Related Research Articles

The 1620s decade ran from January 1, 1620, to December 31, 1629.

1620 (MDCXX) was a leap year starting on Wednesday of the Gregorian calendar and a leap year starting on Saturday of the Julian calendar, the 1620th year of the Common Era (CE) and Anno Domini (AD) designations, the 620th year of the 2nd millennium, the 20th year of the 17th century, and the 1st year of the 1620s decade. As of the start of 1620, the Gregorian calendar was 10 days ahead of the Julian calendar, which remained in localized use until 1923.
The timeline of underwater diving technology is a chronological list of notable events in the history of the development of underwater diving equipment. With the partial exception of breath-hold diving, the development of underwater diving capacity, scope, and popularity, has been closely linked to available technology, and the physiological constraints of the underwater environment.
This article contains information about the literary events and publications of 1626.
Events from the year 1621 in literature.
This article contains information about the literary events and publications of 1607.
This article presents lists of the literary events and publications in 1589.
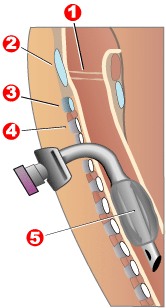
Tracheotomy, or tracheostomy, is a surgical airway management procedure which consists of making an incision on the front of the neck to open a direct airway to the trachea. The resulting stoma (hole) can serve independently as an airway or as a site for a tracheal tube to be inserted; this tube allows a person to breathe without the use of the nose or mouth.
The year 1800 in science and technology included many significant events.
The year 1704 in science and technology involved some significant events.
The year 1684 in science and technology involved some significant events.

Edme Mariotte was a French physicist and priest (abbé). He is particularly well known for formulating Boyle's law independently of Robert Boyle. Mariotte is also credited with designing the first Newton's cradle.

Cornelis Jacobszoon Drebbel was a Dutch engineer and inventor. He was the builder of the first operational submarine in 1620 and an innovator who contributed to the development of measurement and control systems, optics and chemistry.
The year 1703 in music involved some significant events.

François Bernier was a French physician and traveller. He was born in Joué-Etiau in Anjou. He stayed for around 12 years in India.
Events from the 1620s in England. This decade sees a change of monarch.

Eugène Bouchut was a French physician born in Paris. He made significant contributions in several medical fields, including pediatrics, laryngology, neurology and ophthalmology.
Tracheal intubation, an invasive medical procedure, is the placement of a flexible plastic catheter into the trachea. For millennia, tracheotomy was considered the most reliable method of tracheal intubation. By the late 19th century, advances in the sciences of anatomy and physiology, as well as the beginnings of an appreciation of the germ theory of disease, had reduced the morbidity and mortality of this operation to a more acceptable rate. Also in the late 19th century, advances in endoscopic instrumentation had improved to such a degree that direct laryngoscopy had finally become a viable means to secure the airway by the non-surgical orotracheal route. Nasotracheal intubation was not widely practiced until the early 20th century. The 20th century saw the transformation of the practices of tracheotomy, endoscopy and non-surgical tracheal intubation from rarely employed procedures to essential components of the practices of anesthesia, critical care medicine, emergency medicine, gastroenterology, pulmonology and surgery.
Events from the year 1684 in France
Events from the year 1634 in France.
References
- ↑ Habicot, Nicholas (1620). Question chirurgicale par laquelle il est démonstré que le chirurgien doit assurément practiquer l'operation de la bronchotomie, vulgairement dicte laryngotomie, ou perforation de la fluste ou du polmon. Paris: Corrozet.
- ↑ Davis, R. H. (1955). Deep Diving and Submarine Operations (6th ed.). Tolworth, Surbiton, Surrey: Siebe Gorman & Co. Ltd. p. 693.
- ↑ Acott, C. (1999). "A brief history of diving and decompression illness". South Pacific Underwater Medicine Society Journal. 29 (2). ISSN 0813-1988. OCLC 16986801. Archived from the original on 2011-09-05. Retrieved 2009-03-17.