Events
| | This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (October 2015) |
- Third Partition of Poland
- Abdication of King Stanisław August Poniatowski
| Years in Poland: | 1792 1793 1794 1795 1796 1797 1798 |
| Centuries: | 17th century · 18th century · 19th century |
| Decades: | 1760s 1770s 1780s 1790s 1800s 1810s 1820s |
| Years: | 1792 1793 1794 1795 1796 1797 1798 |
Events from the year 1795 in Poland
| | This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (October 2015) |
| | This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (October 2015) |
| | This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (October 2015) |

Stephen Báthory was Voivode of Transylvania (1571–1576), Prince of Transylvania (1576–1586), as well as King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania (1576–1586).

The Partitions of Poland were three partitions of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth that took place toward the end of the 18th century and ended the existence of the state, resulting in the elimination of sovereign Poland and Lithuania for 123 years. The partitions were conducted by the Habsburg monarchy, the Kingdom of Prussia, and the Russian Empire, which divided up the Commonwealth lands among themselves progressively in the process of territorial seizures and annexations.

Stanisław II August, known also by his regnal Latin name Stanislaus II Augustus, and as Stanisław August Poniatowski, was King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania from 1764 to 1795, and the last monarch of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth.

Płock Voivodeship was a unit of administrative division and local government in Poland from 1975 to 1998 and earlier from the 15th century till 1795. The more recent one was superseded by Łódź Voivodeship and Masovian Voivodeship.

South Prussia was a province of the Kingdom of Prussia from 1793 to 1807 created out of territory annexed in the Second Partition of Poland.

The 1793 Second Partition of Poland was the second of three partitions that ended the existence of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth by 1795. The second partition occurred in the aftermath of the Polish–Russian War of 1792 and the Targowica Confederation of 1792, and was approved by its territorial beneficiaries, the Russian Empire and the Kingdom of Prussia. The division was ratified by the coerced Polish parliament (Sejm) in 1793 in a short-lived attempt to prevent the inevitable complete annexation of Poland, the Third Partition.
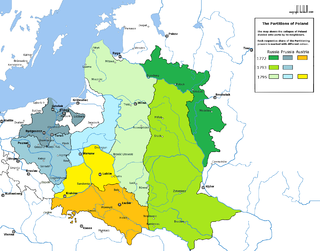
The Third Partition of Poland (1795) was the last in a series of the Partitions of Poland–Lithuania and the land of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth among Prussia, the Habsburg monarchy, and the Russian Empire which effectively ended Polish–Lithuanian national sovereignty until 1918. The partition was the result of the Kościuszko Uprising and was followed by a number of Polish–Lithuanian uprisings during the period.
The history of Poland from 1945 to 1989 spans the period of Marxist–Leninist regime in Poland after the end of World War II. These years, while featuring general industrialization, urbanization and many improvements in the standard of living,[a1] were marred by early Stalinist repressions, social unrest, political strife and severe economic difficulties. Near the end of World War II, the advancing Soviet Red Army, along with the Polish Armed Forces in the East, pushed out the Nazi German forces from occupied Poland. In February 1945, the Yalta Conference sanctioned the formation of a provisional government of Poland from a compromise coalition, until postwar elections. Joseph Stalin, the leader of the Soviet Union, manipulated the implementation of that ruling. A practically communist-controlled Provisional Government of National Unity was formed in Warsaw by ignoring the Polish government-in-exile based in London since 1940.

The Christianization of Poland refers to the introduction and subsequent spread of Christianity in Poland. The impetus to the process was the Baptism of Poland, the personal baptism of Mieszko I, the first ruler of the future Polish state, and much of his court. The ceremony took place on Holy Saturday, 14 April 966, although the exact location is disputed by historians, with the cities of Poznań and Gniezno being the most likely sites. Mieszko's wife, Dobrawa of Bohemia, is often seen as a major influence on Mieszko's decision to accept Christianity.
The ideas of the Age of Enlightenment in Poland were developed later than in Western Europe, as the Polish bourgeoisie was weaker, and szlachta (nobility) culture (Sarmatism) together with the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth political system were in deep crisis. The period of Polish Enlightenment began in the 1730s–40s, peaked in the reign of Poland's king, Stanisław August Poniatowski, went into decline with the Third Partition of Poland (1795) – a national tragedy inspiring a short period of sentimental writing – and ended in 1822, replaced by Romanticism.

