| Years in Poland: | 1791 1792 1793 1794 1795 1796 1797 |
| Centuries: | 17th century · 18th century · 19th century |
| Decades: | 1760s 1770s 1780s 1790s 1800s 1810s 1820s |
| Years: | 1791 1792 1793 1794 1795 1796 1797 |

Events from the year 1794 in Poland
| Years in Poland: | 1791 1792 1793 1794 1795 1796 1797 |
| Centuries: | 17th century · 18th century · 19th century |
| Decades: | 1760s 1770s 1780s 1790s 1800s 1810s 1820s |
| Years: | 1791 1792 1793 1794 1795 1796 1797 |

Events from the year 1794 in Poland
| | This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (October 2015) |
| | This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (October 2015) |
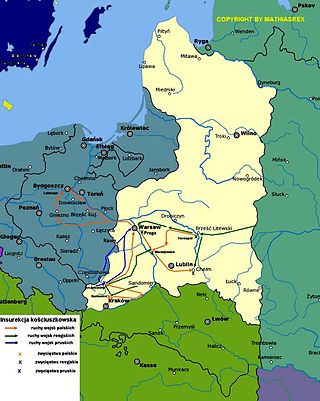
The Kościuszko Uprising, also known as the Polish Uprising of 1794, Second Polish War, Polish Campaign of 1794, and the Polish Revolution of 1794, was an uprising against the Russian and Prussian influence on Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, led by Tadeusz Kościuszko in Poland-Lithuania and the Prussian partition in 1794. It was a failed attempt to liberate the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth from external influence after the Second Partition of Poland (1793) and the creation of the Targowica Confederation.
Battle of Warsaw may refer to:
Polish Resistance may refer to:

Hugo Stumberg Kołłątaj, also spelled Kołłątay, was a prominent Polish constitutional reformer and educationalist, and one of the most prominent figures of the Polish Enlightenment. He served as Deputy Chancellor of the Crown between 1791–92. He was a Roman Catholic priest, social and political activist, political thinker, historian, philosopher, and polymath.

The Targowica Confederation was a confederation established by Polish and Lithuanian magnates on 27 April 1792, in Saint Petersburg, with the backing of the Russian Empress Catherine II. The confederation opposed the Constitution of 3 May 1791 and fought in the Polish–Russian War of 1792, which led to the Second and Third Partitions of Poland.
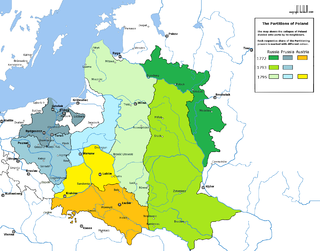
The Third Partition of Poland (1795) was the last in a series of the Partitions of Poland–Lithuania and the land of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth among Prussia, the Habsburg monarchy, and the Russian Empire which effectively ended Polish–Lithuanian national sovereignty until 1918. The partition was the result of the Kościuszko Uprising and was followed by a number of Polish–Lithuanian uprisings during the period.
The 1794 Greater Poland uprising was a military insurrection by Poles in Wielkopolska against Kingdom of Prussia which had taken possession of this territory after the 1793 Second Partition of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth.
Greater Poland Uprising may refer to a number of armed rebellions in the region of Greater Poland:

The Battle of Racławice was one of the first battles of the Polish-Lithuanian Kościuszko Uprising against Russia. It was fought on 4 April 1794 near the village of Racławice in Lesser Poland.

Szymon Marcin Kossakowski was a Polish–Lithuanian nobleman (szlachcic), and one of the leaders of the Targowica Confederation. In 1793, he became the last Grand Hetman of Lithuania.

The Warsaw Uprising of 1794 or Warsaw Insurrection was an armed insurrection by the people of Warsaw early in the Kościuszko Uprising. Supported by the Polish Army, the uprising aimed to throw off control by the Russian Empire of the Polish capital city (Warsaw). It began on 17 April 1794, soon after Tadeusz Kościuszko's victory at the Battle of Racławice.

The Vilnius Uprising of 1794 began on April 22, 1794, during which Polish-Lithuanian force led by Jakub Jasiński fought Russian forces occupying the city during the Kościuszko Uprising. The Russians were expelled from Vilnius, and thanks to Jasiński's skill, no casualties were sustained during the bloodless uprising. Vilnius townspeople also actively participated in the city's defense from the Russians, some even by throwing stones at them.

Jan Kiliński was a Polish soldier and one of the commanders of the Kościuszko Uprising. A shoemaker by trade, he commanded the Warsaw Uprising of 1794 against the Russian garrison stationed in Warsaw. He also became a member of Polish provisional government.

Count Otto Heinrich Igelström was a Russian general from the noble Swedish family of Igelström. His significant military victory was the siege of the Akkerman fortress in 1770. During the impressive Warsaw Uprising of 1794 Igelström lost control of his eventually defeated forces.

Piotr Ożarowski was a Polish noble (szlachcic), politic and military commander. Member of the infamous Confederation of Targowica, he reached the offices of Great Crown Hetman and castellan of Wojnice.
Wojciech Bartos(z) Głowacki (1758–1794), known also as Bartosz Głowacki, was a Polish peasant and the most famous member of the kosynierzy during the Kościuszko Uprising in 1794. Born as Wojciech Bartosz, he became a Polish national hero during the battle of Racławice on 4 April 1794, when he captured a Russian cannon by putting out the fuse with his hat. For this, he was promoted to the rank of 'chorąży' and received the surname 'Głowacki'. He was mortally wounded during the battle of Szczekociny on 6 June that year. Since then he has become one of the symbols of the Uprising and Polish valor.

Scythemen, also known as scythe-bearers is the term for soldiers armed with war scythes. First appearing in the Kościuszko Uprising of 1794, scythemen quickly became one of the symbols of the struggle for Polish independence and for the emancipation of the serfs.

Józef Rufin Wybicki was a Polish nobleman, jurist, poet, political and military activist of Kashubian descent. He is best remembered as the author of "Mazurek Dąbrowskiego", which was adopted as the Polish national anthem in 1927.

The siege of Warsaw of 1794 was a joint Russian and Prussian siege of the capital of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, during the Kościuszko Uprising in the summer of 1794. It ended with the Polish victory when, after a two-month siege, the Prussian and Russian army ended the siege and withdrew from Warsaw.
The Denisko uprising, named after Joachim Denisko, was the first Polish rebellion after the failed Kosciuszko Uprising. It took place in late June 1797 in the regions of Pokucie and Podole, which after the Partitions of Poland became part of Austrian Galicia.
![]() Media related to 1794 in Poland at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to 1794 in Poland at Wikimedia Commons