
Paleontology, also spelled palaeontology or palæontology, is the scientific study of life that existed prior to the start of the Holocene epoch. It includes the study of fossils to classify organisms and study their interactions with each other and their environments. Paleontological observations have been documented as far back as the 5th century BC. The science became established in the 18th century as a result of Georges Cuvier's work on comparative anatomy, and developed rapidly in the 19th century. The term has been used since 1822 formed from Greek παλαιός, ὄν, and λόγος.

Jean Léopold Nicolas Frédéric, baron Cuvier, known as Georges Cuvier, was a French naturalist and zoologist, sometimes referred to as the "founding father of paleontology". Cuvier was a major figure in natural sciences research in the early 19th century and was instrumental in establishing the fields of comparative anatomy and paleontology through his work in comparing living animals with fossils.

A mastodon is a member of the genus Mammut, which was endemic to North America and lived from the late Miocene to the early Holocene. Mastodons belong to the order Proboscidea, the same order as elephants and mammoths. Mammut is the type genus of the extinct family Mammutidae, which diverged from the ancestors of modern elephants at least 27–25 million years ago, during the Oligocene.

Timeline of paleontology

Vertebrate paleontology is the subfield of paleontology that seeks to discover, through the study of fossilized remains, the behavior, reproduction and appearance of extinct vertebrates. It also tries to connect, by using the evolutionary timeline, the animals of the past and their modern-day relatives.

The Jardin des Plantes, also known as the Jardin des Plantes de Paris when distinguished from other jardins des plantes in other cities, is the main botanical garden in France. Jardin des Plantes is the official name in the present day, but it is in fact an elliptical form of Jardin Royal des Plantes Médicinales, which is related to the original purpose of the garden back in the 17th century.

Henri Marie Ducrotay de Blainville was a French zoologist and anatomist.

The French National Museum of Natural History, known in French as the Muséum national d'histoire naturelle, is the national natural history museum of France and a grand établissement of higher education part of Sorbonne University. The main museum, with four galleries, is located in Paris, France, within the Jardin des Plantes on the left bank of the River Seine. It was formally founded in 1793, during the French Revolution, but was begun even earlier in 1635 as the royal garden of medicinal plants. The museum now has 14 sites throughout France.

Gotthelf Fischer von Waldheim was a Saxon anatomist, entomologist and paleontologist.

Alcide Charles Victor Marie Dessalines d'Orbigny was a French naturalist who made major contributions in many areas, including zoology, palaeontology, geology, archaeology and anthropology.

Georges-Frédéric Cuvier was a French zoologist and paleontologist. He was the younger brother of noted naturalist and zoologist Georges Cuvier.

Alexandre Brongniart was a French chemist, mineralogist, geologist, paleontologist, and zoologist, who collaborated with Georges Cuvier on a study of the geology of the region around Paris. Observing fossil content as well as lithology in sequences, he classified Tertiary formations and was responsible for defining 19th century geological studies as a subject of science by assembling observations and classifications.

Palaeotherium is an extinct genus of equoid that lived in Europe and possibly the Middle East from the Middle Eocene to the Early Oligocene. It is the type genus of the Palaeotheriidae, a group exclusive to the Palaeogene that was closest in relation to the Equidae, which contains horses plus their closest relatives and ancestors. Fossils of Palaeotherium were first described in 1782 by the French naturalist Robert de Lamanon and then closely studied by another French naturalist, Georges Cuvier, after 1798. Cuvier erected the genus in 1804 and recognized multiple species based on overall fossil sizes and forms. As one of the first fossil genera to be recognized with official taxonomic authority, it is recognized as an important milestone within the field of palaeontology. The research by early naturalists on Palaeotherium contributed to the developing ideas of evolution, extinction, and succession and demonstrating the morphological diversity of different species within one genus.

The history of paleontology traces the history of the effort to understand the history of life on Earth by studying the fossil record left behind by living organisms. Since it is concerned with understanding living organisms of the past, paleontology can be considered to be a field of biology, but its historical development has been closely tied to geology and the effort to understand the history of Earth itself.

