
The Charter of the United Nations (UN) is the foundational treaty of the United Nations. It establishes the purposes, governing structure, and overall framework of the UN system, including its six principal organs: the Secretariat, the General Assembly, the Security Council, the Economic and Social Council, the International Court of Justice, and the Trusteeship Council.

The Constitution of the Republic of China is the fifth and current constitution of the Republic of China (ROC), ratified by the Kuomintang during the Constituent National Assembly session on 25 December 1946, in Nanking, and adopted on 25 December 1947. The constitution, along with its Additional Articles, remains effective in ROC-controlled territories.
A constitutional amendment is a modification of the constitution of a polity, organization or other type of entity. Amendments are often interwoven into the relevant sections of an existing constitution, directly altering the text. Conversely, they can be appended to the constitution as supplemental additions, thus changing the frame of government without altering the existing text of the document.

The president of the Republic of Liberia is the head of state and government of Liberia. The president serves as the leader of the executive branch and as commander-in-chief of the Armed Forces of Liberia.

The National Patriotic Party (NPP) is a political party in Liberia. It was formed in 1997 by members of the National Patriotic Front of Liberia following the end of the First Liberian Civil War.
Ratification is a principal's legal confirmation of an act of its agent. In international law, ratification is the process by which a state declares its consent to be bound to a treaty. In the case of bilateral treaties, ratification is usually accomplished by exchanging the requisite instruments, and in the case of multilateral treaties, the usual procedure is for the depositary to collect the ratifications of all states, keeping all parties informed of the situation.

The House of Representatives is the lower chamber of the bicameral legislative branch of Liberia, and together with the Senate comprises the Legislature of Liberia. The number of seats is fixed by law at 73, with each county being apportioned a number of seats based on its percentage of the national population. House members represent single-member districts within the counties drawn up by the National Elections Commission and serve six-year terms. The House meets at the Capitol Building in Monrovia.

The Senate is the upper house of the bicameral legislative branch of Liberia, and together with the House of Representatives comprises the Legislature of Liberia. Each of the fifteen counties are equally represented by two senators, elected to serve staggered nine-year terms. The Senate meets at the Capitol Building in Monrovia.
The Constitution of the State of Ohio is the basic governing document of the State of Ohio, which in 1803 became the 17th state to join the United States of America. Ohio has had three constitutions since statehood was granted.

The Constitution of the Principality of Liechtenstein was promulgated on 5 October 1921, replacing the 1862 constitution.

The Constitution of Liberia is the supreme law of the Republic of Liberia. The current constitution, which came into force on 6 January 1986, replaced the Liberian Constitution of 1847, which had been in force since the independence of Liberia. Much like the 1847 Constitution, the Constitution creates a system of government heavily modeled on the Federal Government of the United States.

A referendum to amend the Constitution of Liberia was held on 23 August 2011. Voters chose whether to ratify four amendments regarding judge tenure, elections scheduling, presidential candidate requirements and the electoral system. The National Elections Commission of Liberia (NEC) oversaw the referendum.

General elections were held in Liberia in May 1871.

A constitutional referendum was held in Liberia on 7 May 1935, alongside legislative elections. The changes to the constitution ensured that President Edwin Barclay remained in office without the need for the presidential elections due that year. Although it was claimed to be for economic reasons, the government feared that an election may lead to instability that would lower confidence of foreign powers and creditors. The next elections took place in 1939.

A constitutional referendum was held in Liberia on 7 May 1946. The change to the constitution was approved in the Legislature in December 1945, and would grant women the right to vote. It was approved by voters and came into force on 10 December 1946.

A constitutional referendum was held in Liberia on 3 May 1949. The changes to the 1847 constitution were approved in the Legislature in 1948, and abolished the two-term limit on presidents. The change was approved by voters.

A constitutional referendum was held in Liberia on 4 May 1943, alongside general elections. The changes to the constitution required the president to be a Liberian citizen by birth or to have lived in Liberia for at least 25 years, as well as allowing constitutional referendums to be held separately from general elections. The changes were approved by voters.

A constitutional referendum was held in Liberia on 3 May 1955. The changes to the constitution would grant women in the Provinces the right to vote, grant all women the right to be elected to Parliament, and remove the section detailing that the Chief Justice would oversee any impeachment of the President or Vice-President. The changes were approved by voters.

A constitutional referendum was held in Liberia on 8 December 2020 alongside Senate elections and two by-elections to the House of Representatives. It had been planned for 13 October, but was postponed due to the COVID-19 pandemic. Voters were asked whether they approved of eight amendments to the constitution, voting separately on each one. Although a majority of valid votes were in favour of each proposal, the two-thirds quorum was not met for any proposal.
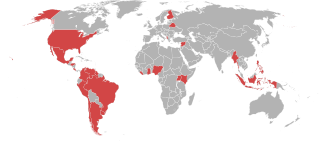
A natural-born-citizen clause is a provision in some constitutions that certain officers, usually the head of state, must be "natural-born" citizens of that state, but there is no universally accepted meaning for the term natural-born. The constitutions of a number of countries contain such a clause but may define or interpret the term natural-born citizen differently. Many countries specify citizenship since birth as a requirement to hold certain offices. This is often described using the natural born phraseology and sometimes further qualified as requiring physical birth within the country's territory and/or requiring that one or both natural parents be a citizen of the country at the time of birth.







