In organic chemistry, a ketone is an organic compound with the structure R−C(=O)−R', where R and R' can be a variety of carbon-containing substituents. Ketones contain a carbonyl group −C(=O)−. The simplest ketone is acetone, with the formula (CH3)2CO. Many ketones are of great importance in biology and in industry. Examples include many sugars (ketoses), many steroids, and the solvent acetone.

In organic chemistry, a dicarbonyl is a molecule containing two carbonyl groups. Although this term could refer to any organic compound containing two carbonyl groups, it is used more specifically to describe molecules in which both carbonyls are in close enough proximity that their reactivity is changed, such as 1,2-, 1,3-, and 1,4-dicarbonyls. Their properties often differ from those of monocarbonyls, and so they are usually considered functional groups of their own. These compounds can have symmetrical or unsymmetrical substituents on each carbonyl, and may also be functionally symmetrical or unsymmetrical.

In organic chemistry, alkenols are a type of reactive structure or intermediate in organic chemistry that is represented as an alkene (olefin) with a hydroxyl group attached to one end of the alkene double bond. The terms enol and alkenol are portmanteaus deriving from "-ene"/"alkene" and the "-ol" suffix indicating the hydroxyl group of alcohols, dropping the terminal "-e" of the first term. Generation of enols often involves deprotonation at the α position to the carbonyl group—i.e., removal of the hydrogen atom there as a proton H+. When this proton is not returned at the end of the stepwise process, the result is an anion termed an enolate. The enolate structures shown are schematic; a more modern representation considers the molecular orbitals that are formed and occupied by electrons in the enolate. Similarly, generation of the enol often is accompanied by "trapping" or masking of the hydroxy group as an ether, such as a silyl enol ether.

Acetylacetone is an organic compound with the chemical formula CH3−C(=O)−CH2−C(=O)−CH3. It is classified as a 1,3-diketone. It exists in equilibrium with a tautomer CH3−C(=O)−CH=C(−OH)−CH3. The mixture is a colorless liquid. These tautomers interconvert so rapidly under most conditions that they are treated as a single compound in most applications. Acetylacetone is a building block for the synthesis of many coordination complexes as well as heterocyclic compounds.

Selenium dioxide is the chemical compound with the formula SeO2. This colorless solid is one of the most frequently encountered compounds of selenium.
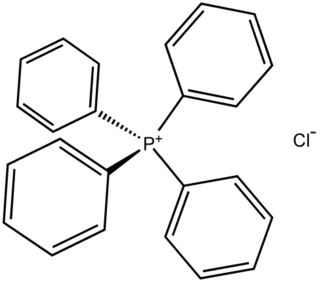
Tetraphenylphosphonium chloride is the chemical compound with the formula [(C6H5)4P]Cl, abbreviated Ph4PCl or PPh4Cl or [PPh4]Cl, where Ph stands for phenyl. Tetraphenylphosphonium and especially tetraphenylarsonium salts were formerly of interest in gravimetric analysis of perchlorate and related oxyanions. This colourless salt is used to generate lipophilic salts from inorganic and organometallic anions. Thus, [Ph4P]+ is useful as a phase-transfer catalyst, again because it allows inorganic anions to dissolve in organic solvents.

1,3-Dimethyl-2-imidazolidinone (DMI) is a cyclic urea used as a high-boiling polar aprotic solvent. It is colourless, highly polar solvent has high thermal and chemical stability. It is a homolog of the related solvent DMPU. It can be prepared from 1,2-dimethylethylenediamine by reaction with phosgene.
Dimedone is an organic compound with the formula (CH3)2C(CH2)2(CO)2(CH2). Classified as a cyclic diketone, it is a derivative of 1,3-cyclohexanedione. It is a white solid that is soluble in water, as well as ethanol and methanol. It once was used as a reagent to test for the aldehyde functional group.

Cyclohexenone is an organic compound which is a versatile intermediate used in the synthesis of a variety of chemical products such as pharmaceuticals and fragrances. It is colorless liquid, but commercial samples are often yellow.
1,4-Cyclohexanedione is an organic compound with the formula (CH2)4(CO)2. This white solid is one of the three isomeric cyclohexanediones. This particular diketone is used as a building block in the synthesis of more complex molecules.
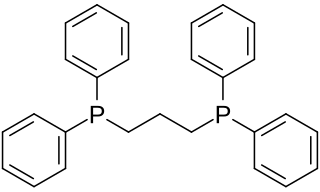
1,3-Bis(diphenylphosphino)propane (dppp) is an organophosphorus compound with the formula Ph2P(CH2)3PPh2. The compound is a white solid that is soluble in organic solvents. It is slightly air-sensitive, degrading in air to the phosphine oxide. It is classified as a diphosphine ligand in coordination chemistry and homogeneous catalysis.
1,2-Difluorobenzene, also known as DFB, is an aromatic compound with formula C6H4F2. This colorless flammable liquid is a solvent used in the electrochemical studies of transition metal complexes. Compared to most conventional halogenated aliphatic and aromatic solvents, it possesses an exceptionally high dielectric constant (ε0 = 13.8 at 300 K). Thus, it can be a suitable solvent for cationic, and/or highly electrophilic organometallic complexes.

Dichloro[1,3-bis(diphenylphosphino)propane]nickel a coordination complex with the formula NiCl2(dppp); where dppp is the diphosphine 1,3-bis(diphenylphosphino)propane. It is used as a catalyst in organic synthesis. The compound is a bright orange-red crystalline powder.

1,2-Diiodoethane is an organoiodine compound.

2-Hydroxy-3-methyl-2-cyclopenten-1-one is an organic compound related to 1,2-cyclopentanedione. It is the enol tautomer of the diketone 3-methylcyclopentane-1,2-dione. Being an enol, the compound is often called methylcyclopentenolone. It is a colorless solid.
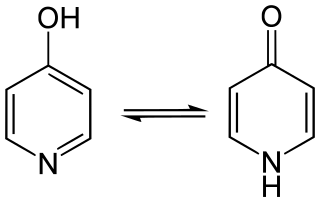
4-Pyridone is an organic compound with the formula C
5H
4NH(O). It is a colorless solid.

1,3-Cyclohexanedione is an organic compound with the formula (CH2)4(CO)2. It is one of three isomeric cyclohexanediones. It is a colorless compound that occurs naturally. It is the substrate for cyclohexanedione hydrolase. The compound exists mainly as the enol tautomer.

Diethylsuccinoylsuccinate is an organic compound with the formula [CH2C(OH)=C(CO2Et)]2 (Et = ethyl). A tetrasubstituted derivative of 1,4-cyclohexadiene, the compound is the enol tautomer of the corresponding cyclohexadione. It is produced by base-induced condensation of diethyl succinate:

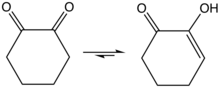
1,2-Cyclopentanedione is the organic compound with the formula (CH2)3(CO)2. It is one of two isomeric cyclopentanediones, the other being 1,3-cyclopentanedione. It was first prepared by base-induced condensation of di ethylglutarate with diethyloxalate, followed by hydrolysis of the resulting diketodiester followed by decarboxylation. The enol is predicted to be about 1-3 kcal/mol more stable than the diketo form. The enol structure has been confirmed by X-ray crystallography.
1,3-Cyclopentanedione is an organic compound with the formula (CH2)3(CO)2. It is one of two isomeric cyclopentanediones, the other being 1,2-cyclopentanedione. The enol is predicted to be about 1-3 kcal/mol more stable than the diketo form. The enol structure has been confirmed by X-ray crystallography.