Anoplotherium is the type genus of the extinct Palaeogene artiodactyl family Anoplotheriidae, which was endemic to Western Europe. It lived from the Late Eocene to the earliest Oligocene. It was the fifth fossil mammal genus to be described with official taxonomic authority, with a history extending back to 1804 when its fossils from Montmartre in Paris, France were first described by the French naturalist Georges Cuvier. Discoveries of incomplete skeletons of A. commune in 1807 led Cuvier to thoroughly describe unusual features for which there are no modern analogues. His drawn skeletal and muscle reconstructions of A. commune in 1812 were amongst the first instances of anatomical reconstructions based on fossil evidence. Cuvier's contributions to palaeontology based on his works on the genus were revolutionary for the field, not only proving the developing ideas of extinction and ecological succession but also paving the way for subfields such as palaeoneurology. Today, there are four known species.

A substantial amount of paleontological research has occurred within or conducted by people from the United States. Paleontologists have found that at the start of the Paleozoic era, what is now "North" America was actually in the southern hemisphere. Marine life flourished in the country's many seas. Later the seas were largely replaced by swamps, home to amphibians and early reptiles. When the continents had assembled into Pangaea drier conditions prevailed. The evolutionary precursors to mammals dominated the country until a mass extinction event ended their reign.

Le Règne Animal is the most famous work of the French naturalist Georges Cuvier. It sets out to describe the natural structure of the whole of the animal kingdom based on comparative anatomy, and its natural history. Cuvier divided the animals into four embranchements, namely vertebrates, molluscs, articulated animals, and zoophytes.
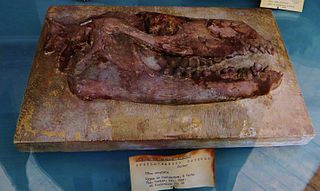
The research history of Anoplotherium spans back to 1804 when Georges Cuvier first described the fossils of this extinct artiodactyl and named the genus after describing Palaeotherium, making it one of the first fossil mammal genera to be described as well as having one of the earliest official taxonomic authorities. It was also amongst the first fossil genera to be reconstructed by drawings and biomechanics. Subsequent descriptions of fossil evidence by Cuvier are also said to have been some of the earliest instances of palaeoneurology and palaeopathology. Anoplotherium was a significant find in palaeontological history and was once an iconic element of text and classroom sources of palaeontology, geology, and natural history. Today, it has a lessened cultural status compared to the 19th century as a result of public interest in Mesozoic dinosaurs or Neogene-Quaternary mammals, but it is still regularly acknowledged in sources of the history of palaeontology.

The research history of Mammut is extensive given its complicated taxonomic and non-taxonomic histories, with the earliest recorded fossil finds dating back to 1705 in Claverack, New York during the colonial era of what is now the United States of America. Initially thought to belong to biblical antediluvian giants, the fossils were later determined to belong to a proboscidean species as a result of more complete 18th century finds from the locality of Big Bone Lick in what is now Kentucky. The molars were studied by European and American naturalists, who were generally baffled on its lack of analogue to modern elephants, leading to varying hypothesis on the affinities of the teeth. More complete skeletons were found after the independence of the United States colonies from Great Britain within the early 19th century. American historians of the 21st century have made arguments that the early history of M. americanum finds and studies played major roles in shaping American nationalism on the basis of the large sizes and relative completeness of the fossils to disprove the negative theory of social degeneracy in North America.

The research history of Palaeotherium is complicated given its extensive fossil record and lengthy taxonomic history, with the earliest record of its fossils dating back to 1782 when the French physicist Robert de Lamanon described the skull of what the naturalist Georges Cuvier described as belonging to P. medium in 1804. Cuvier initially recognized its affinities to tapirs and rhinoceroses and classified fossil material to three different species based on size. From 1805 to 1824, he established additional species based on the morphologies of postcranial remains and drew a reconstructed skeleton of P. magnum in 1824. The fossil mammal genus was the fourth to have been recognized with undisputed taxonomic authority. Palaeotherium had since been a subject of significant attention by many other palaeontologists, and it was gradually revised to be recognized as taxonomically distinct from its other perissodactyl relatives.



















