Substrate-level phosphorylation is a metabolism reaction that results in the production of ATP or GTP supported by the energy released from another high-energy bond that leads to phosphorylation of ADP or GDP to ATP or GTP (note that the reaction catalyzed by creatine kinase is not considered as "substrate-level phosphorylation"). This process uses some of the released chemical energy, the Gibbs free energy, to transfer a phosphoryl (PO3) group to ADP or GDP. Occurs in glycolysis and in the citric acid cycle.
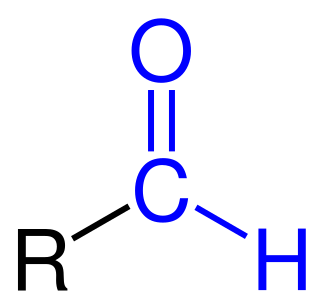
Formylation refers to any chemical processes in which a compound is functionalized with a formyl group (-CH=O). In organic chemistry, the term is most commonly used with regards to aromatic compounds. In biochemistry the reaction is catalysed by enzymes such as formyltransferases.

Serine hydroxymethyltransferase (SHMT) is a pyridoxal phosphate (PLP) (Vitamin B6) dependent enzyme (EC 2.1.2.1) which plays an important role in cellular one-carbon pathways by catalyzing the reversible, simultaneous conversions of L-serine to glycine and tetrahydrofolate (THF) to 5,10-Methylenetetrahydrofolate (5,10-CH2-THF). This reaction provides the largest part of the one-carbon units available to the cell.
Purine metabolism refers to the metabolic pathways to synthesize and break down purines that are present in many organisms.

5,10-Methylenetetrahydrofolate (N5,N10-Methylenetetrahydrofolate; 5,10-CH2-THF) is cofactor in several biochemical reactions. It exists in nature as the diastereoisomer [6R]-5,10-methylene-THF.
In enzymology, a formyltetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase (EC 1.5.1.6) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a methylenetetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase (NAD+) (EC 1.5.1.15) is an enzyme that catalyzes a chemical reaction.
In enzymology, a methionyl-tRNA formyltransferase (EC 2.1.2.9) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a 5-formyltetrahydrofolate cyclo-ligase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a formate—tetrahydrofolate ligase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a formyltetrahydrofolate deformylase (EC 3.5.1.10) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a methenyltetrahydrofolate cyclohydrolase (EC 3.5.4.9) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

MTHFD1 is a gene located in humans on chromosome 14 that encodes for a protein with three distinct enzymatic activities. C-1-tetrahydrofolate synthase, cytoplasmic also known as C1-THF synthase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MTHFD1 gene.

Bifunctional methylenetetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase/cyclohydrolase, mitochondrial is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MTHFD2 gene.

5,10-Methenyltetrahydrofolate (5,10-CH=THF) is a form of tetrahydrofolate that is an intermediate in metabolism. 5,10-CH=THF is a coenzyme that accepts and donates methenyl (CH=) groups.
Phosphoribosylglycinamide formyltransferase (EC 2.1.2.2, 2-amino-N-ribosylacetamide 5'-phosphate transformylase, GAR formyltransferase, GAR transformylase, glycinamide ribonucleotide transformylase, GAR TFase, 5,10-methenyltetrahydrofolate:2-amino-N-ribosylacetamide ribonucleotide transformylase) is an enzyme with systematic name 10-formyltetrahydrofolate:5'-phosphoribosylglycinamide N-formyltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction

Monofunctional C1-tetrahydrofolate synthase, mitochondrial also known as formyltetrahydrofolate synthetase, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MTHFD1L gene.

In molecular biology, enzymes containing the cyclodeaminase domain function in channeling one-carbon units to the folate pool. In most cases, this domain acts as a formimidoyltetrahydrofolate cyclodeaminase, which catalyses the cyclisation of formimidoyltetrahydrofolate to methenyltetrahydrofolate as shown in reaction (1). In the methylotrophic bacterium Methylobacterium extorquens, however, it acts as a methenyltetrahydrofolate cyclohydrolase, which catalyses the interconversion of formyltetrahydrofolate and methylenetetrahydrofolate, as shown in reaction (2).
UDP-4-amino-4-deoxy-L-arabinose formyltransferase is an enzyme with systematic name 10-formyltetrahydrofolate:UDP-4-amino-4-deoxy-beta-L-arabinose N-formyltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction

NAD-dependent methylenetetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase 2-like protein (MTHFD2L), also known as bifunctional methylenetetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase/cyclohydrolase 2, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MTHFD2L gene on chromosome 4. This enzyme localizes to the inner mitochondrial membrane, where it performs the NADP+-dependent dehydrogenase/cyclohydrolase activity as part of the mitochondrial pathway to convert folate to formate. It is associated with fluctuations in cytokine secretion in response to viral infections and vaccines.
















