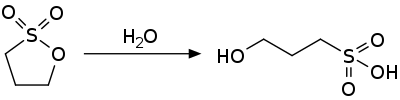
In organosulfur chemistry, a sulfonate is a salt or ester of a sulfonic acid. It contains the functional group R−S(=O)2−O−, where R is an organic group. Sulfonates are the conjugate bases of sulfonic acids. Sulfonates are generally stable in water, non-oxidizing, and colorless. Many useful compounds and even some biochemicals feature sulfonates.

Diazomethane is an organic chemical compound with the formula CH2N2, discovered by German chemist Hans von Pechmann in 1894. It is the simplest diazo compound. In the pure form at room temperature, it is an extremely sensitive explosive yellow gas; thus, it is almost universally used as a solution in diethyl ether. The compound is a popular methylating agent in the laboratory, but it is too hazardous to be employed on an industrial scale without special precautions. Use of diazomethane has been significantly reduced by the introduction of the safer and equivalent reagent trimethylsilyldiazomethane.

Acrylic acid (IUPAC: propenoic acid) is an organic compound with the formula CH2=CHCOOH. It is the simplest unsaturated carboxylic acid, consisting of a vinyl group connected directly to a carboxylic acid terminus. This colorless liquid has a characteristic acrid or tart smell. It is miscible with water, alcohols, ethers, and chloroform. More than a million tons are produced annually.
Cyclohexene is a hydrocarbon with the formula (CH2)4C2H2. It is a colorless liquid with a sharp odor. Although it is one of the simplest cycloalkene, it has few applications.
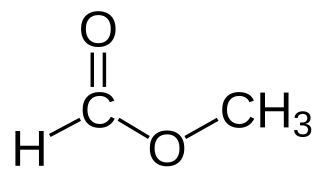
Methyl formate, also called methyl methanoate, is the methyl ester of formic acid. The simplest example of a carboxylate ester, it is a colorless liquid with an ethereal odour, high vapor pressure, and low surface tension. It is a precursor to many other compounds of commercial interest.

Ethyl acetate is the organic compound with the formula CH3CO2CH2CH3, simplified to C4H8O2. This colorless liquid has a characteristic sweet smell and is used in glues, nail polish removers, and in the decaffeination process of tea and coffee. Ethyl acetate is the ester of ethanol and acetic acid; it is manufactured on a large scale for use as a solvent.

Methyl methacrylate (MMA) is an organic compound with the formula CH2=C(CH3)COOCH3. This colorless liquid, the methyl ester of methacrylic acid (MAA), is a monomer produced on a large scale for the production of poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA).

Hexamethylphosphoramide, often abbreviated HMPA, is a phosphoramide (an amide of phosphoric acid) with the formula [(CH3)2N]3PO. This colorless liquid is a useful reagent in organic synthesis.

Maleic anhydride is an organic compound with the formula C2H2(CO)2O. It is the acid anhydride of maleic acid. It is a colorless or white solid with an acrid odor. It is produced industrially on a large scale for applications in coatings and polymers.
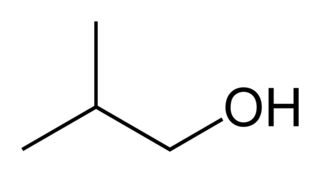
Isobutanol (IUPAC nomenclature: 2-methylpropan-1-ol) is an organic compound with the formula (CH3)2CHCH2OH (sometimes represented as i-BuOH). This colorless, flammable liquid with a characteristic smell is mainly used as a solvent either directly or as its esters. Its isomers are 1-butanol, 2-butanol, and tert-butanol, all of which are important industrially.
Benzyl chloride, or α-chlorotoluene, is an organic compound with the formula C6H5CH2Cl. This colorless liquid is a reactive organochlorine compound that is a widely used chemical building block.
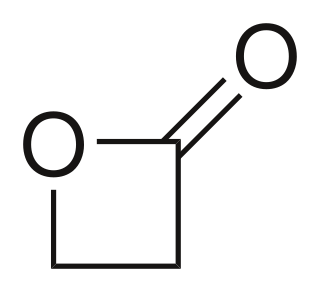
β-Propiolactone, often simply called propiolactone, is an organic compound with the formula CH2CH2CO2. It is a lactone family, with a four-membered ring. It is a colorless liquid with a slightly sweet odor, highly soluble in water and organic solvents. The carcinogenicity of this compound has limited its commercial applications.

Nitroethane is an organic compound having the chemical formula C2H5NO2. Similar in many regards to nitromethane, nitroethane is an oily liquid at standard temperature and pressure. Pure nitroethane is colorless and has a fruity odor.

Glycidol is an organic compound that contains both epoxide and alcohol functional groups. Being bifunctional, it has a variety of industrial uses. The compound is a slightly viscous liquid that is slightly unstable and is not often encountered in pure form.

Ethyl acrylate is an organic compound with the formula CH2CHCO2CH2CH3. It is the ethyl ester of acrylic acid. It is a colourless liquid with a characteristic acrid odor. It is mainly produced for paints, textiles, and non-woven fibers. It is also a reagent in the synthesis of various pharmaceutical intermediates.

1,3-Dichloropropene, sold under diverse trade names, is an organochlorine compound with the formula C3H4Cl2. It is a colorless liquid with a sweet smell. It is feebly soluble in water and evaporates easily. It is used mainly in farming as a pesticide, specifically as a preplant fumigant and nematicide. It is widely used in the US and other countries, but is banned in 34 countries.
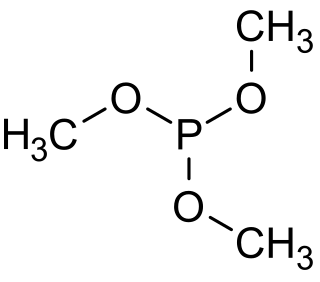
Trimethyl phosphite is an organophosphorus compound with the formula P(OCH3)3, often abbreviated P(OMe)3. It is a colorless liquid with a highly pungent odor. It is the simplest phosphite ester and finds used as a ligand in organometallic chemistry and as a reagent in organic synthesis. The molecule features a pyramidal phosphorus(III) center bound to three methoxy groups.

Chloroacetyl chloride is a chlorinated acyl chloride. It is a bifunctional compound, making it a useful building block chemical.
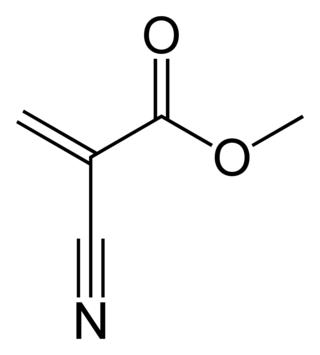
Methyl cyanoacrylate is an organic compound that contains several functional groups: a methyl ester, a nitrile, and an alkene. It is a colorless liquid with low viscosity. Its chief use is as the main component of cyanoacrylate glues. It can be encountered under many trade names. Methyl cyanoacrylate is less commonly encountered than ethyl cyanoacrylate.

Perchloromethyl mercaptan is the organosulfur compound with the formula CCl3SCl. It is mainly used as an intermediate for the synthesis of dyes and fungicides (captan, folpet). It is a colorless oil, although commercial samples are yellowish. It is insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents. It has a foul, unbearable, acrid odor. Perchloromethyl mercaptan is the original name. The systematic name is trichloromethanesulfenyl chloride, because the compound is a sulfenyl chloride, not a mercaptan.