 | |
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name N,N,N′,N′-Tetramethylguanidine | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) | |
| 969608 | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.185 |
| EC Number |
|
| MeSH | 1,1,3,3-tetramethylguanidine |
PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| UN number | 2920 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C5H13N3 | |
| Molar mass | 115.180 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colourless liquid |
| Density | 918 mg mL−1 |
| Melting point | −30 °C (−22 °F; 243 K) |
| Boiling point | 160 to 162 °C (320 to 324 °F; 433 to 435 K) |
| Miscible | |
| Vapor pressure | 30 Pa (at 20 °C) |
| Acidity (pKa) | 13.0±1.0 [1] (pKa of conjugate acid in water) |
Refractive index (nD) | 1.469 |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
   | |
| Danger | |
| H226, H302, H314 | |
| P280, P305+P351+P338, P310 | |
| Flash point | 60 °C (140 °F; 333 K) |
| Explosive limits | 1–7.5% |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
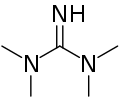
Tetramethylguanidine is an organic compound with the formula HNC(N(CH3)2)2. This colourless liquid is a strong base, as judged by the high pKa of its conjugate acid. [2]
It was originally prepared from tetramethylthiourea via S-methylation and amination, but alternative methods start from cyanogen iodide. [3]