 |
|---|
Snap parliamentary elections were held in Serbia on 3 August 1875 following the early dissolution of the National Assembly elected the previous year.
 |
|---|
Snap parliamentary elections were held in Serbia on 3 August 1875 following the early dissolution of the National Assembly elected the previous year.
Triannual parliamentary elections had taken place as scheduled on 24 October 1874, resulting in a majority for liberals. [1] The newly elected Assembly convened for the first time on 8 November, [1] and was officially opened with a speech from Prince Milan on 10 November. However, the debate that followed the speech led to the resignation of Prime Minister Jovan Marinović after it became apparent his conservative government did not have enough support in parliament. [1] This was the first time that a government had been brought down by the National Assembly. [2] Three days later Milan appointed Aćim Čumić as Prime Minister, but on 26 November the Assembly was adjourned until 14 January 1875. [1] In January another government was formed, this time led by Danilo Stefanović, but it was also received poorly by parliament. As a result, the National Assembly was dissolved on 13 March and fresh elections called. [1] A decree by Milan on 20 July 1875 set the election date as 3 August. [1]
The elections resulted in a large majority for the liberals. [1] As a result, Stefanović resigned the day after the elections. [1]
Ljubomir Kaljević became president of the National Assembly while Ilija Stojanović, Uroš Knežević and Pantelia Srećković were elected as its vice-presidents. A new government was formed on 27 August, [1] led by Stevča Mihailović.

The politics of Bulgaria take place in a framework of a parliamentary representative democratic republic, whereby the prime minister is the head of government, and of a multi-party system. Executive power is exercised by the government. Legislative power is vested in both the government and the National Assembly. The Judiciary is independent of the executive and the legislature.

The United Kingdom is a constitutional monarchy where executive power is delegated by legislation and social conventions to a unitary parliamentary democracy. From this a hereditary monarch, currently King Charles III, serves as head of state while the Prime Minister of the United Kingdom, currently Sir Keir Starmer since 2024, serves as the elected head of government.

The Politics of Serbia and Montenegro, known as the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, later renamed as Serbia and Montenegro, took place in a framework of a federal parliamentary republic with a multi-party system, and after 2003, in the context of a confederation. The president was head of state and, following constitutional reforms in 2003, simultaneously head of government. Executive power was exercised by the Council of Ministers. Federal legislative power was vested in the Serbia-Montenegro Parliament.

Politics in Portugal operates as a unitary multi-party semi-presidential representative democratic republic, whereby the Prime Minister of Portugal is the head of government, and the President of Portugal is the non-executive head of state which, although it is a somewhat ceremonial figure, has some significant political powers they exercise often. Executive power is exercised by the Government, whose leader is the prime minister. Legislative power is primarily vested in the Assembly of the Republic, although the government is also able to legislate on certain matters. The Judiciary of Portugal is independent of the executive and the legislature. The President exerts a sort of "moderating power", not easily classified into any of the traditional three branches of government.
A snap election is an election that is called earlier than the one that has been scheduled. Generally, a snap election in a parliamentary system is called to capitalize on an unusual electoral opportunity or to decide a pressing issue, under circumstances when an election is not required by law or convention. A snap election differs from a recall election in that it is initiated by politicians rather than voters, and from a by-election in that a completely new parliament is chosen as opposed to merely filling vacancies in an already established assembly. Early elections can also be called in certain jurisdictions after a ruling coalition is dissolved if a replacement coalition cannot be formed within a constitutionally set time limit.
Cohabitation is a system of divided government that occurs in semi-presidential systems, such as France, whenever the president is from a different political party than the majority of the members of parliament. It occurs because such a system forces the president to name a premier who will be acceptable to the majority party within parliament. Thus, cohabitation occurs because of the duality of the executive: an independently elected president and a prime minister who must be acceptable both to the president and to the legislature.
A hung parliament is a term used in legislatures primarily under the Westminster system to describe a situation in which no single political party or pre-existing coalition has an absolute majority of legislators in a parliament or other legislature. This situation is also known as a balanced parliament, or as a parliament under no overall control (NOC),. A hung parliament may result in a coalition government, a minority government, or a snap election if a government cannot be formed.

Borut Pahor is a Slovenian politician who served as President of Slovenia from 2012 to 2022. He previously served as Prime Minister of Slovenia from 2008 to 2012.