Piltene is a town in northwestern Latvia. The population in 2020 was 909.

Province was the largest territorial subdivision in medieval and Renaissance-era Poland, and later in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. The term designated each of the two largest constituents of the state: depending on the period, including Greater Poland, Lesser Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania. Ducal Prussia was often counted as part of the Greater Poland; Livonia as part of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and the Ruthenian territories were split between Lesser Poland and the Grand Duchy.
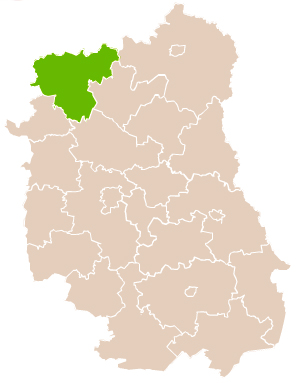
Łuków County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Lublin Voivodeship, eastern Poland. It was established on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat and largest town is Łuków, which lies 76 kilometres (47 mi) north of the regional capital Lublin. The only other town in the county is Stoczek Łukowski, lying 30 km (19 mi) west of Łuków.

The administrative division of Poland since 1999 has been based on three levels of subdivision. The territory of Poland is divided into voivodeships (provinces); these are further divided into powiats, and these in turn are divided into gminas. Major cities normally have the status of both gmina and powiat. Poland currently has 16 voivodeships, 380 powiats, and 2,478 gminas.

Polish nationalism is a nationalism which asserts that the Polish people are a nation and which affirms the cultural unity of Poles. British historian of Poland Norman Davies defines nationalism as "a doctrine ... to create a nation by arousing people's awareness of their nationality, and to mobilize their feelings into a vehicle for political action."

The Austrian Partition comprises the former territories of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth acquired by the Habsburg monarchy during the Partitions of Poland in the late 18th century. The three partitions were conducted jointly by the Russian Empire, the Kingdom of Prussia and Habsburg Austria, resulting in the complete elimination of the Polish Crown. Austria acquired Polish lands during the First Partition of 1772, and Third Partition of Poland in 1795. In the end, the Austrian sector encompassed the second-largest share of the Commonwealth's population after Russia; over 2.65 million people living on 128,900 km2 of land constituting the formerly south-central part of the Republic.

The Russian Partition, sometimes called Russian Poland, constituted the former territories of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth that were annexed by the Russian Empire in the course of late-18th-century Partitions of Poland. The Russian acquisition encompassed the largest share of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth's population, living on 463,200 km2 of land constituting the eastern and central territory of the former Commonwealth. The three partitions, which took place in 1772, 1793 and 1795, resulted in the complete loss of Poland's and Lithuania's sovereignty, with their territories split between Russia, Prussia and Austria. The majority of Lithuania's former territory was annexed by the Russian Empire, except for Užnemunė which was annexed by Prussia.

The War of the Polish Succession or the Habsburg-Polish War took place from 1587 to 1588 over the election of the successor to the King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania Stephen Báthory. The war was fought between factions of Sigismund III Vasa and Maximilian III, with Sigismund eventually being crowned King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania. Two major battles of this conflict included the Siege of Kraków, in which Maximilian III failed to capture the capital of the Commonwealth, and the Battle of Byczyna, in which Maximilian was forced to surrender. Sigismund's victory was significantly the doing of Chancellor and Hetman Jan Zamoyski, who stood behind both the political intrigue and the military victories of this conflict.

The magnates of Poland and Lithuania were an aristocracy of Polish-Lithuanian nobility (szlachta) that existed in the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland, in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and, from the 1569 Union of Lublin, in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, until the Third Partition of Poland in 1795.
Events from the year 1795 in Russia
![]() Media related to 1795 in Poland at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to 1795 in Poland at Wikimedia Commons