
A carcinogen is any agent that promotes the development of cancer. Carcinogens can include synthetic chemicals, naturally occurring substances, physical agents such as ionizing and non-ionizing radiation, and biologic agents such as viruses and bacteria. Most carcinogens act by creating mutations in DNA that disrupt a cell's normal processes for regulating growth, leading to uncontrolled cellular proliferation. This occurs when the cell's DNA repair processes fail to identify DNA damage allowing the defect to be passed down to daughter cells. The damage accumulates over time. This is typically a multi-step process during which the regulatory mechanisms within the cell are gradually dismantled allowing for unchecked cellular division.

Roundup is a brand name of herbicide originally produced by Monsanto, which Bayer acquired in 2018. Prior to the late-2010s formulations, it used broad-spectrum glyphosate-based herbicides. As of 2009, sales of Roundup herbicides still represented about 10 percent of Monsanto's revenue despite competition from Chinese producers of other glyphosate-based herbicides. The overall Roundup line of products represented about half of Monsanto's yearly revenue in 2009. The product is marketed to consumers by Scotts Miracle-Gro Company. In the late-2010s other non-glyphosate containing herbicides were also sold under the Roundup brand.

Mothballs are small balls of chemical pesticide and deodorant, sometimes used when storing clothing and other materials susceptible to damage from silverfish, mold or moth larvae.

Glyphosate is a broad-spectrum systemic herbicide and crop desiccant. It is an organophosphorus compound, specifically a phosphonate, which acts by inhibiting the plant enzyme 5-enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthase (EPSP). It is used to kill weeds, especially annual broadleaf weeds and grasses that compete with crops. Its herbicidal effectiveness was discovered by Monsanto chemist John E. Franz in 1970. Monsanto brought it to market for agricultural use in 1974 under the trade name Roundup. Monsanto's last commercially relevant United States patent expired in 2000.

Ethyl carbamate (also called urethane) is an organic compound with the formula CH3CH2OC(O)NH2. It is an ester of carbamic acid and a white solid. Despite its name, it is not a component of polyurethanes. Because it is a carcinogen, it is rarely used, but naturally forms in low quantities in many types of fermented foods and drinks.

Nitrobenzene is an aromatic nitro compound and the simplest of the nitrobenzenes, with the chemical formula C6H5NO2. It is a water-insoluble pale yellow oil with an almond-like odor. It freezes to give greenish-yellow crystals. It is produced on a large scale from benzene as a precursor to aniline. In the laboratory, it is occasionally used as a solvent, especially for electrophilic reagents.

Chemical hazards are hazards present in hazardous chemicals and hazardous materials. Exposure to certain chemicals can cause acute or long-term adverse health effects. Chemical hazards are usually classified separately from biological hazards (biohazards). Chemical hazards are classified into groups that include asphyxiants, corrosives, irritants, sensitizers, carcinogens, mutagens, teratogens, reactants, and flammables. In the workplace, exposure to chemical hazards is a type of occupational hazard. The use of personal protective equipment may substantially reduce the risk of adverse health effects from contact with hazardous materials.
The International Agency for Research on Cancer is an intergovernmental agency forming part of the World Health Organization of the United Nations. Its role is to conduct and coordinate research into the causes of cancer. It also collects and publishes surveillance data regarding the occurrence of cancer worldwide.
IARC group 1 Carcinogens are substances, chemical mixtures, and exposure circumstances which have been classified as carcinogenic to humans by the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC). This category is used when there is sufficient evidence of carcinogenicity in humans. Exceptionally, an agent may be placed in this category when evidence of carcinogenicity in humans is less than sufficient, but when there is sufficient evidence of carcinogenicity in experimental animals and strong evidence in exposed humans that the agent (mixture) acts through a relevant mechanism of carcinogenicity.
IARC group 3 substances, chemical mixtures and exposure circumstances are those that can not be classified in regard to their carcinogenicity to humans by the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC). This category is used most commonly for agents, mixtures and exposure circumstances for which the level of evidence of carcinogenicity is inadequate in humans and inadequate or limited in experimental animals. Exceptionally, agents (mixtures) for which the evidence of carcinogenicity is inadequate in humans, but sufficient in experimental animals may be placed in this category when there is strong evidence that the mechanism of carcinogenicity in experimental animals does not operate in humans. Agents, mixtures and exposure circumstances that do not fall into any other group are also placed in this category.