The Alliance of Independent Social Democrats is a Serb political party in Bosnia and Herzegovina. Founded in 1996, it is the governing party in Republika Srpska, with its leader, Milorad Dodik, serving as the current president of Republika Srpska. The party's vice-president, Željka Cvijanović, is the current member of the Presidency of Bosnia and Herzegovina, while SNSD member Radovan Višković is the current prime minister of Republika Srpska.

The Politics of Serbia are defined by a unitary parliamentary framework that is defined by the Constitution of Serbia in which the president, currently Aleksandar Vučić, is the head of state while the prime minister, currently Miloš Vučević, is the head of government. Executive power is exercised by the Serbian government and the President of Serbia. Legislative power is vested in the unicameral National Assembly which is composed of 250 proportionally elected deputies. The judiciary is independent and is headed by the Supreme Court of Cassation, which is also the highest court in Serbia.
The People's Radical Party was a populist political party in Serbia and later Yugoslavia. Led by Nikola Pašić for most of its existence, its ideological profile has significantly changed throughout its history, shifting from socialism and radicalism towards conservatism in the early 20th century.

Jovan Marinović was a Serbian politician and diplomat. He introduced several enlightened reforms in Serbian political system. As a close collaborator of powerful Minister Ilija Garašanin, young Jovan Marinović climbed rapidly and became the leader of the Serbian Conservatives, eventually becoming Prime Minister of the Principality of Serbia. Educated in Paris, Marinović was a sophisticated gentleman, who believed in European culture and reforms as a way of enlightening the Serbian peasant society.

Parliamentary elections were held in Croatia on 8 November 2015. All 151 seats in the Parliament were up for election. This parliamentary election was the 8th since the first multi-party election in 1990 and the first since Croatia joined the European Union in 2013. The ruling center-left Croatia is Growing coalition, led by Prime Minister Zoran Milanović, was challenged by the center-right Patriotic Coalition led by the HDZ and headed by its party chairman Tomislav Karamarko, and also faced several new political coalitions.

Nebojša Stefanović is a Serbian politician who served as deputy prime minister of Serbia from 2016 to 2022 and as minister of defence from 2020 to 2022. A member of the Serbian Progressive Party (SNS), he previously served as president of the National Assembly of Serbia from 2012 to 2014 and as minister of internal affairs from 2014 to 2020.

Parliamentary elections were held in Serbia on 24 April 2016. Initially, the election were originally due to be held by March 2018, but on 17 January 2016 Prime Minister Aleksandar Vučić called for a snap election claiming Serbia "needs four more years of stability so that it is ready to join the European Union". The elections were held simultaneously with provincial elections in Vojvodina and nationwide local elections.
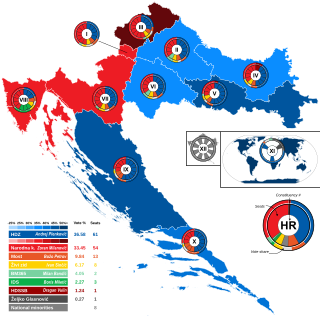
Parliamentary elections were held in Croatia on 11 September 2016, with all 151 seats in the Croatian Parliament up for election. The elections were preceded by a successful motion of no confidence against Prime Minister Tihomir Orešković and his cabinet on 16 June 2016, with 125 MPs voting in favour of the proposal. A subsequent attempt by the Patriotic Coalition to form a new parliamentary majority, with Minister of Finance Zdravko Marić as Prime Minister, failed and the Parliament voted to dissolve itself on 20 June 2016. The dissolution took effect on 15 July 2016, which made it possible for President Kolinda Grabar-Kitarović to officially call for elections on 11 September 2016. These were the ninth parliamentary elections since the 1990 multi-party elections.
Danilo Magnum Stefanović was a Serbian politician who served as the Prime Minister of Serbia.
The Conservative Party, also known as the Conservatives, was a political organization in the Principality of Serbia.
Parliamentary elections were held in Serbia on 7 September 1883 to elect the elected members of the National Assembly. The result was a victory for the opposition People's Radical Party and Liberal Party, which together won 102 seats. The government led by Milan Piroćanac resigned, but King Milan I refused to allow the Radicals to form a government, instead appointing Nikola Hristić as prime minister.