selective, competitive, and irreversible in its inhibition of aromatase.

Basketane is a polycyclic alkane with the chemical formula C10H12. The name is taken from its structural similarity to a basket shape. Basketane was first synthesized in 1966, independently by Masamune and Dauben and Whalen. A patent application published in 1988 used basketane, which is a hydrocarbon, as a source material in doping thin diamond layers because of the molecule's high vapor pressure, carbon ring structure, and fewer hydrogen-to-carbon bond ratio.
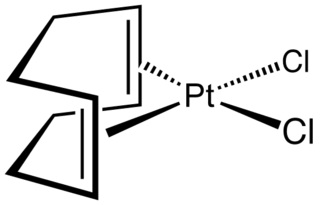
Dichloro(1,5-cyclooctadiene)platinum(II) (Pt(cod)Cl2) is an organometallic compound of platinum. This colourless solid is an entry point to other platinum compounds through the displacement of the cod and/or chloride ligands. It is one of several complexes of cycloocta-1,5-diene.

Organocobalt chemistry is the chemistry of organometallic compounds containing a carbon to cobalt chemical bond. Organocobalt compounds are involved in several organic reactions and the important biomolecule vitamin B12 has a cobalt-carbon bond. Many organocobalt compounds exhibit useful catalytic properties, the preeminent example being dicobalt octacarbonyl.
Organoplatinum chemistry is the chemistry of organometallic compounds containing a carbon to platinum chemical bond, and the study of platinum as a catalyst in organic reactions. Organoplatinum compounds exist in oxidation state 0 to IV, with oxidation state II most abundant. The general order in bond strength is Pt-C (sp) > Pt-O > Pt-N > Pt-C (sp3). Organoplatinum and organopalladium chemistry are similar, but organoplatinum compounds are more stable and therefore less useful as catalysts.
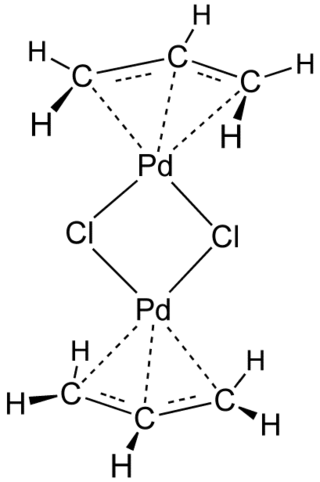
Transition-metal allyl complexes are coordination complexes with allyl and its derivatives as ligands. Allyl is the radical with the connectivity CH2CHCH2, although as a ligand it is usually viewed as an allyl anion CH2=CH−CH2−, which is usually described as two equivalent resonance structures.

Dichloro(1,5-cyclooctadiene)palladium is the organopalladium compound with the formula PdCl2(C8H12) where C8H12 is cycloocta-1,5-diene (cod) or abbreviated PdCl2(cod). It is a yellow solid that is soluble in chloroform. According to X-ray crystallography, the Pd center is square planar. This complex can be synthesized by reaction of tetrachloropalladate in hydrochloric acid with cycloocta-1,5-diene.

Stibinin, also known as stibabenzene, is an organic chemical compound. Stibinin has the chemical formula C5H5Sb. The molecule, stibinin, is a derivative of benzene, with one of the carbon atoms in the 6-membered ring replaced by an antimony (Sb) atom. Stibinin is a molecule that is considered to be an organoantimony compound due to it containing carbon, hydrogen, and antimony atoms.