Diethyl sulfate (DES) is an organosulfur compound with the formula (C2H5)2SO4. It occurs as a colorless, oily liquid with a faint peppermint odor. It is toxic, combustible, and likely carcinogenic chemical compound. Diethyl sulfate is used as an ethylating agent.
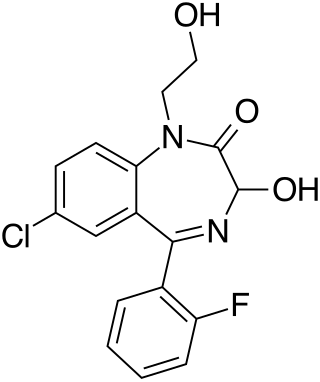
Doxefazepam is a benzodiazepine medication It possesses anxiolytic, anticonvulsant, sedative and skeletal muscle relaxant properties. It is used therapeutically as a hypnotic. According to Babbini and colleagues in 1975, this derivative of flurazepam was between 2 and 4 times more potent than the latter while at the same time being half as toxic in laboratory animals.
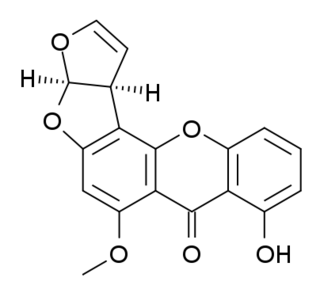
Sterigmatocystin is a polyketide mycotoxin produced by certain species of Aspergillus. The toxin is naturally found in some cheeses.

Dichlorprop is a chlorophenoxy herbicide similar in structure to 2,4-D that is used to kill annual and perennial broadleaf weeds. It is a component of many common weedkillers. About 4 million pounds of dichlorprop are used annually in the United States.
4,4′-Methylenebis(2-chloroaniline) is a substance used as a curing agent in polyurethane production. MOCA is an aromatic amine which is structurally similar to benzidine, a known human bladder carcinogen. MOCA has been shown to cause hepatomas in mice and rats, lung and mammary carcinomas in rats and bladder cancer in dogs. It is a proven human carcinogen standing on the WHO List of IARC Group 1 carcinogens, with a current threshold limit value of 0.01 ppm in the industrial atmosphere. Animal studies have resulted in tumor growth in the liver, lung, and bladder.
Cobalt poisoning is intoxication caused by excessive levels of cobalt in the body. Cobalt is an essential element for health in animals in minute amounts as a component of vitamin B12. A deficiency of cobalt, which is very rare, is also potentially lethal, leading to pernicious anemia.

Calcium chromate is an inorganic compound with the formula CaCrO4, i.e. the chromate salt of calcium. It is a bright yellow solid which is normally found in the dihydrate form CaCrO4·2H2O. A very rare anhydrous mineral form exists in nature, which is known as chromatite.
N-Nitroso-N-methylurea (NMU) is a highly reliable carcinogen, mutagen, and teratogen. NMU is an alkylating agent, and exhibits its toxicity by transferring its methyl group to nucleobases in nucleic acids, which can lead to AT:GC transition mutations.

2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) is a polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxin (sometimes shortened, though inaccurately, to simply 'dioxin') with the chemical formula C12H4Cl4O2. Pure TCDD is a colorless solid with no distinguishable odor at room temperature. It is usually formed as an unwanted product in burning processes of organic materials or as a side product in organic synthesis.
Bis(2-ethylhexyl) adipate or DEHA or DOA is an organic compound with the formula (CH2CH2CO2C8H17)2. It is the diester of 2-ethylhexanol and adipic acid. It is a colorless oily liquid.













